Related Research Articles
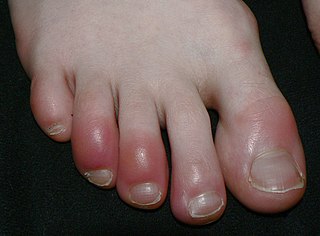
Chilblains, also known as pernio, is a medical condition in which damage occurs to capillary beds in the skin, most often in the hands or feet, when blood perfuses into the nearby tissue, resulting in redness, itching, inflammation, and possibly blisters.

Lichen planus (LP) is a chronic inflammatory and immune-mediated disease that affects the skin, nails, hair, and mucous membranes. It is not an actual lichen, but is named for its appearance. It is characterized by polygonal, flat-topped, violaceous papules and plaques with overlying, reticulated, fine white scale, commonly affecting dorsal hands, flexural wrists and forearms, trunk, anterior lower legs and oral mucosa. The hue may be gray-brown in people with darker skin. Although there is a broad clinical range of LP manifestations, the skin and oral cavity remain as the major sites of involvement. The cause is unknown, but it is thought to be the result of an autoimmune process with an unknown initial trigger. There is no cure, but many different medications and procedures have been used in efforts to control the symptoms.

Mycosis fungoides, also known as Alibert-Bazin syndrome or granuloma fungoides, is the most common form of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. It generally affects the skin, but may progress internally over time. Symptoms include rash, tumors, skin lesions, and itchy skin.

A maculopapular rash is a type of rash characterized by a flat, red area on the skin that is covered with small confluent bumps. It may only appear red in lighter-skinned people. The term "maculopapular" is a compound: macules are small, flat discolored spots on the surface of the skin; and papules are small, raised bumps. It is also described as erythematous, or red.

Erythema ab igneEAI, also known as hot water bottle rash, is a skin condition caused by long-term exposure to heat. Prolonged thermal radiation exposure to the skin can lead to the development of reticulated erythema, hyperpigmentation, scaling, and telangiectasias in the affected area. Some people may complain of mild itchiness and a burning sensation, but often, unless a change in pigmentation is seen, it can go unnoticed.

Livedo reticularis is a common skin finding consisting of a mottled reticulated vascular pattern that appears as a lace-like purplish discoloration of the skin. The discoloration is caused by reduction in blood flow through the arterioles that supply the cutaneous capillaries, resulting in deoxygenated blood showing as blue discoloration. This can be a secondary effect of a condition that increases a person's risk of forming blood clots, including a wide array of pathological and nonpathological conditions. Examples include hyperlipidemia, microvascular hematological or anemia states, nutritional deficiencies, hyper- and autoimmune diseases, and drugs/toxins.

Erythema toxicum neonatorum is a common, non-threatening rash in newborns. It appears in 4-70% of newborns within the first week of life, and it typically improves within 1–2 weeks. It only occurs during the newborn period, but may appear slightly later in premature babies. The rash has a variable appearance. It typically includes blotchy red spots, often with overlying firm, yellow-white bumps or pus-filled boils. There may be only a few or many lesions. The lesions can appear almost anywhere on the body, and individual lesions may appear and disappear within hours. There are no other symptoms associated with erythema toxicum neonatorum, and the rash does not have any long-term effects on the skin. Erythema toxicum neonatorum is not harmful and does not require any treatment.

Pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy (PUPPP), known in United Kingdom as polymorphic eruption of pregnancy (PEP), is a chronic hives-like rash that strikes some women during pregnancy. Some skin changes are known to occur in people who are pregnant while other skin conditions, or dermatoses, that people have prior to getting pregnant will become altered or symptoms will increase. Pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy (PUPPP) is one of many skin conditions that is specific to pregnancy and occurs in about 1 in every 160 (0.625%) of pregnancies.

Sneddon's syndrome is a form of arteriopathy characterized by several symptoms, including:
Purpura fulminans is an acute, often fatal, thrombotic disorder which manifests as blood spots, bruising and discolouration of the skin resulting from coagulation in small blood vessels within the skin and rapidly leads to skin necrosis and disseminated intravascular coagulation.

