Related Research Articles

The Brooklyn Rapid Transit Company (BRT) was a public transit holding company formed in 1896 to acquire and consolidate railway lines in Brooklyn and Queens, New York City, United States. It was a prominent corporation and industry leader using the single-letter symbol B on the New York Stock Exchange.
The BMT Jamaica Line, also known as the Broadway - Brooklyn Line, is an elevated rapid transit line of the B Division of the New York City Subway, in Brooklyn and Queens, New York City, United States. It runs from the Williamsburg Bridge southeast over Broadway to East New York, Brooklyn, and then east over Fulton Street and Jamaica Avenue to Jamaica, Queens. In western Jamaica, the line goes into a tunnel, becoming the lower level of the Archer Avenue lines in central Jamaica. The J and Z trains serve the entire length of the Jamaica Line, and the M serves the line west of Myrtle Avenue.
The Myrtle Avenue Line, also called the Myrtle Avenue Elevated, is a fully elevated line of the New York City Subway as part of the BMT division. The line is the last surviving remnant of one of the original Brooklyn elevated railroads. The remnant line operates as a spur branch from the Jamaica Line to Bushwick, Ridgewood, and Middle Village, terminating at its original eastern terminal across the street from Lutheran Cemetery. Until 1969, the line continued west into Downtown Brooklyn and, until 1944, over the Brooklyn Bridge to the Park Row Terminal in Manhattan.

The Brooklyn City Railroad (BCRR) was the oldest and one of the largest operators of streetcars in the City of Brooklyn, New York, continuing in that role when Brooklyn became a borough of New York City in 1898.
Starting in 1899, the Brooklyn Rapid Transit Company and Brooklyn–Manhattan Transit Corporation operated rapid transit lines in New York City — at first only elevated railways and later also subways.
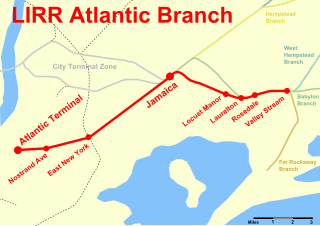
The Atlantic Branch is an electrified rail line owned and operated by the Long Island Rail Road in the U.S. state of New York. It is the only LIRR line with revenue passenger service in the borough of Brooklyn.

The Cypress Hills station is a skip-stop station on the BMT Jamaica Line of the New York City Subway, located on Jamaica Avenue in the Cypress Hills neighborhood of northeastern Brooklyn. It is served by the J train at all times. The Z train skips this station when it operates.

The DeKalb Avenue Line is a public transit line in Brooklyn and Queens, New York City, running mostly along DeKalb Avenue, as well as eastbound on Lafayette Avenue, between Downtown Brooklyn and Ridgewood, Queens. Originally a streetcar line, it is now the B38 DeKalb/Lafayette Avenues bus route, operated by the New York City Transit Authority.
The Brooklyn Heights Railroad was a street railway company in the U.S. state of New York. It leased and operated the streetcar lines of the Brooklyn Rapid Transit Company, but started out with the Montague Street Line, a short cable car line connecting the Wall Street Ferry with downtown Brooklyn along Montague Street. Eliphalet Williams Bliss owned the railroad.
The Bushwick Avenue Line or Bushwick Line was a public transit line in Brooklyn, New York City, United States, running mostly along Bushwick Avenue and Myrtle Avenue between Williamsburg and Ridgewood, Queens.

The Nassau Electric Railroad was an electric street railway company in the U.S. state of New York. The company operated throughout the borough of Brooklyn, as well as over the Brooklyn Bridge and Williamsburg Bridge into Manhattan.
The Brooklyn, Queens County and Suburban Railroad (BQC&S) was a street railway company in Brooklyn and Queens, New York, United States. It originated as a horsecar line until it was acquired by the Long Island Traction Company on November 24, 1893 and convert it into a subsidiary. The railroad was electrified in 1894.

The B63 is a bus route in Brooklyn, New York City, running mainly along Fifth Avenue and Atlantic Avenue between Fort Hamilton and Cobble Hill. Originally a streetcar line called the Fifth Avenue Line, it is now operated by the New York City Transit Authority as the Fifth/Atlantic Avenues bus.
The Broadway Line was a public transit line in Brooklyn, New York City, United States along Broadway between Williamsburg and East New York. Originally a streetcar line, it later became a bus route, but no bus currently operates over the entire length of Broadway, with the BMT Jamaica Line above.

The New York Railways Company operated street railways in Manhattan, New York City, between 1911 and 1925. The company went into receivership in 1919 and control was passed to the New York Railways Corporation in 1925 after which all of its remaining lines were replaced with bus routes.
The Long Island Rail Road is a railroad owned by the Metropolitan Transportation Authority in the U.S. state of New York. It is the oldest United States railroad still operating under its original name and charter. It consolidated several other companies in the late 19th century. The Pennsylvania Railroad owned the Long Island Rail Road for the majority of the 20th century and sold it to the State in 1966.
The Brooklyn Elevated Railroad was an elevated railroad company in Brooklyn, New York City, United States. It operated from 1885 until 1899, when it was merged into the Brooklyn Rapid Transit Company-controlled Brooklyn Union Elevated Railroad.

The West End Line or New Utrecht Avenue Line was a surface transit line in Brooklyn, New York City, United States, running along New Utrecht Avenue and other streets between Coney Island and Sunset Park. Built by the Brooklyn, Bath and Coney Island Railroad as a steam line, it became a trolley line, along which elevated trains ran until the new elevated BMT West End Line opened. This route is no longer part of any bus line; its southern part was part of a bus route. In 2013, the B64 route to Coney Island was restored.

The Q65 bus route constitutes a public transit line in Queens, New York City. The south-to-north route runs primarily on 164th Street, operating between two major bus-subway hubs: Sutphin Boulevard–Archer Avenue station in Jamaica and Flushing–Main Street station in Flushing. It then extends north along College Point Boulevard to College Point at the north end of the borough. The route is city-operated under the MTA Bus Company brand of MTA Regional Bus Operations.
References
- ↑ "The Montague Street Road". Brooklyn Daily Eagle . Brooklyn, NY. 18 July 1890. p. 6.
- ↑ Frank Parsons, The City for the People: Or, The Municipalization of the City Government and of Local Franchises, page 96
- ↑ William Z. Ripley, Trusts, Pools and Corporations, page 146
- ↑ "The Lease of the City Lines". Brooklyn Daily Eagle . Brooklyn, NY. 7 June 1893. p. 10.
- ↑ "Reaching for Routes". Brooklyn Daily Eagle . Brooklyn, NY. 31 May 1893. p. 10.
- ↑ "Surface Railroad Deals". Brooklyn Daily Eagle . Brooklyn, NY. 25 November 1893. p. 1.
- ↑ "Local Stocks and Bonds". Brooklyn Daily Eagle . Brooklyn, NY. 2 June 1895. p. 23.
- ↑ "The Tie Up". Brooklyn Daily Eagle . Brooklyn, NY. 14 January 1895. p. 1.
- ↑ "L.I. Traction Reorganization". Brooklyn Daily Eagle . Brooklyn, NY. 18 January 1896. p. 1.
- ↑ "Local Stocks and Bonds". Brooklyn Daily Eagle . Brooklyn, NY. 9 February 1896. p. 23.
- ↑ Report of the Special Committee of the Assembly Appointed to Investigate the Causes of the Strike of the Surface Railroads in the City of Brooklyn, 1895, pages 33-34
- 1 2 3 Report of the Special Committee of the Assembly Appointed to Investigate the Causes of the Strike of the Surface Railroads in the City of Brooklyn, 1895, pages 52-53

