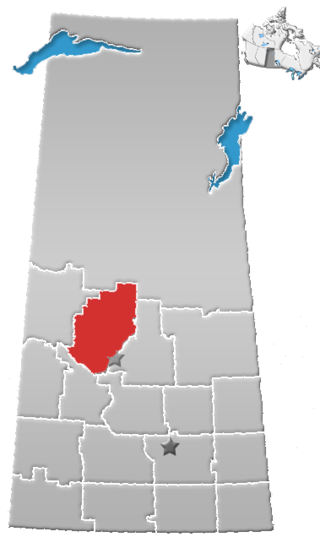
Quill Lake is a village in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan within the Rural Municipality of Lakeside No. 338 and Census Division No. 10. It is 170 km east of Saskatoon and 200 km northeast of Regina.
Yellow Quill First Nation (formerly Nut Lake Band of Saulteaux) is a Saulteaux First Nation band government in Saskatchewan, Canada. Their reserve is twenty kilometres northwest of Kelvington. The Yellow Quill First Nation is a signatory of Treaty No. 4, which was signed by Chief Yellow-quill on August 24, 1876.

Division No. 14 is one of eighteen census divisions in the province of Saskatchewan, Canada, as defined by Statistics Canada. It is located on the northern portion of Southeast Saskatchewan, bordering Manitoba. The most populous community in this division is the city of Melfort. Other important communities are the towns of Nipawin and Tisdale.
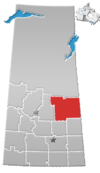
Division No. 16 is one of eighteen census divisions in the province of Saskatchewan, Canada, as defined by Statistics Canada. It is located in the north-central part of the province. The most populous community in this division is North Battleford.
Fishing Lake First Nation is a First Nation of the Saulteaux branch of the Ojibwe nation. Fishing Lake First Nation are Anishinabek people. The band can trace their origins to central Canada, and were pushed westward to avoid encroachment by European settlers. The First Nation was originally part of the Yellow-quill Saulteaux Band, a Treaty Band named after a Treaty 4 signatory Chief Ošāwaškokwanēpi, whose name means "Green/Blue-quill." However, due to "š" merging with "s" in Nakawēmowin, this led to a mistranslation of his name as "Yellow-quill"—"yellow" being osāw-, while "green/blue" being ošāwaško-. The band was given three reserves, at Fishing and Nut Lakes and Kinistino, Saskatchewan. The Fishing Lake Indian Reserve 89 was approximately 22,850 acres (92.5 km2). Soon after the death of Chief Ošāwaškokwanēpi, the Band divided into three groups, the Fishing Lake First Nation, the Yellow Quill First Nation, and the Kinistin Saulteaux Nation

The Kinistin Saulteaux Nation is a Saulteaux band government in Saskatchewan. Their reserve is 39 kilometres (24 mi) southeast of Melfort. The Kinistin Saulteaux Nation is a signatory of Treaty No. 4, which was signed by Chief Yellow-quill on August 24, 1876.

The Okanese First Nation is a Cree-Saulteaux First Nation band government in Balcarres, Saskatchewan, Canada.

The Cote First Nation is a Saulteaux First Nations band government in Kamsack, Saskatchewan. This Saulteaux reserve is connected to the Keeseekoose First Nation and only a couple of miles from the Key First Nation. Their land is situated just south of the boreal forest in the aspen parkland ecosystem of Canada. The Ojibwe of this region of Saskatchewan and Manitoba were both hunters of the plains bison and hunters of the forests which were more abundant during the 19th century. They also fished the endless lakes and other waterways in the land. They seldom went hungry as a result of the large bison herds. However, by the 1870s, commercial hunting had reduced the bison to near extinction and the Ojibwe of Saskatchewan and Manitoba began to suffer from famine.

The Treaty Four Reserve Grounds 77 are an Indian reserve in Saskatchewan, Canada, shared by 33 band governments from Saskatchewan and Manitoba. The Reserve Grounds are located adjacent to and west of Fort Qu'Appelle. In the 2016 Canadian Census, they recorded a population of 15 living in 6 of their 8 total private dwellings.