Discoid lupus erythematosus is the most common type of chronic cutaneous lupus (CCLE), an autoimmune skin condition on the lupus erythematosus spectrum of illnesses. It presents with red, painful, inflamed and coin-shaped patches of skin with a scaly and crusty appearance, most often on the scalp, cheeks, and ears. Hair loss may occur if the lesions are on the scalp. The lesions can then develop severe scarring, and the centre areas may appear lighter in color with a rim darker than the normal skin. These lesions can last for years without treatment.
Erythema gyratum repens is a skin condition that has a strong association with internal cancers. It characteristically presents with red wavy lines, generally in older adults. These regular whirly rings rapidly and repetitively appear within existing ones, giving the impression that the rash is moving. The resulting pattern is similar to wood grain. There is often an intense itch and scale over the leading edge, which may be slightly raised.
Necrotizing vasculitis, also called systemic necrotizing vasculitus, is a category of vasculitis, comprising vasculitides that present with necrosis.
Anticonvulsant/sulfonamide hypersensitivity syndrome is a potentially serious hypersensitivity reaction that can be seen with medications with an aromatic amine chemical structure, such as aromatic anticonvulsants, sulfonamides, or other medications with an aromatic amine. Cross-reactivity should not occur between medications with an aromatic amine and medications without an aromatic amine ; therefore, these medications can be safely used in the future.

Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) is a rare skin reaction that in 90% of cases is related to medication.

Cutaneous small-vessel vasculitis (CSVV), is inflammation of small blood vessels, usually accompanied by small lumps beneath the skin. The condition is also known as hypersensitivity vasculitis, cutaneous leukocytoclastic vasculitis, hypersensitivity angiitis, cutaneous leukocytoclastic angiitis, cutaneous necrotizing vasculitis and cutaneous necrotizing venulitis,
The term morbilliform refers to a rash that looks like measles. The rash consists of macular lesions that are red and usually 2–10 mm in diameter but may be confluent in places. A morbilliform rash is a rose-red flat (macular) or slightly elevated (maculopapular) eruption, showing circular or elliptical lesions varying in diameter from 1 to 3 mm, with healthy-looking skin intervening.
Acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus is a cutaneous condition characterized by a bilateral malar rash and lesions that tend to be transient, and that follow sun exposure. The acute form is distinct from chronic and subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus, which may have different types of skin lesions. Cutaneous lupus erythematosus is associated with both lupus erythematosus-specific lesions and cutaneous manifestations that are not specific to lupus erythematosus, such as oral ulcers and urticaria. Because of the diagnostic criteria used to diagnose systemic lupus erythematosus, a patient with only cutaneous manifestations may be diagnosed with the systemic form of the disease.
IgG4-related skin disease is the recommended name for skin manifestations in IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD). Multiple different skin manifestations have been described.
References
- 1 2 Freeman EE, McMahon DE, Lipoff JB, Rosenbach M, Kovarik C, Desai SR, et al. (October 2020). "The spectrum of COVID-19-associated dermatologic manifestations: An international registry of 716 patients from 31 countries". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 83 (4): 1118–1129. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.06.1016 . PMC 7331510 . PMID 32622888.
- ↑ "COVID-19 dermatology registry". American Academy of Dermatology. Retrieved 1 March 2021.
- ↑ Freeman EE, McMahon DE, Hruza GJ, Irvine AD, Spuls PI, Smith CH, et al. (September 2020). "International collaboration and rapid harmonization across dermatologic COVID-19 registries". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 83 (3): e261–e266. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.06.050 . PMC 7833847 . PMID 32562840.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Genovese G, Moltrasio C, Berti E, Marzano AV (2021). "Skin Manifestations Associated with COVID-19: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives". review. Dermatology. 237 (1): 1–12. doi: 10.1159/000512932 . PMC 7801998 . PMID 33232965.
- ↑ Feldman SR, Freeman EE (June 2021). Callen J, Duffin KC, Ofori AO, Corona R (eds.). "COVID-19: Cutaneous manifestations and issues related to dermatologic care". UpToDate. Wolters Kluwer. Retrieved 1 March 2021.
- 1 2 Shams S, Rathore SS, Anvekar P, Sondhi M, Kancherla N, Tousif S, et al. (March 2021). "Maculopapular skin eruptions associated with Covid-19: A systematic review". review. Dermatologic Therapy. 34 (2): e14788. doi:10.1111/dth.14788. PMC 7995033 . PMID 33481314.
- ↑ Kaya G, Kaya A, Saurat JH (June 2020). "Clinical and Histopathological Features and Potential Pathological Mechanisms of Skin Lesions in COVID-19: Review of the Literature". review. Dermatopathology. Basel, Switzerland. 7 (1): 3–16. doi: 10.3390/dermatopathology7010002 . PMC 7583593 . PMID 32608380.