
Ammonoids are extinct spiral shelled cephalopods comprising the subclass Ammonoidea. They are more closely related to living coleoids than they are to shelled nautiloids. The earliest ammonoids appeared during the Devonian, with the last species vanishing during or soon after the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. They are often called ammonites, which is most frequently used for members of the order Ammonitida, the only remaining group of ammonoids from the Jurassic up until their extinction.

Ammonitida or "True ammonites" are an order of ammonoid cephalopods that lived from the Jurassic through Paleocene time periods, commonly with intricate ammonitic sutures.
The Muschelkalk is a sequence of sedimentary rock strata in the geology of central and western Europe. It has a Middle Triassic age and forms the middle part of the three-part Germanic Trias lying above the older Buntsandstein and below the younger Keuper. The Muschelkalk ("mussel-chalk") consists of a sequence of limestone and dolomite beds.

The Carnian is the lowermost stage of the Upper Triassic Series. It lasted from 237 to 227 million years ago (Ma). The Carnian is preceded by the Ladinian and is followed by the Norian. Its boundaries are not characterized by major extinctions or biotic turnovers, but a climatic event occurred during the Carnian and seems to be associated with important extinctions or biotic radiations. Another extinction occurred at the Carnian-Norian boundary, ending the Carnian age.

The Early Triassic is the first of three epochs of the Triassic Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between 251.9 Ma and 247.2 Ma. Rocks from this epoch are collectively known as the Lower Triassic Series, which is a unit in chronostratigraphy. The Early Triassic is the oldest epoch of the Mesozoic Era. It is preceded by the Lopingian Epoch and followed by the Middle Triassic Epoch. The Early Triassic is divided into the Induan and Olenekian ages. The Induan is subdivided into the Griesbachian and Dienerian subages and the Olenekian is subdivided into the Smithian and Spathian subages.

In the geologic timescale, the Olenekian is an age in the Early Triassic epoch; in chronostratigraphy, it is a stage in the Lower Triassic series. It spans the time between 251.2 Ma and 247.2 Ma. The Olenekian is sometimes divided into the Smithian and the Spathian subages or substages. The Olenekian follows the Induan and is followed by the Anisian.

In the geologic timescale, the Middle Triassic is the second of three epochs of the Triassic period or the middle of three series in which the Triassic system is divided in chronostratigraphy. The Middle Triassic spans the time between 247.2 Ma and 237 Ma. It is preceded by the Early Triassic Epoch and followed by the Late Triassic Epoch. The Middle Triassic is divided into the Anisian and Ladinian ages or stages.

The Induan is the first age of the Early Triassic epoch in the geologic timescale, or the lowest stage of the Lower Triassic series in chronostratigraphy. It spans the time between 251.9 Ma and 251.2 Ma. The Induan is sometimes divided into the Griesbachian and the Dienerian subages or substages. The Induan is preceded by the Changhsingian and is followed by the Olenekian.

Xenodiscus is an extinct genus of ammonoid cephalopod and one of the earliest known ceratites, found in the Upper Permian of northern India and Timor. Xenodiscus is included in the family Xenodiscidae which is part of the ceratite superfamily Xenodiscaceae.
Frechites is an early Triassic ammonite, a kind of cephalopod with an external shell, included in the ceratitid family Beyrichitidae.

Ceratites is an extinct genus of ammonite cephalopods. These nektonic carnivores lived in marine habitats in what is now Europe, during the Triassic, from the upper-most Anisian to the lower Ladinian age.

Xenodiscoidea, formerly Xenodiscaceae, is a superfamily within the ammonoid order Ceratitida. The superfamily was named by Frech in 1902, presently contains ten families, only one of which was included in the original Otocerataceae of Hyatt, 1900, the remaining having been added.

Prolecanitida is an order of extinct ammonoid cephalopods, the major Late Paleozoic group of ammonoids alongside the order Goniatitida. Prolecanitids had narrow shells, discoidal (disc-shaped) to thinly lenticular (lens-shaped). They retained a retrochoanitic siphuncle, a simple form with septal necks extending backwards. As is typical for ammonoids, the siphuncle sits along the ventral margin of the shell.
The Danubitoidea is a large and diverse superfamily in the order Ceratitida of the Ammonoidea that combines five families removed from the Ceratitaceae, Clydonitaceae, and Ptychitaceae.
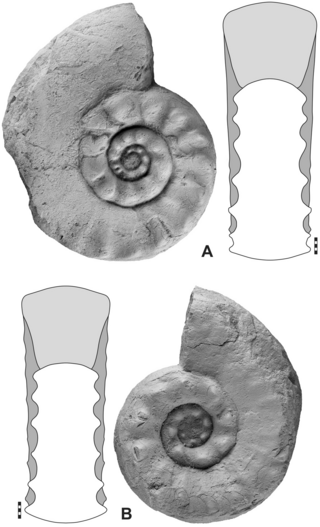
Paratirolites is a genus of latest Permian and earliest Triassic ceratites from Armenia, Azerbaijan, Afghanistan, China and Iran with distinct ribs, prominent ventro-lateral tubercles, and a broadly arched venter. The suture is ceratitic with a large ventral saddle. Ceratites are ammonoid cephalopods that lived during the Late Permian and Triassic.

Ophiceras is an extinct genus of smooth, evolute ceratitid ammonites from the Griesbachian, with a rounded venter. Fossils of the genus have been found in Armenia, Azerbaijan, China, Greenland, and India.

Meekoceras is an extinct genus of ceratitid ammonites with a discoidal shell that lived during the Early Triassic Epoch.
The Vikinghøgda Formation is a geologic formation in Svalbard, Norway. It preserves fossils dating back to the Early Triassic (Griesbachian-Spathian) period. It is split into three members, from oldest to youngest: the Deltadalen Member (Induan), Lusitaniadalen Member (Smithian), and Vendomdalen Member (Spathian). The formation can be found in central Spitsbergen, southern Spitsbergen, as well as the smaller islands of Barentsøya and Edgeøya. The type locality is positioned in the vicinity of Vikinghøgda and Sticky Keep, two low peaks along the southeast edge of Sassendalen in Spitsbergen. The two upper members of the Vikinghøgda Formation were previously grouped together as the Sticky Keep Formation.
Owenites is a genus of a ceratite ammonoid that lived during the Early Triassic.

Tirolites is an extinct genus of ammonoid cephalopod. Its first appearance defines the Smithian-Spathian boundary in the Olenekian stage of the Early Triassic epoch. It is prominent in the Paris biota.














