
United States gubernatorial elections were held on November 6, 1990, in 36 states and two territories. Most elected in these elections would serve for a 4-year term, while those in New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont would serve for a 2-year term. The elections coincided with the mid-term elections for the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. Heading into the elections, there were 20 seats held by Democrats and 16 held by Republicans. By the end of the elections, 19 seats would be held by a Democrat, 15 would be held by a Republican, and two would be held by other parties.

United States gubernatorial elections were held 6 November 1962 in 35 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1958, in 34 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 4, 1958. Alaska held its first gubernatorial election on achieving statehood.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1942, in 33 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 3, 1942. Elections took place on September 14 in Maine.
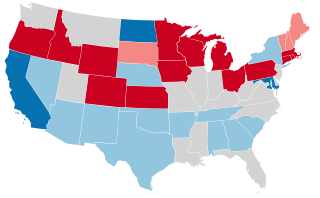
United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1938, in 33 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 8, 1938. Elections took place on September 12 in Maine.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1926, in 33 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 2, 1926. Elections took place on October 5 in Arkansas, and September 13 in Maine.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1924, in 36 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 4, 1924. Elections took place on October 7, 1924 in Arkansas, and September 8, 1924 in Maine.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1916, in 36 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 7, 1916. Elections took place on September 11 in Maine.
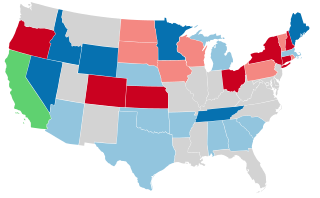
United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1914, in 31 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 3, 1914.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1912, in 33 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 5, 1912. In addition, there was a special election in Georgia on January 10, 1912.

United States gubernatorial elections were held 31 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 8, 1910.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1908, in 33 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 3, 1908.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1906, in 28 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 6, 1906.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1904, in 33 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 8, 1904.
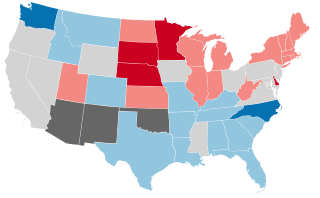
United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1900, in 34 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 6, 1900.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1898, in 28 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 8, 1898.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1896, in 32 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 3, 1896.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1894, in 28 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 6, 1894.
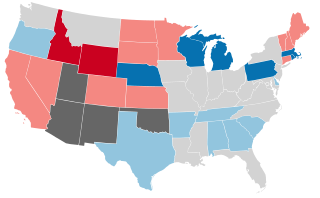
United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1890, in 27 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 4, 1890.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1888, in 26 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 6, 1888.




















