Arcturus Therapeutics is an American RNA medicines biotechnology company focused on the discovery, development and commercialization of therapeutics for rare diseases and infectious diseases. Arcturus has developed proprietary lipid nanoparticle RNA therapeutics for nucleic acid medicines including small interfering RNA (siRNA), messenger RNA (mRNA), gene editing RNA, DNA, antisense oligonucleotides, and microRNA.

An mRNAvaccine is a type of vaccine that uses a copy of a molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA) to produce an immune response. The vaccine delivers molecules of antigen-encoding mRNA into immune cells, which use the designed mRNA as a blueprint to build foreign protein that would normally be produced by a pathogen or by a cancer cell. These protein molecules stimulate an adaptive immune response that teaches the body to identify and destroy the corresponding pathogen or cancer cells. The mRNA is delivered by a co-formulation of the RNA encapsulated in lipid nanoparticles that protect the RNA strands and help their absorption into the cells.
A COVID‑19 vaccine is a vaccine intended to provide acquired immunity against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‑19).

COVID-19 drug development is the research process to develop preventative therapeutic prescription drugs that would alleviate the severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). From early 2020 through 2021, several hundred drug companies, biotechnology firms, university research groups, and health organizations were developing therapeutic candidates for COVID-19 disease in various stages of preclinical or clinical research, with 419 potential COVID-19 drugs in clinical trials, as of April 2021.

Valneva COVID-19 vaccine is a COVID-19 vaccine developed by French biotechnology company Valneva SE in collaboration with the American biopharmaceutical company Dynavax Technologies.

The Novavax COVID-19 vaccine, sold under the brand names Nuvaxovid and Covovax, among others, is a subunit COVID-19 vaccine developed by Novavax and the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI).

ZF2001, trade-named Zifivax or ZF-UZ-VAC-2001, is an adjuvanted protein subunit COVID-19 vaccine developed by Anhui Zhifei Longcom in collaboration with the Institute of Microbiology at the Chinese Academy of Sciences. The vaccine candidate is in Phase III trials with 29,000 participants in China, Ecuador, Malaysia, Pakistan, and Uzbekistan.

The CureVac COVID-19 vaccine was a COVID-19 vaccine candidate developed by CureVac N.V. and the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI). The vaccine showed inadequate results in its Phase III trials with only 47% efficacy. In October 2021 CureVac abandoned further development and production plans for CVnCoV and refocused efforts on a cooperation with GlaxoSmithKline.

ZyCoV-D is a DNA plasmid-based COVID-19 vaccine developed by Indian pharmaceutical company Cadila Healthcare, with support from the Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council. It is approved for emergency use in India.

The Sanofi–GSK COVID-19 vaccine sold under the brand name VidPrevtyn Beta, is a COVID-19 vaccine developed by Sanofi Pasteur and GSK.

The MVC COVID-19 vaccine, designated MVC-COV1901 and also known as the Medigen COVID-19 vaccine, is a protein subunit COVID-19 vaccine developed by Medigen Vaccine Biologics Corporation in Taiwan, American company Dynavax Technologies, and the U.S. National Institutes of Health.

AWcorna, originally termed ARCoV and also known as the Walvax COVID-19 vaccine, is an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine developed by Walvax Biotechnology, Suzhou Abogen Biosciences, and the PLA Academy of Military Science. In contrast to other mRNA COVID vaccines, such as those by Pfizer-BioNtech and Moderna, this vaccine primarily targets the Sars-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain of the spike protein, rather than the entire spike protein. It is approved for Phase III trials in China, Mexico, Indonesia, and Nepal.

Corbevax is a protein subunit COVID-19 vaccine developed by Texas Children's Hospital Center for Vaccine Development and Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, Texas and Dynavax technologies based in Emeryville, California. It is licensed to Indian biopharmaceutical firm Biological E. Limited (BioE) for development and production.

NDV-HXP-S is a COVID-19 vaccine candidate developed under the leadership of Peter Palese, Adolfo García-Sastre, and Florian Krammer at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
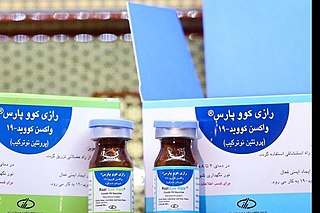
Razi Cov Pars is a COVID-19 vaccine developed by the Iranian Razi Vaccine and Serum Research Institute. Razi Cov Pars is a covid-19 vaccine based on recombinant protein, which is being produced by Razi Vaccine and Serum Research Institute, Iran. This vaccine is the first injectable-intranasal recombinant protein corona vaccine in the world, which Dr. Seyed Reza Banihashemi is the main researcher of this In the pre-clinical article of this vaccine, for the first time in the world, the use of intranasal doses after intramuscular injection was introduced to reduce the circulation of this virus..It's the second Iranian COVID-19 vaccine reaching human trials and is currently in phase III of clinical research during which it's compared to the Sinopharm BIBP vaccine. It received emergency use authorization in Iran on 31 October 2021.

COVAX-19 is the result of a collaboration between Vaxine and CinnaGen, a private company with operations in the Middle East. COVAX-19 is a recombinant protein-based COVID-19 vaccine developed by South Australian-based biotech company Vaxine. It is under clinical trial in collaboration with the Iranian company CinnaGen.

Skycovione is a COVID-19 vaccine candidate developed by SK Bioscience and the Institute for Protein Design of the University of Washington, It is South Korea's first homegrown COVID-19 vaccine and utilizes GSK's AS03 adjuvant technology.

COVID-19 vaccine clinical research uses clinical research to establish the characteristics of COVID-19 vaccines. These characteristics include efficacy, effectiveness, and safety. As of November 2022, 40 vaccines are authorized by at least one national regulatory authority for public use:

A universal coronavirus vaccine, also known as a pan-coronavirus vaccine, is a theoretical coronavirus vaccine that would be effective against all coronavirus strains. A universal vaccine would provide protection against coronavirus strains that have caused disease in humans, such as SARS-CoV-2, while also providing protection against future coronavirus strains. Such a vaccine has been proposed to prevent or mitigate future coronavirus epidemics and pandemics.

S-268019-b is a protein subunit COVID-19 vaccine candidate developed by Shionogi.






