
John Hardy Isakson was an American businessman and politician who served as a United States senator from Georgia from 2005 to 2019. A member of the Republican Party, he previously served in the Georgia legislature and the United States House of Representatives.

The 1972 United States Senate elections were held on November 7, with the 33 seats of Class 2 contested in regular elections. They coincided with the landslide re-election of Republican President Richard Nixon. Despite Nixon's landslide victory, Democrats increased their majority by two seats. The Democrats picked up open seats in Kentucky and South Dakota, and defeated four incumbent senators: Gordon Allott of Colorado, J. Caleb Boggs of Delaware, Jack Miller of Iowa, and Margaret Chase Smith of Maine. The Republicans picked up open seats in New Mexico, North Carolina, and Oklahoma, and defeated one incumbent, William B. Spong Jr. of Virginia.

The 1936 United States Senate elections coincided with the reelection of President Franklin D. Roosevelt. The 32 seats of Class 2 were contested in regular elections, and special elections were held to fill vacancies. The Great Depression continued and voters backed progressive candidates favoring Roosevelt's New Deal in races across the country. The Democrats gained 5 net seats during the election, and in combination with Democratic and Farmer–Labor interim appointments and the defection of George W. Norris from the Republican Party to become independent, the Republicans were reduced to 16 seats. Democrats gained a further two seats due to mid-term vacancies. The Democrats' 77 seats and their 62-seat majority remain their largest in history.

The 1932 United States Senate elections coincided with Democrat Franklin D. Roosevelt's landslide victory over incumbent Herbert Hoover in the presidential election. The 32 seats of Class 3 were contested in regular elections, and special elections were held to fill vacancies.

The 1940 United States House of Representatives elections were elections for the United States House of Representatives to elect members to serve in the 77th United States Congress. They were held for the most part on November 5, 1940, while Maine held theirs on September 9. They coincided with President Franklin D. Roosevelt's re-election to an unprecedented third term. His Democratic Party narrowly gained seats from the opposition Republican Party, cementing their majority. However, the election gave firm control of the US House of Representatives and Senate to the New Dealers once again, as Progressives dominated the election.

The 1980 United States Senate election in Georgia was held on November 4, 1980. Incumbent Democratic U.S. Senator and former Governor of Georgia Herman Talmadge ran for reelection to a fifth term, but lost narrowly to Mack Mattingly, Chairman of the Georgia Republican Party.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1956, in 30 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and the presidential election, on November 6, 1956. The special election in Oregon was due to the death of incumbent governor Paul L. Patterson on January 31.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1952, in 30 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and the presidential election, on November 4, 1952. Elections took place on September 8 in Maine. This was the last 2-year gubernatorial election Tennessee held, as they would switch from 2-year to 4-year terms in 1954.
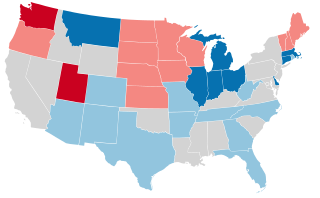
United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1948, in 33 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 2, 1948. Elections took place on September 13 in Maine.
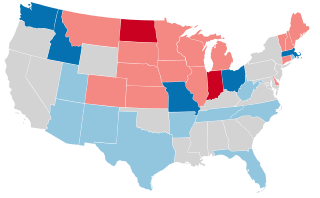
United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1944, in 32 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 7, 1944. Elections took place on September 11 in Maine.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1942, in 33 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 3, 1942. Elections took place on September 14 in Maine.
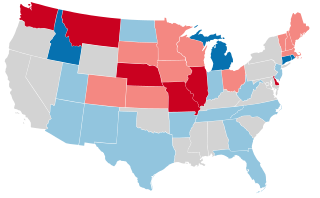
United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1940, in 34 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 5, 1940. Elections took place on September 9 in Maine.
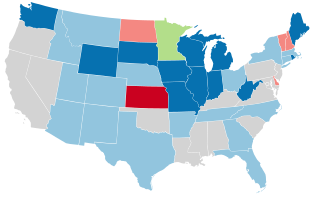
United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1932, in 35 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 8, 1932. Elections took place on September 12 in Maine.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1928, in 35 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 6, 1928. Elections took place on September 10 in Maine.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1926, in 33 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 2, 1926. Elections took place on October 5 in Arkansas, and September 13 in Maine.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1924, in 36 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 4, 1924. Elections took place on October 7, 1924 in Arkansas, and September 8, 1924 in Maine.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1920, in 35 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 2, 1920. Elections took place on September 13 in Maine.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1916, in 36 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 7, 1916. Elections took place on September 11 in Maine.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1912, in 33 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 5, 1912. In addition, there was a special election in Georgia on January 10, 1912.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1908, in 33 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 3, 1908.




















