| | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
All 417 seats in the Chamber of Deputies 209 seats needed for a majority | ||||||||||
This lists parties that won seats. See the complete results below. | ||||||||||
Legislative elections were held in France on 5 and 13 July 1830, with a second round on 19 July.
| | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
All 417 seats in the Chamber of Deputies 209 seats needed for a majority | ||||||||||
This lists parties that won seats. See the complete results below. | ||||||||||
Legislative elections were held in France on 5 and 13 July 1830, with a second round on 19 July.
The Chamber of Deputies, the lower house of the French Parliament, was constituted by the Charter of 1814. Deputies were elected for five years, with one-fifth being re-elected each year.
The electoral system, which was used for the last time, was the Loi du double vote ("double voting") as defined in June 1820, combining single-member districts for three-fifths of the deputies, elected by 94,000 registered voters, with at-large voting in each of the departments of France for the remaining seats. This meant that many men could vote twice. [1]
 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Party | Seats | |
| Liberal opposition | 274 | |
| Supporters of the Polignac government | 143 | |
| Total | 417 | |
| Source: Alexander [2] | ||
On 25 July, by the July Ordinances published the next day, King Charles attempted to dissolve the Chamber of Deputies. However, this led to the July Revolution, and as a result of the king's abdication on 2 August, the Chamber was able to proclaim his cousin Louis-Philippe of Orleans as king and continued its term.
The mixed "double voting" system was abolished by the Charter of 1830, adopted on 14 August 1830, which greatly broadened the electorate and established single-member districts only. [1]
119 seats were made subject to by-elections in October 1830, leading to the defeat of many Ultra-royalists.

The Bourbon Restoration was the period of French history during which the House of Bourbon returned to power after the fall of Napoleon Bonaparte in 1814 and 1815. The second Bourbon Restoration lasted until the July Revolution of 1830, during the reigns of Louis XVIII and Charles X (1824-1830), brothers of the late King, Louis XVI. Exiled supporters of the monarchy returned to France, which had been profoundly changed by the French Revolution. Exhausted by the Napoleonic Wars, the kingdom experienced a period of internal and external peace, stable economic prosperity and the preliminaries of industrialisation.

The National Assembly is the lower house of the bicameral French Parliament under the Fifth Republic, the upper house being the Senate. The National Assembly's legislators are known as députés, meaning "delegate" or "envoy" in English; etymologically, it is a cognate of the English word deputy, the standard term for legislators in many parliamentary systems.

The July Monarchy, officially the Kingdom of France, was a liberal constitutional monarchy in France under Louis Philippe I, starting on 26 July 1830, with the revolutionary victory after the July Revolution of 1830, and ending 23 February 1848, with the Revolution of 1848. It marks the end of the Bourbon Restoration (1814–1830). It began with the overthrow of the conservative government of Charles X, the last king of the main line House of Bourbon.

The Chamber of Deputies is the lower house of the Congress of the Union, the bicameral parliament of Mexico. The other chamber is the Senate. The structure and responsibilities of both chambers of Congress are defined in Articles 50 to 70 of the Constitution.

The National Assembly is the federal legislature of the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, which was first elected in 2000 under the 1999 constitution. It is a unicameral body made up of a variable number of members, who are elected by a "universal, direct, personal, and secret" vote partly by direct election in state-based voting districts, and partly on a state-based party-list proportional representation system.
Canada holds elections for legislatures or governments in several jurisdictions: for the federal (national) government, provincial and territorial governments, and municipal governments. Elections are also held for self-governing First Nations and for many other public and private organizations including corporations and trade unions. Municipal elections can also be held for both upper-tier and lower-tier governments.

