In the United States, a governor serves as the chief executive and commander-in-chief in each of the fifty states and in the five permanently inhabited territories, functioning as head of state and head of government therein. As such, governors are responsible for implementing state laws and overseeing the operation of the state executive branch. As state leaders, governors advance and pursue new and revised policies and programs using a variety of tools, among them executive orders, executive budgets, and legislative proposals and vetoes. Governors carry out their management and leadership responsibilities and objectives with the support and assistance of department and agency heads, many of whom they are empowered to appoint. A majority of governors have the authority to appoint state court judges as well, in most cases from a list of names submitted by a nominations committee.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1958, in 34 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 4, 1958. Alaska held its first gubernatorial election on achieving statehood.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1926, in 33 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 2, 1926.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1924, in 36 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 4, 1924.
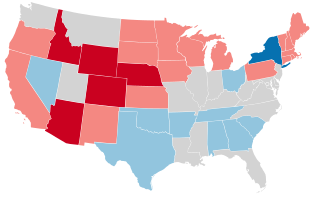
United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1918, in 32 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 5, 1918.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1916, in 36 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 7, 1916.
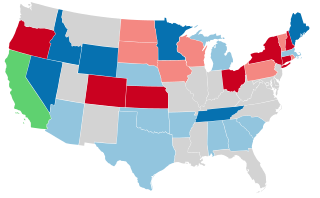
United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1914, in 31 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 3, 1914.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1912, in 33 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 5, 1912. In addition, there was a special election in Georgia on January 10, 1912.

United States gubernatorial elections were held 31 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 8, 1910.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1906, in 28 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 6, 1906.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1902, in 27 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 4, 1902.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1904, in 33 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 8, 1904.
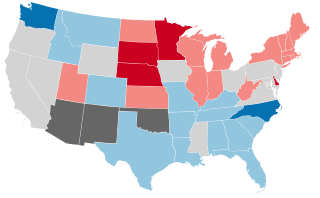
United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1900, in 34 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 6, 1900.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1898, in 28 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 8, 1898.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1896, in 32 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 3, 1896.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1894, in 28 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 6, 1894.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1892, in 32 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 8, 1892.
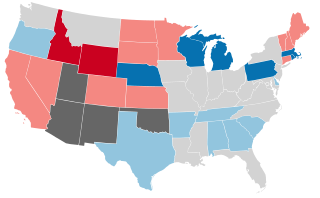
United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1890, in 27 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 4, 1890.
United States gubernatorial elections were held on Tuesday November 6, in 26 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 6, 1888.

















