
The Brooklyn Rapid Transit Company (BRT) was a public transit holding company formed in 1896 to acquire and consolidate railway lines in Brooklyn and Queens, New York City, United States. It was a prominent corporation and industry leader using the single-letter symbol B on the New York Stock Exchange. It operated both passenger and freight services on its rail rapid transit, elevated and subway network, making it unique among the 3 companies which built and operated subway lines in New York City. It became insolvent in 1919 and was restructured and released from bankruptcy as the Brooklyn–Manhattan Transit Corporation in 1923.
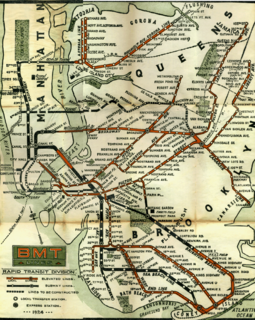
The BMT Lexington Avenue Line was the first standard elevated railway in Brooklyn, New York, operated in its later days by the Brooklyn Rapid Transit Company, the Brooklyn–Manhattan Transit Corporation, and then the City of New York.
The Myrtle Avenue Line, also called the Myrtle Avenue Elevated, is a fully elevated line of the New York City Subway as part of the BMT division. The line is the last surviving remnant of one of the original Brooklyn elevated railroads. The remnant line operates as a spur branch from the Jamaica Line to Bushwick, Ridgewood, and Middle Village, terminating at its original eastern terminal across the street from Lutheran Cemetery. Until 1969, the line continued west into Downtown Brooklyn and, until 1944, over the Brooklyn Bridge to the Park Row Terminal in Manhattan.

The Brooklyn City Railroad (BCRR) was the oldest and one of the largest operators of streetcars in the City of Brooklyn, New York, continuing in that role when Brooklyn became a borough of New York City in 1898.
Starting in 1899, the Brooklyn Rapid Transit Company and Brooklyn–Manhattan Transit Corporation operated rapid transit lines in New York City — at first only elevated railways and later also subways.

The Grand Street Line is a public transit line in Brooklyn and Queens, New York City, running mostly along the continuous Grand Street and Grand Avenue between Williamsburg, Brooklyn and Maspeth, Queens. It then continues down Queens Blvd to the 63rd Drive station. Originally a streetcar line, it is now the Q59 bus route, operated by the New York City Transit Authority between Williamsburg and Rego Park, Queens.
The Bushwick Avenue Line or Bushwick Line was a public transit line in Brooklyn, New York City, United States, running mostly along Bushwick Avenue and Myrtle Avenue between Williamsburg and Ridgewood, Queens.
The Nassau Electric Railroad was an electric street railway company in the U.S. state of New York. The company operated throughout the borough of Brooklyn, as well as over the Brooklyn Bridge and Williamsburg Bridge into Manhattan.

The Sumner Avenue Line and New Lots Avenue Line were two streetcar lines in Brooklyn, New York City, running mainly along Marcus Garvey Boulevard, East 98th Street, and New Lots Avenue between northern Bedford–Stuyvesant and New Lots. Originally streetcar lines, the two lines were combined as a bus route in 1947. That bus route became the present B15 Marcus Garvey Boulevard / New Lots Avenue service, operated by MTA New York City Bus' East New York Depot in East New York. The B15 continues east from New Lots to John F. Kennedy International Airport in Queens.
The Vanderbilt Avenue Line is a public transit line in Brooklyn, New York City, running along 7th Avenue and Vanderbilt Avenue between Kensington and Dumbo. Originally a streetcar line, it is now the B69 bus route, operated by MTA New York City Bus' Jackie Gleason Depot in Sunset Park.

The St. Johns Place Line is a public transit line in Brooklyn, New York, mainly along Atlantic Avenue, Washington Avenue, Sterling Place, and St. Johns Place between Downtown Brooklyn and Crown Heights. Originally a streetcar line, it is now the B45 bus route, operated by the New York City Transit Authority.

The Graham Avenue Line and Tompkins Avenue Line were two public transit lines in Brooklyn, New York City with the Graham Avenue Line running mainly along Graham Avenue and Manhattan Avenue and the Tompkins Avenue Line running mainly along Tompkins Avenue. The Graham Avenue line ran between Downtown Brooklyn and Greenpoint and the Tompkins Avenue Line ran between Prospect Lefferts Gardens and Williamsburg. Originally streetcar lines, they were replaced by the B47 and B62 bus routes which were then combined to form the B43 route which currently operates between Prospect-Lefferts Gardens and Greenpoint. The line is dispatched from Jackie Gleason Depot in Sunset Park, Brooklyn.
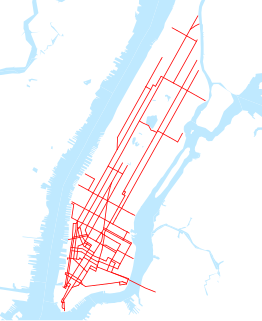
The New York Railways Company operated street railways in Manhattan, New York City, United States between 1911 and 1925. The company went into receivership in 1919 and control was passed to the New York Railways Corporation in 1925 after which all of its remaining lines were replaced with bus routes.
The Long Island Traction Company was a street railway holding company in Brooklyn and Queens, New York City, United States.
The Union Avenue Line was a public transit line in Brooklyn, New York City, United States, running mostly along Myrtle Avenue, Knickerbocker Avenue, Flushing Avenue, Throop Avenue, and Union Avenue from Ridgewood, Queens northwest to Greenpoint, Brooklyn.
The B48 bus route constitutes a public transit line in Brooklyn, New York City, running along Lorimer Street, Franklin Avenue, and Classon Avenue between Flatbush and Greenpoint. Originally the Lorimer Street streetcar line, it is now a bus route operated by MTA New York City Bus.
The Meeker and Marcy Avenues Line was a public transit line in Brooklyn, New York City, running along Marcy Avenue, Metropolitan Avenue, Graham Avenue, and Meeker Avenue from Fulton Street in Bedford-Stuyvesant to Penny Bridge in Williamsburg. The line was owned by the Grand Street and Newtown Railroad.

The West End Line or New Utrecht Avenue Line was a surface transit line in Brooklyn, New York City, United States, running along New Utrecht Avenue and other streets between Coney Island and Sunset Park. Built by the Brooklyn, Bath and Coney Island Railroad as a steam line, it became a trolley line, along which elevated trains ran until the new elevated BMT West End Line opened. This route is no longer part of any bus line; its southern part was part of a bus route. In 2013, the B64 route to Coney Island was restored.

The Williamsburg Bridge Plaza, sometimes called Washington Plaza or the Williamsburg Bridge Transit Center, is a major bus terminal and former trolley terminal located at the foot of the Williamsburg Bridge in the New York City borough of Brooklyn, one block west of the Brooklyn-Queens Expressway (I-278). It is situated by the boundaries of Broadway, Havemeyer Street, Roebling Street, and South 5th Street, south of the LaGuardia Playground. It contains five bus lanes, and serves as a terminal for numerous MTA New York City Transit Authority bus routes of Brooklyn and Queens that start and end their runs there.

The Williamsburg Bridge Trolley Terminal, also called the Essex Street Trolley Terminal or Delancey Street Trolley Terminal, was a trolley terminal located underground adjacent to the Essex Street subway station in the Lower East Side of Manhattan. Passenger trolley service operated through the terminal from 1908 until 1948 when trolley service over the Williamsburg Bridge ended. The station was constructed with balloon loops for turning around streetcars after they crossed over the Williamsburg Bridge to send them back to Brooklyn.