Elections in Mexico are held for officials at federal, state, and municipal levels. At the federal level, the nation's head of state, the president, is directly elected with the popular vote by all Mexican citizens for a six-year non-renewable term. All members of the bicameral federal legislature, the Congress of the Union, are also elected by all Mexican citizens. At the state level, each state has an elective governor and unicameral congress. At the municipal level, the municipal presidents are also elected by their citizens. Since 2016, a constitutional amendment has designed Mexico City to be a fully autonomous entity on par with the states. Its city mayor, city congress, and borough mayors are elected by their citizens in a similar fashion to those states.

Bolivia elects on national level a head of state – the president – and a legislature. The president and the vice-president are elected for a five-year term by the people. The National Congress has two chambers. The Chamber of Deputies has 130 members, elected for a five-year term using a two vote seat linkage compensatory system and in the case of seven indigenous seats by usos y costumbres. The Chamber of Senators has 36 members: each of the country's nine departments returns four senators allocated proportionally.

The Chamber of Deputies is the lower house of the Plurinational Legislative Assembly of Bolivia. The composition and powers of this house are established in the Political Constitution of the State. The session room is located in the Legislative Palace building in Plaza Murillo.

The French Charter of 1814 was a constitutional text granted by King Louis XVIII of France shortly after the Bourbon Restoration, in form of royal charter. The Congress of Vienna demanded that Louis bring in a constitution of some form before he was restored. After refusing the proposed constitution, the Constitution sénatoriale, set forth on 6 April 1814 by the provisional government and the Sénat conservateur, Louis Stanislas Xavier, count of Provence, bestowed a different constitutional Charter, on 4 June 1814. With the Congress of Vienna's demands met, the count of Provence was officially named Louis XVIII, and the monarchy was restored.

The Charter of 1830 instigated the July Monarchy in France. It was considered a compromise between constitutional monarchists and republicans.

The Chamber of Deputies was the lower house of Parliament in France at various times in the 19th and 20th centuries:
Electoral districts go by different names depending on the country and the office being elected.

Parliamentary elections in the First Czechoslovak Republic were held in 1920, 1925, 1929 and 1935. The Czechoslovak National Assembly consisted of two chambers, the Chamber of Deputies and the Senate, both elected through universal suffrage. During the First Republic, many political parties struggled for political influence and only once did a single party muster a quarter of the national vote. Parties were generally set up along ethnic lines.
The electoral regions of Mexico are geographic areas composed of various states used for the election of the 200 proportional representation legislators to the Chamber of Deputies.
The Italian electoral law of 2017, colloquially known by the nickname Rosatellum after Ettore Rosato, the Democratic Party (PD) leader in the Chamber of Deputies who first proposed the new law, is a parallel voting system, which acts as a mixed electoral system, with 37% of seats allocated using a first-past-the-post electoral system and 63% using a proportional method, with one round of voting. The Chamber and Senate of the Republic did not differ in the way they allocated the proportional seats, both using the largest remainder method of allocating seats.
Parliamentary elections were held in Portugal on 8 and 17 October 1826.
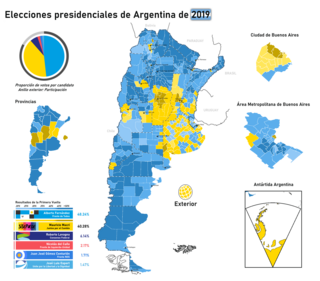
General elections were held in Argentina on 27 October 2019, to elect the president of Argentina, members of the national congress and the governors of most provinces.
Legislative elections were held in France between 8 and 22 May 1815 for the period of the Hundred Days. The elections were held to appoint deputies to the Chamber of Representatives established by the Additional Charter of 22 April 1815. The elections were the first since April 1799 and last of the 'republican system' until the Charter of 1830.
The Liberals was a short lived French liberal political party which was active in several elections before being absorbed into the Doctrinaires, a fellow constitutional monarchy party. Several members of the Liberals eventually went on to serve in the Movement Party and even later in the Orléanist parties. The precedent set by the party would help form modern French classical liberalism, something used in the modern centre-right Republicans party.