A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is a type of configurable integrated circuit that can be repeatedly programmed post manufacturing. FPGAs are a subset of logic devices referred to as programmable logic devices ("PLDs"). They consist of an array of programmable logic blocks with a connecting grid, that can be configured "in the field" to interconnect with other logic blocks to perform various digital functions. FPGAs are often used in limited (low) quantity production of custom-made products, and in research and development, where the higher cost of individual FPGAs is not as important, and where creating and manufacturing a custom circuit wouldn't be feasible. Other applications for FPGAs include the telecommunications, automotive, aerospace, and industrial sectors, which benefit from their flexibility, high signal processing speed, and parallel processing abilities.
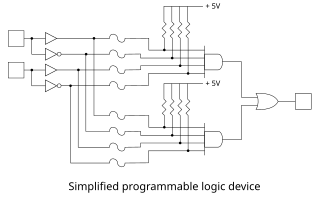
A programmable logic device (PLD) is an electronic component used to build reconfigurable digital circuits. Unlike digital logic constructed using discrete logic gates with fixed functions, the function of a PLD is undefined at the time of manufacture. Before the PLD can be used in a circuit it must be programmed to implement the desired function. Compared to fixed logic devices, programmable logic devices simplify the design of complex logic and may offer superior performance. Unlike for microprocessors, programming a PLD changes the connections made between the gates in the device.
Reconfigurable computing is a computer architecture combining some of the flexibility of software with the high performance of hardware by processing with flexible hardware platforms like field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs). The principal difference when compared to using ordinary microprocessors is the ability to add custom computational blocks using FPGAs. On the other hand, the main difference from custom hardware, i.e. application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) is the possibility to adapt the hardware during runtime by "loading" a new circuit on the reconfigurable fabric, thus providing new computational blocks without the need to manufacture and add new chips to the existing system.

Altera Corporation is a manufacturer of programmable logic devices (PLDs) headquartered in San Jose, California. It was founded in 1983 and acquired by Intel in 2015 before becoming independent once again in 2024 as a company focused on development of Field-Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) technology and system on a chip FPGAs.

Programmable Array Logic (PAL) is a family of programmable logic device semiconductors used to implement logic functions in digital circuits that was introduced by Monolithic Memories, Inc. (MMI) in March 1978. MMI obtained a registered trademark on the term PAL for use in "Programmable Semiconductor Logic Circuits". The trademark is currently held by Lattice Semiconductor.

Xilinx, Inc. was an American technology and semiconductor company that primarily supplied programmable logic devices. The company is known for inventing the first commercially viable field-programmable gate array (FPGA). It also created the first fabless manufacturing model.
Nios II is a 32-bit embedded processor architecture designed specifically for the Altera family of field-programmable gate array (FPGA) integrated circuits. Nios II incorporates many enhancements over the original Nios architecture, making it more suitable for a wider range of embedded computing applications, from digital signal processing (DSP) to system-control.

A multi-core processor is a microprocessor on a single integrated circuit with two or more separate processing units, called cores, each of which reads and executes program instructions. The instructions are ordinary CPU instructions but the single processor can run instructions on separate cores at the same time, increasing overall speed for programs that support multithreading or other parallel computing techniques. Manufacturers typically integrate the cores onto a single integrated circuit die or onto multiple dies in a single chip package. The microprocessors currently used in almost all personal computers are multi-core.
The transistor count is the number of transistors in an electronic device. It is the most common measure of integrated circuit complexity. The rate at which MOS transistor counts have increased generally follows Moore's law, which observes that transistor count doubles approximately every two years. However, being directly proportional to the area of a die, transistor count does not represent how advanced the corresponding manufacturing technology is. A better indication of this is transistor density which is the ratio of a semiconductor's transistor count to its die area.
Intel Quartus Prime is programmable logic device design software produced by Intel; prior to Intel's acquisition of Altera the tool was called Altera Quartus Prime, earlier Altera Quartus II. Quartus Prime enables analysis and synthesis of HDL designs, which enables the developer to compile their designs, perform timing analysis, examine RTL diagrams, simulate a design's reaction to different stimuli, and configure the target device with the programmer. Quartus Prime includes an implementation of VHDL and Verilog for hardware description, visual editing of logic circuits, and vector waveform simulation.

The ARM Cortex-A9 MPCore is a 32-bit multi-core processor that provides up to 4 cache-coherent cores, each implementing the ARM v7 architecture instruction set. It was introduced in 2007.

Intel Core is a line of multi-core central processing units (CPUs) for midrange, embedded, workstation, high-end and enthusiast computer markets marketed by Intel Corporation. These processors displaced the existing mid- to high-end Pentium processors at the time of their introduction, moving the Pentium to the entry level. Identical or more capable versions of Core processors are also sold as Xeon processors for the server and workstation markets.
Rockchip is a Chinese fabless semiconductor company based in Fuzhou, Fujian province. Rockchip has been providing SoC products for tablets & PCs, streaming media TV boxes, AI audio & vision, IoT hardware since founded in 2001. It has offices in Shanghai, Beijing, Shenzhen, Hangzhou and Hong Kong. It designs system on a chip (SoC) products, using the ARM architecture licensed from ARM Holdings for the majority of its projects.
Virtex is the flagship family of FPGA products currently developed by AMD, originally Xilinx before being acquired by the former. Other current product lines include Kintex (mid-range) and Artix (low-cost), each including configurations and models optimized for different applications. In addition, AMD offers the Spartan low-cost series, which continues to be updated and is nearing production utilizing the same underlying architecture and process node as the larger 7-series devices.
Achronix Semiconductor Corporation is an American fabless semiconductor company based in Santa Clara, California with an additional R&D facility in Bangalore, India, and an additional sales office in Shenzhen, China. Achronix is a diversified fabless semiconductor company that sells FPGA products, embedded FPGA (eFPGA) products, system-level products and supporting design tools. Achronix was founded in 2004 in Ithaca, New York based on technology licensed from Cornell University. In 2006, Achronix moved its headquarters to Silicon Valley.

Stratix is a brand of FPGA products developed by Intel, Programmable Solutions Group. Other current FPGA product lines include e.g. Agilex, Arria and Cyclone families.
In computing, a logic block or configurable logic block (CLB) is a fundamental building block of field-programmable gate array (FPGA) technology. Logic blocks can be configured by the engineer to provide reconfigurable logic gates.
The ARM Cortex-A55 is a central processing unit implementing the ARMv8.2-A 64-bit instruction set designed by ARM Holdings' Cambridge design centre. The Cortex-A55 is a 2-wide decode in-order superscalar pipeline.
The ARM Cortex-A76 is a central processing unit implementing the ARMv8.2-A 64-bit instruction set designed by ARM Holdings' Austin design centre. ARM states a 25% and 35% increase in integer and floating point performance, respectively, over a Cortex-A75 of the previous generation.