A breakthrough infection is a case of illness in which a vaccinated individual becomes infected with the illness, because the vaccine has failed to provide complete immunity against the pathogen. Breakthrough infections have been identified in individuals immunized against a variety of diseases including mumps, varicella (Chickenpox), influenza, and COVID-19. The characteristics of the breakthrough infection are dependent on the virus itself. Often, infection of the vaccinated individual results in milder symptoms and shorter duration than if the infection were contracted naturally.
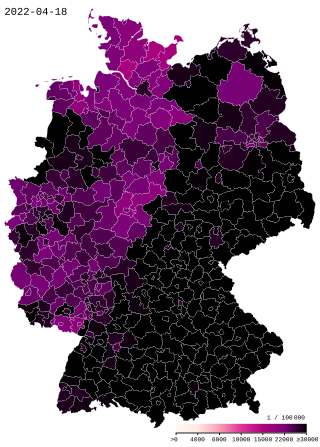
The COVID-19 pandemic in Germany has resulted in 38,368,891 confirmed cases of COVID-19 and 171,411 deaths.

The COVID-19 pandemic in Austria is part of the ongoing worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. In Austria, a pair of cases were confirmed on 25 February 2020. The cases involved a 24-year-old man and a 24-year-old woman who were travelling from Lombardy, Italy, and were treated at a hospital in Innsbruck. According to new figures released by Austrian authorities on 23 June, the first case in the country was recorded in Ischgl, Tyrol on 8 February.

The COVID-19 pandemic in Latvia is part of the ongoing worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus was confirmed to have reached Latvia on 2 March 2020, having been brought along with people returning from abroad.

The COVID-19 pandemic in Egypt is part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus was confirmed to have reached Egypt on 14 February 2020.
A COVID‑19 vaccine is a vaccine intended to provide acquired immunity against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‑19).
The COVID-19 pandemic was confirmed to have reached Cyprus on 9 March 2020. Data released by the Cypriot government includes cases in the British Overseas Territory of Akrotiri and Dhekelia, but does not include cases in Northern Cyprus due to the long-running Cyprus dispute.

The COVID-19 pandemic in Cuba is part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus was confirmed to have spread to Cuba on 11 March 2020 when three Italian tourists tested positive for the virus.

The COVID-19 pandemic in the Cook Islands is part of the ongoing worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. As of 30 October 2021, 12,841 first doses and 12,498 second doses of vaccine had been administered, which represents over 97% of the eligible population (12+) fully vaccinated.
The following is a timeline of the COVID-19 pandemic in the Republic of Ireland in 2021.
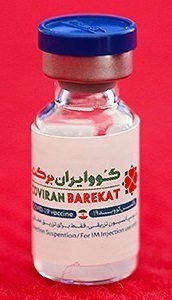
COVIran Barekat is a COVID-19 vaccine developed in Iran by Shifa Pharmed Industrial Group, a subsidiary of the Barkat Pharmaceutical Group. It is an inactivated virus-based vaccine. Iranian authorities have authorized its emergency use. This makes it the first locally developed COVID-19 vaccine to be approved for emergency use in the Middle East.

EpiVacCorona is a peptide-based vaccine against COVID-19 developed by the VECTOR center of Virology. The lack of protective effectiveness of EpiVacCorona, which is still in use in Russia, has been reported in scientific literature and in the media. The vaccine consists of three chemically synthesized peptides that are conjugated to a large carrier protein. This protein is a fusion product of a viral nucleocapsid protein and a bacterial MBP protein. A phase three clinical trial to show whether or not the vaccine can protect people against COVID-19 was launched in November 2020 with more than three thousand participants. The facts of the end of the trial and the result of the trial have not been made public.

COVID-19 vaccination in New Zealand began on 20 February 2021, and will continue throughout the pandemic with the goal of vaccinating all willing New Zealanders aged 5 or older. Those aged 5 to 11 require a parent, caregiver or legal guardian accompany them to their appointment and provide consent for them to be vaccinated. As of 1 September, anyone in New Zealand, regardless of their immigration status, is eligible to be vaccinated.

The Delta variant (B.1.617.2) was a variant of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. It was first detected in India on 5 October 2020. The Delta variant was named on 31 May 2021 and had spread to over 179 countries by 22 November 2021. The World Health Organization (WHO) indicated in June 2021 that the Delta variant was becoming the dominant strain globally.
COVID-19 vaccination in Djibouti is an ongoing immunisation campaign against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), in response to the ongoing pandemic in the country.

COVID-19 vaccine clinical research uses clinical research to establish the characteristics of COVID-19 vaccines. These characteristics include efficacy, effectiveness and safety. As of November 2022, 40 vaccines are authorized by at least one national regulatory authority for public use:

Anti-vaccination activists and other people in many countries have spread a variety of unfounded conspiracy theories and other misinformation about COVID-19 vaccines based on misunderstood or misrepresented science, religion, and law. These have included exaggerated claims about side effects, misrepresentations about how the immune system works and when and how COVID-19 vaccines are made, a story about COVID-19 being spread by 5G, and other false or distorted information. This misinformation has proliferated and may have made many people averse to vaccination. This has led to governments and private organizations around the world introducing measures to incentivize/coerce vaccination, such as lotteries, mandates and free entry to events, which has in turn led to further misinformation about the legality and effect of these measures themselves.

A vaccine passport or proof of vaccination is an immunity passport employed as a credential in countries and jurisdictions as part of efforts to control the COVID-19 pandemic via vaccination. A vaccine passport is typically issued by a government or health authority, and usually consists of a digital or printed record. Some credentials may include a scannable QR code, which can also be provisioned via mobile app. It may or may not use a COVID-19 vaccine card as a basis of authentication.

The government of Germany has initially responded to the COVID-19 pandemic in the country with preventive measures to curb the spread of the coronavirus disease 2019 in the country. With the nationwide spread of the disease from March 2020, preventive measures were replaced by containment measures, including a lockdown from March. On 25 March, the Bundestag made the determination of an epidemic situation of national significance. This created a legal framework for the government of chancellor Angela Merkel and the heads of the 16 German states to agree on nationwide pandemic restrictions. Implementation of decisions by that panel remained a matter of individual states, however, leading to differences in anti-pandemic rules and regulations across states.

Omicron (B.1.1.529) is a variant of SARS-CoV-2 first reported to the World Health Organization (WHO) by the Network for Genomics Surveillance in South Africa on 24 November 2021. It was first detected in Botswana and has spread to become the predominant variant in circulation around the world. Following the original B.1.1.529 variant, several subvariants of Omicron have emerged including: BA.1, BA.2, BA.3, BA.4, and BA.5. Since October 2022, two subvariants of BA.5 called BQ.1 and BQ.1.1 have emerged.













