
Trajan was a Roman emperor from AD 98 to 117, the second of the Five Good Emperors of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty. He was a philanthropic ruler and a successful soldier-emperor who led the Roman Empire to its greatest territorial extent by the time of his death. He was given the title of Optimus by the Roman Senate.
AD 68 (LXVIII) was a leap year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Silius Italicus and Trachalus, or the start of the Year of the Four Emperors. The denomination AD 68 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. These are now used throughout the world.
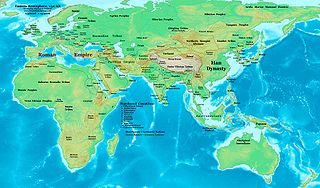
The 50s decade ran from January 1, 50, to December 31, 59. It was the sixth decade in the Anno Domini/Common Era, if the nine-year period from 1 AD to 9 AD is considered as a "decade".

The 60s decade ran from January 1, AD 60, to December 31, AD 69.

The 80s was a decade that ran from January 1, AD 80, to December 31, AD 89.

The 100s was a decade that ran from January 1, AD 100, to December 31, AD 109.

The 120s was a decade that ran from January 1, AD 120, to December 31, AD 129.

The 130s was a decade that ran from January 1, 130, to December 31, 139.
The 160s decade ran from January 1, 160, to December 31, 169.
The 190s decade ran from January 1, 190, to December 31, 199.
Year 115 (CXV) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Messalla and Vergilianus. The denomination 115 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 116 (CXVI) was a leap year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Lamia and Vetus. The denomination 116 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
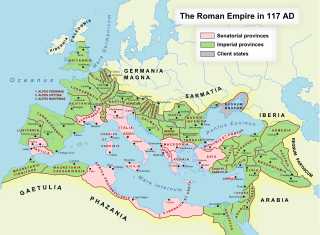
Year 117 (CXVII) was a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Niger and Apronianus. The denomination 117 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 119 (CXIX) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Hadrianus and Rusticus. The denomination 119 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Parthamaspates was a Parthian prince who ruled as a Roman client king in Mesopotamia, and later of Osroene during the early second century AD. He was the son of the Parthian emperor Osroes I.

The Kitos War was one of the major Jewish–Roman wars (66–136). The rebellions erupted in 115 when most of the Roman armies were fighting Trajan's Parthian War on the eastern border of the Roman Empire. Major uprisings by Jews in Cyrenaica, Cyprus and Egypt spiralled out of control, resulting in a widespread slaughter of the remaining Roman garrisons and Roman citizens by Jewish rebels.

Mesopotamia was the name of a Roman province, initially a short-lived creation of the Roman emperor Trajan in 116–117 and then re-established by Emperor Septimius Severus in c. 198. Control of the province was subsequently fought over between the Roman and the Sassanian empires until the Muslim conquests of the 7th century.
The Roman–Parthian Wars were a series of conflicts between the Parthian Empire and the Roman Republic and Roman Empire. It was the first series of conflicts in what would be 682 years of Roman–Persian Wars.
Romans in Persia is related to the brief invasion and occupation of western and central areas of Parthia by the Romans during their empire. Emperor Trajan was even temporarily able to nominate a king of western parts of Parthia, Parthamaspates, as ruler of a Roman "client state" in Parthia.

Trajan's Parthian campaign was engaged by Roman Emperor Trajan in 115 against the Parthian Empire in Mesopotamia. The war was initially successful for the Romans, but a series of setbacks, including wide-scale rebellions in the Eastern Mediterranean and North Africa and Trajan's death in 117, ended in a Roman withdrawal.












