
The Newark Light Rail (NLR) is a light rail system serving Newark, New Jersey and surrounding areas, owned by New Jersey Transit and operated by its bus operations division. The service consists of two segments, the original Newark City Subway (NCS), and the extension to Broad Street station. The City Subway opened on May 16, 1935, while the combined Newark Light Rail service was officially inaugurated on July 17, 2006.

Brookville Equipment Corporation, based in Brookville, Pennsylvania, United States, manufactures railroad locomotives for industrial and light capacity switching needs. The company also builds and restores streetcars. The company used to be known as Brookville Locomotive Company.

The Public Service Terminal was a three-level streetcar station in Newark, New Jersey, owned and operated by the Public Service Corporation, adjacent to the Hudson and Manhattan Railroad's Park Place station. It served as the terminus for streetcar lines from as far as Trenton. Public Service was both a transportation company and a utility, providing electric and gas service to much of northern New Jersey. The six office stories above the terminal served as company headquarters.

The Public Service Corporation (PSC) was an energy and transportation company in New Jersey. It was formed to shore up financing and development of New Jersey's streetcar and power companies at a time when they were growing but exhausting capital. It did this by leasing their operations or buying them outright, and using the size and integration of the systems to get favorable financing for improvements.

The San Diego Electric Railway (SDERy) was a mass transit system in Southern California, United States, using 600 volt DC streetcars and buses.

The Toronto streetcar system is a network of eleven streetcar routes in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, operated by the Toronto Transit Commission (TTC). It is the third busiest light-rail system in North America. The network is concentrated primarily in Downtown Toronto and in proximity to the city's waterfront. Much of the streetcar route network dates from the 19th century. Three streetcar routes operate in their own right-of-way, one in a partial right-of-way, and six operate on street trackage shared with vehicular traffic with streetcars stopping on demand at frequent stops like buses. Since 2019, the network has used low-floor streetcars, making it fully accessible.

509 Harbourfront is a Toronto streetcar route in Ontario, Canada, operated by the Toronto Transit Commission and connecting Union Station with Exhibition Loop.
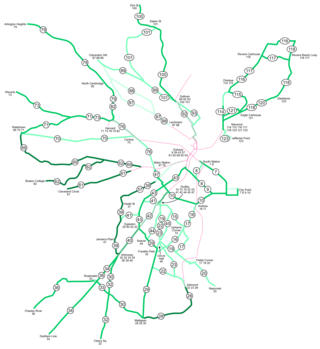
As with many large cities, a large number of Boston-area streetcar lines once existed, and many continued operating into the 1950s. However, only a few now remain, namely the four branches of the Green Line and the Ashmont–Mattapan High-Speed Line, with only one running regular service on an undivided street.
The Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) maintains a large public transit system in the Boston, Massachusetts area, and uses various methods to name and number their services for the convenience of users.

The Blue Night Network is the overnight public transit service operated by the Toronto Transit Commission (TTC) in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. The network consists of a basic grid of 27 bus and 4 streetcar routes, distributed so that almost all of the city is within 2 km (1.2 mi) of at least one route. It is the largest and most frequent overnight network in North America.

NJ Transit Bus Operations is the bus division of NJ Transit, providing bus service throughout New Jersey along with service along with the Newark Light Rail service. Many of the agency’s bus routes travel over state lines to New York City or Philadelphia. In 2022, the bus system had a ridership of 112,626,600.

The International Railway Company (IRC) was a transportation company formed in a 1902 merger between several Buffalo-area interurban and street railways. The city railways that merged were the West Side Street Railway, the Crosstown Street Railway and the Buffalo Traction Company. The suburban railroads that merged included the Buffalo & Niagara Electric Street Railway, and its subsidiary the Buffalo, Lockport & Olcott Beach Railway; the Buffalo, Depew & Lancaster Railway; and the Niagara Falls Park & River Railway. Later the IRC acquired the Niagara Gorge Railroad (NGRR) as a subsidiary, which was sold in 1924 to the Niagara Falls Power Company. The NGRR also leased the Lewiston & Youngstown Frontier Railroad.

Transport of New Jersey (TNJ), earlier Public Service Transportation and then Public Service Coordinated Transport, was a street railway and bus company in the U.S. state of New Jersey from 1917 to 1980, when NJ Transit took over their operations. It was owned by the Public Service Corporation, now the Public Service Electric and Gas Company.

Light rail is a mode of rail-based transport, usually urban in nature. When compared to heavy rail systems like commuter rail or rapid transit (subway), light rail systems are typically designed to carry fewer passengers and are capable of operating in mixed traffic or on routes that are not entirely grade-separated. Systems typically take one of four forms: the "first-generation" legacy systems, the "second-generation" modern light rail systems, streetcars, and hybrid rail systems. All of the systems use similar technologies, and some systems blur the lines between the different forms.

Public transport bus services are generally based on regular operation of transit buses along a route calling at agreed bus stops according to a published public transport timetable.

The Benjamin Franklin Bridge, originally named the Delaware River Bridge and known locally as the Ben Franklin Bridge, is a suspension bridge across the Delaware River connecting Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and Camden, New Jersey. Owned and operated by the Delaware River Port Authority, it is one of four primary vehicular bridges between Philadelphia and southern New Jersey, along with the Betsy Ross, Walt Whitman, and Tacony-Palmyra bridges. It carries Interstate 676/U.S. Route 30, pedestrians/cyclists, and the PATCO Speedline.

Transportation in metropolitan Detroit comprises an expansive system of roadways, multiple public transit systems, a major international airport, freight railroads, and ports. Located on the Detroit River along the Great Lakes Waterway, Detroit is a significant city in international trade, with two land crossings to Canada. Three primary Interstate highways serve the region.

The Bx15 and M125 bus routes constitute the Third Avenue/125th Street Line, a public transit line in New York City. The Bx15 runs between Fordham Plaza and the Hub in the Bronx, running primarily along Third Avenue. The M125 runs between the Hub in the Bronx and Manhattanville in Manhattan, running along Willis Avenue in the South Bronx and along 125th Street in Harlem, Manhattan.

The Ipswich Street line was a streetcar line in Boston and Brookline, Massachusetts. The line ran on Boylston Street and Ipswich Street in the Fenway–Kenmore neighborhood, and on Brookline Avenue through what is now the Longwood Medical Area to Brookline Village.
