Kinistin 91 is an Indian reserve of the Kinistin Saulteaux Nation in Saskatchewan. It is about 39 kilometres (24 mi) south-east of Melfort. In the 2016 Canadian Census, it recorded a population of 321 living in 82 of its 90 total private dwellings. In the same year, its Community Well-Being index was calculated at 46 of 100, compared to 58.4 for the average First Nations community and 77.5 for the average non-Indigenous community.

Star Blanket 83 is an Indian reserve of the Star Blanket Cree Nation in Saskatchewan. It is about 18 kilometres (11 mi) north-east of Fort Qu'Appelle. In the 2016 Canadian Census, it recorded a population of 175 living in 48 of its 59 total private dwellings. In the same year, its Community Well-Being index was calculated at 50 of 100, compared to 58.4 for the average First Nations community and 77.5 for the average non-Indigenous community.

Star Blanket 83C is an Indian reserve of the Star Blanket Cree Nation in Saskatchewan. It is about 18 kilometres (11 mi) north-east of Lipton. In the 2016 Canadian Census, it recorded a population of 0 living in 1 of its 1 total private dwellings.
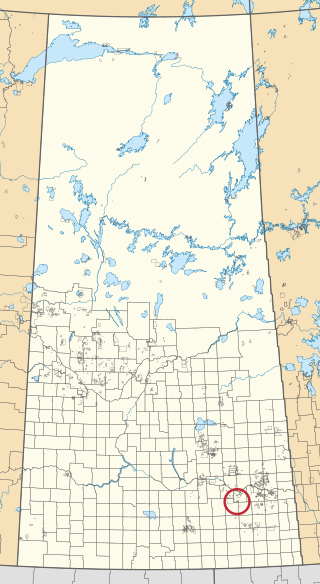
Carry the Kettle 76-1 is an Indian reserve of the Carry the Kettle Nakoda First Nation in Saskatchewan. It is 21 kilometres north-east of Sintaluta.
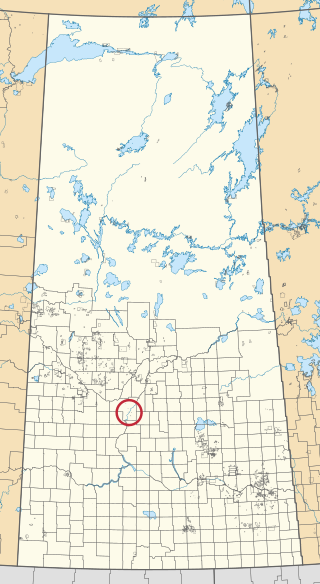
The Nakaway Ahkeeng Reserve is an Indian reserve of the Yellow Quill First Nation in Saskatchewan. It is in the city of Saskatoon.

Yellow Quill 90 is an Indian reserve of the Yellow Quill First Nation in Saskatchewan on the eastern shore of Nut Lake. It is about 19 kilometres (12 mi) north-west of Kelvington. In the 2016 Canadian Census, it recorded a population of 436 living in 110 of its 121 total private dwellings. In the same year, its Community Well-Being index was calculated at 45 of 100, compared to 58.4 for the average First Nations community and 77.5 for the average non-Indigenous community.

Yellow Quill 90-8 is an Indian reserve of the Yellow Quill First Nation in Saskatchewan. It is about 27 kilometres (17 mi) north of Kelvington.

Yellow Quill 90-9 is an Indian reserve of the Yellow Quill First Nation in Saskatchewan, Canada. In the 2016 Canadian Census, it recorded a population of 50 living in 14 of its 15 total private dwellings.
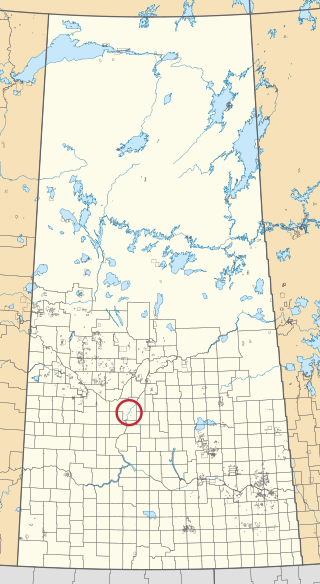
Yellow Quill 90-10 is an Indian reserve of the Yellow Quill First Nation in Saskatchewan.

Yellow Quill 90-18 is an Indian reserve of the Yellow Quill First Nation in Saskatchewan.