Live attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV) is a type of influenza vaccine in the form of a nasal spray that is recommended for the prevention of influenza.
A COVID‑19 vaccine is a vaccine intended to provide acquired immunity against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‑19).
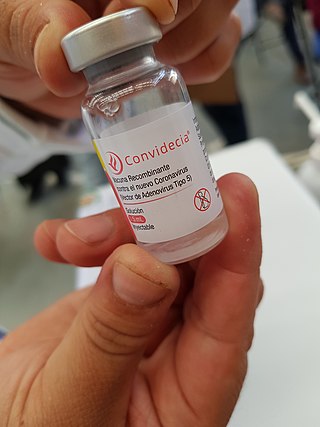
AD5-nCOV, trade-named Convidecia, is a single-dose viral vector vaccine for COVID-19 that is also used as an inhaled booster. It was developed by CanSino Biologics, with Phase III trials conducted in Argentina, Chile, Mexico, Pakistan, Russia, and Saudi Arabia with 40,000 participants.
A nasal vaccine is a vaccine administered through the nose that stimulates an immune response without an injection. It induces immunity through the inner surface of the nose, a surface that naturally comes in contact with many airborne microbes. Nasal vaccines are emerging as an alternative to injectable vaccines because they do not use needles and can be introduced through the mucosal route. Nasal vaccines can be delivered through nasal sprays to prevent respiratory infections, such as influenza.

ZF2001, trade-named Zifivax or ZF-UZ-VAC-2001, is an adjuvanted protein subunit COVID-19 vaccine developed by Anhui Zhifei Longcom in collaboration with the Institute of Microbiology at the Chinese Academy of Sciences. The vaccine candidate is in Phase III trials with 29,000 participants in China, Ecuador, Malaysia, Pakistan, and Uzbekistan.

Soberana 02 or Soberana 2, technical name FINLAY-FR-2, is a COVID-19 vaccine produced by the Finlay Institute, a Cuban epidemiological research institute. The vaccine is known as PastoCovac in Iran, where it has been developed in collaboration with the Pasteur Institute of Iran.

The Sanofi–GSK COVID-19 vaccine sold under the brand name VidPrevtyn Beta, is a COVID-19 vaccine developed by Sanofi Pasteur and GSK.

iNCOVACC is an intranasal COVID-19 vaccine candidate developed by Bharat Biotech, American company Precision Virologics and the Washington University School of Medicine in St Louis, Missouri, United States.

The MVC COVID-19 vaccine, designated MVC-COV1901 and also known as the Medigen COVID-19 vaccine, is a protein subunit COVID-19 vaccine developed by Medigen Vaccine Biologics Corporation in Taiwan, American company Dynavax Technologies, and the U.S. National Institutes of Health.

A viral vector vaccine is a vaccine that uses a viral vector to deliver genetic material (DNA) that can be transcribed by the recipient's host cells as mRNA coding for a desired protein, or antigen, to elicit an immune response. As of April 2021, six viral vector vaccines, four COVID-19 vaccines and two Ebola vaccines, have been authorized for use in humans.

AWcorna, originally termed ARCoV and also known as the Walvax COVID-19 vaccine, is an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine developed by Walvax Biotechnology, Suzhou Abogen Biosciences, and the PLA Academy of Military Science. In contrast to other mRNA COVID vaccines, such as those by Pfizer-BioNtech and Moderna, this vaccine primarily targets the Sars-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain of the spike protein, rather than the entire spike protein. It is approved for Phase III trials in China, Mexico, Indonesia, and Nepal.

NDV-HXP-S is a COVID-19 vaccine candidate developed under the leadership of Peter Palese, Adolfo García-Sastre, and Florian Krammer at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.

V-01 is a protein subunit COVID-19 vaccine candidate developed by a subsidiary of Livzon Pharmaceutical Group Inc.
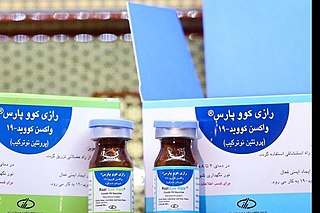
Razi Cov Pars is a COVID-19 vaccine developed by the Iranian Razi Vaccine and Serum Research Institute.

COVI-VAC is a COVID-19 vaccine developed by Codagenix, Inc. In December 2020, COVI-VAC started a Phase I clinical trial, involving 48 participants. The trial was scheduled to complete in June 2021, with results to be reported by May 2022. On September 29, 2021, Codagenix presented positive phase 1 data for COVI-VAC at IDWEEK2021. Data indicates that COVI-VAC is well tolerated, with no significant adverse events reported and that administration of the intranasal vaccine was immunogenic and capable of blocking nasal replication of the virus with minimal viral shedding, recorded at levels lower than those likely to result in subsequent transmission of COVID-19. Furthermore, COVI-VAC was shown to stimulate both serum and mucosal antibody immune responses.

COVID-19 vaccine clinical research uses clinical research to establish the characteristics of COVID-19 vaccines. These characteristics include efficacy, effectiveness and safety. As of November 2022, 40 vaccines are authorized by at least one national regulatory authority for public use:

Noora is a COVID-19 vaccine candidate developed by Baqiyatallah University of Medical Sciences in collaboration with Plasma Darman Sarv Sepid Co. in Iran.

Soberana Plus, technical name FINLAY-FR-1A, is a COVID-19 candidate vaccine produced by the Finlay Institute, a Cuban epidemiological research institute.

S-268019-b is a protein subunit COVID-19 vaccine candidate developed by Shionogi.

LYB001 is a COVID-19 vaccine candidate developed by Yantai Patronus Biotech Co., Ltd.







