
Moeritherium is an extinct genus of basal proboscideans from the Eocene of North and West Africa. It was related to elephants and, more distantly, to sea cows and hyraxes.

Aegyptopithecus is an early fossil catarrhine that predates the divergence between hominoids (apes) and cercopithecids. It is known from a single species, Aegyptopithecus zeuxis, which lived around 38-29.5 million years ago in the early part of the Oligocene epoch. It likely resembled modern-day New World monkeys, and was about the same size as a modern howler monkey, which is about 56 to 92 cm long. Aegyptopithecus fossils have been found in the Jebel Qatrani Formation of modern-day Egypt. Aegyptopithecus is believed to be a stem-catarrhine, a crucial link between Eocene and Miocene fossils.

Mouse-tailed bats are a group of insectivorous microbats of the family Rhinopomatidae with only three to six species, all contained in the single genus Rhinopoma. They are found in the Old World, from North Africa to Thailand and Sumatra, in arid and semiarid regions, roosting in caves, houses and even the Egyptian pyramids. They are relatively small, with a body length of just 5 to 6 cm. They weigh between 6 and 14 g.

Palaeochiropteryx is an extinct genus of bat from the Middle Eocene of Europe and North America. It contains three very similar species – Palaeochiropteryx tupaiodon and Palaeochiropteryx spiegeli, both from the famous Messel Pit of Germany, as well as Palaeochiropteryx sambuceus from the Sheep Pass Formation. They are usually found complete and exceptionally preserved, even retaining the outlines of their fur, ears, and wing membranes.

Onychonycteris is the more primitive of the three oldest bats known from complete skeletons, having lived in the area that is current day Wyoming during the Eocene period, 52.5 million years ago.
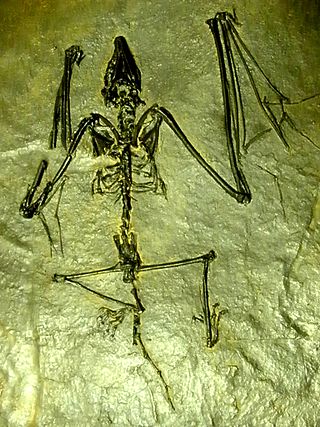
Archaeonycteris is an archaic bat genus whose fossilised remains have been found in Germany, France, England and India.
Biretia is an extinct genus of Old World monkey belonging to the extinct family Parapithecidae. Fossils are found from Late Eocene strata in Egypt.

The Jebel Qatrani Formation is a geologic formation located in the Faiyum Governorate of central Egypt. It is exposed between the Jebel Qatrani escarpment and the Qasr el Sagha escarpment, north of Birket Qarun lake near Faiyum. The formation conformably overlies the Qasr el Sagha Formation and is topped by the Widan el Faras Basalt. The age of the formation has been subject to debate, but the most recent research indicates that it covers both the latest parts of the Eocene and the Early Oligocene, spanning over the boundary between these two time periods.
Nosmips aenigmaticus is a rare fossil primate known only from 12 teeth. Most teeth were found at a site in the Fayum Depression about 40 miles (64 km) outside Cairo, Egypt.
This paleomammalogy list records new fossil mammal taxa that were described during the year 2012, as well as notes other significant paleomammalogy discoveries and events which occurred during that year.
Philisidae is an extinct family of bats of the suborder Microchiroptera that lived between the Eocene to the Late Miocene in the continent of Africa.
This paleomammalogy list records new fossil mammal taxa that were described during the year 2010, as well as notes other significant paleomammalogy discoveries and events which occurred during that year.
Dizzya is an extinct, monotypic genus of bat that occurred in the Chambi region, Tunisia, in the Middle Eocene. It was described based on a single upper molar, a lower dentary with two broken teeth, and a humerus. It is the smallest and, along with Witwatia sigei, the oldest representative of the Philisidae, an extinct family of bats related to the Vespertilionidae.
Aegyptonycteris is a genus of extinct bat from the Late Eocene of North Africa. It is currently known from a single specimen from the Birket Qarun Formation in the Fayum Depression in western Egypt.

Hesham Sallam is an Egyptian paleontologist and the founder of the Mansoura University Vertebrate Paleontology Center (MUVP-C), the first vertebrate paleontology program in the Middle East. He works as an associate professor at the American University in Cairo and Mansoura University. Sallam led the discovery and description of Mansourasaurus shahinae, a species of sauropod dinosaur from Egypt, which has improved understanding of the prehistory of Africa during the latest Cretaceous period. His work has helped popularize paleontology in Egypt.
Propotto is an extinct monotypic genus of strepsirrhine primate from the early Miocene of Kenya. It contains one described species, Propotto leakeyi. Although long considered a pteropodid fruit-eating bat after spending a brief sojourn as a prehistoric relative of lorises, recent research shows it to be an extinct relative of the aye-aye.

Onychonycteridae is an extinct family of bats known only from the early Eocene of Europe and North America. The type species, Onychonycteris finneyi, was described in 2008 from two nearly complete skeletons found in the Green River Formation of southwestern Wyoming. Since that time a number of previously described fossil bat species have been assigned to Onychonycteridae, as well as two more recently discovered species.

Noctilionoidea is a superfamily of bats containing seven families: Thyropteridae, Furipteridae, Noctilionidae, Mormoopidae, Phyllostomidae, Myzopodidae, and Mystacinidae.

The Birket Qarun Formation is an Eocene aged formation in Egypt. It is part of the famous Wadi al Hitan. Notable fossils include the ancient whales Basilosaurus and Dorudon as well as sirenians Eotheroides and Eosiren. It also contains the teeth of various sharks and reptiles. The area was likely a mix of both marine and freshwater area with many freshwater deposits being found alongside a marine influence from the Tethys Sea. Fossils here also preserve a shallow marine nursery for the whale Dorudon and it seems that this area would have also been the site of active predation from Basilosaurus as it attacked the newly born Dorudon calves.

The Fayyum is a region and an important fossil Lagerstätte in northern Egypt. The region comprises the Fayyum Basin, which is intensively used for agriculture, and adjoining areas; the important areas of discovery are mostly north and west of Lake Qarun. The Wadi al-Hitan, known for its numerous whale fossils and since 2005 UNESCO World Natural Heritage Site, forms the south-western end. The deposits of the Fayyum belong to various geological formations. They are mainly composed of limestone, siltstone and sandstone. The lower sections consist of marine sediments, while the upper, continental sediments were formed in a coastal landscape. The formation period ranges from the Middle to the Upper Eocene to the Lower Oligocene, which corresponds to an age of around 41 to 28 million years ago. The entire sedimentary complex is overlain by basalt, which dates back to volcanic activity around 24 million years ago.










