
Scandinavia is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. Scandinavia most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It can sometimes also refer more narrowly to the Scandinavian Peninsula. In English usage, Scandinavia is sometimes used as a synonym for Nordic countries. Iceland and the Faroe Islands are sometimes included in Scandinavia for their ethnolinguistic relations with Sweden, Norway and Denmark. While Finland differs from other Nordic countries in this respect, some authors call it Scandinavian due to its economic and other similarities.

The Sámi are the traditionally Sámi-speaking people inhabiting the region of Sápmi, which today encompasses large northern parts of Norway, Sweden, Finland, and of the Kola Peninsula in Russia. The region of Sápmi was formerly known as Lapland, and the Sámi have historically been known in English as Lapps or Laplanders, but these terms are regarded as offensive by the Sámi, who prefer the area's name in their own languages, e.g. Northern Sámi Sápmi. Their traditional languages are the Sámi languages, which are classified as a branch of the Uralic language family.

Norrbotten County is the northernmost county or län of Sweden. It is also the largest county by land area, almost a quarter of Sweden's total area. It shares borders with Västerbotten County to the southwest, the Gulf of Bothnia to the southeast, the counties of Nordland and Troms og Finnmark in Norway to the northwest, and Lapland Province in Finland to the northeast.
Laestadianism, also known as Laestadian Lutheranism and Apostolic Lutheranism, is a pietistic Lutheran revival movement started in Sápmi in the middle of the 19th century. Named after Swedish Lutheran state church administrator and temperance movement leader Lars Levi Laestadius, it is the biggest pietistic revivalist movement in the Nordic countries. It has members mainly in Finland, Northern America, Norway, Russia and Sweden. There are also smaller congregations in Africa, South America and Central Europe. In addition Laestadian Lutherans have missionaries in 23 countries. The number of Laestadians worldwide is estimated to be between 144,000 and 219,000.
A joik or yoik is a traditional form of song in Sámi music performed by the Sámi people of Sapmi in Northern Europe. A performer of joik is called a joikaaja, a joiker or jojkare. Originally, joik referred to only one of several Sami singing styles, but in English the word is often used to refer to all types of traditional Sami singing. As an art form, each joik is meant to reflect or evoke a person, animal, or place..

Southern or South Sámi is the southwesternmost of the Sámi languages, and is spoken in Norway and Sweden. It is an endangered language; the strongholds of this language are the municipalities of Snåsa, Røyrvik, Røros and Hattfjelldal in Norway. Of the approximately 2000 Southern Sami, only about 500 still speak fluent Southern Sami. This language belongs to the Saamic group within the uralic language family and the family comprises nine groups, Saami, Finnic, Mordvin, Mari, Permic, Mansi, Khanty, Samoyed and Hungarian.

Lars Levi Læstadius was a Swedish Sami pastor and administrator of the Swedish state Lutheran church in Lapland who founded the Laestadian pietist revival movement to help his largely Sami congregations, who were being ravaged by alcoholism. Laestadius was also a noted botanist and an author. Laestadius himself became a teetotaller in the 1840s, when he began successfully awakening his Sami parishioners to the misery and destruction alcohol was causing them.

Jokkmokk is a locality and the seat of Jokkmokk Municipality in Norrbotten County, province of Lapland, Sweden, with 2,786 inhabitants in 2010. The Lule Sami name of the place means "River's Curve," due to the meandering river that runs through it. As in other towns in Lapland, the Swedish language is dominant at an official level in Jokkmokk in modern times. The settlement is just north of the Arctic Circle. Talvatissjön is located at the southern part of Jokkmokk.

The Institute for the Languages of Finland, better known as Kotus, is a governmental linguistic research institute of Finland geared to studies of Finnish, Swedish, the Sami languages, Romani language, and Finnish Sign Language.

Lule Sámi is a Uralic, Sámi language spoken around the Lule River, Sweden, and in the northern parts of Nordland county in Norway, especially the Hamarøy municipality, where Lule Sámi is an official language. It is written in the Latin script, having an official alphabet.

Pite Sámi or Arjeplog Sámi is a Sámi language traditionally spoken in Sweden and used to be spoken in Norway. It is a critically endangered language that has only about 25–50 native speakers left and is now only spoken on the Swedish side of the border along the Pite River in the north of Arjeplog and Arvidsjaur and in the mountainous areas of the Arjeplog municipality.

Lapland, also known by its Swedish name Lappland, is a province in northernmost Sweden. It borders Jämtland, Ångermanland, Västerbotten, Norrbotten, Norway and Finland. Nearly a quarter of Sweden's land area is in Lappland.

The two main official languages of Finland are Finnish and Swedish. There are also several official minority languages: three variants of Sami, as well as Romani, Finnish Sign Language and Karelian.
Siiddašjávri (Northern Sami) or Sijdasjávrre (Lule Sami) or Sitasjaure (Swedish) is a lake on the border between Norway and Sweden. The lake covers an area of 71.91 square kilometres (27.76 sq mi), with 0.96 square kilometres (0.37 sq mi) of the lake in Norway and 70.95 square kilometres (27.39 sq mi) in Sweden. The name of the lake comes from the Sami languages, with the ending -jávri or -jávrre being the word for "lake".

Many languages are spoken, written and signed in Norway.
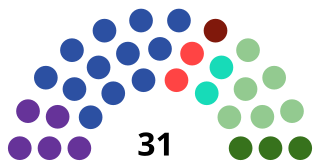
The Sámi Parliament of Sweden is the representative body for people of Sámi heritage in Sweden based in Kiruna. It acts as an institution of cultural autonomy for the indigenous Sámi people.

Sámi languages, in English also rendered as Sami and Saami, are a group of Uralic languages spoken by the Sámi people in Northern Europe. There are, depending on the nature and terms of division, ten or more Sami languages. Several spellings have been used for the Sámi languages, including Sámi, Sami, Saami, Saame, Sámic, Samic and Saamic, as well as the exonyms Lappish and Lappic. The last two, along with the term Lapp, are now often considered pejorative.
Sámi politics refers to politics that concern the Sámi ethnic group in Norway, Sweden, Finland and Russia. In a more narrow sense, it has come to indicate the government of Sámi affairs by Sámi political institutions. This article deals with Sámi political structures, with an emphasis on the contemporary institutions.

Events from the year 1693 in Sweden














