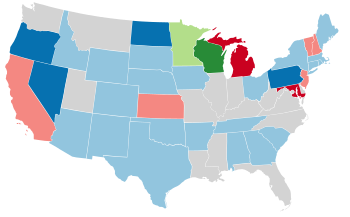
United States gubernatorial elections were held on November 2, 1954, in 34 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections. Elections also took place on September 13 in Maine. The special election in Florida was due to the death of incumbent governor Daniel T. McCarty on September 28, 1953.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1950, in 33 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 7, 1950. Elections took place on September 11 in Maine.
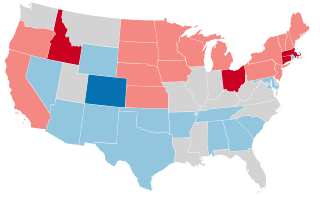
United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1946, in 34 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 5, 1946. Elections took place on September 9 in Maine.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1942, in 33 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 3, 1942. Elections took place on September 14 in Maine.
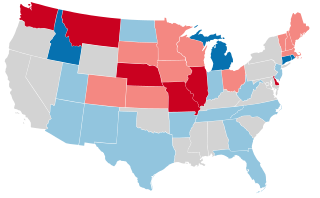
United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1940, in 34 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 5, 1940. Elections took place on September 9 in Maine.
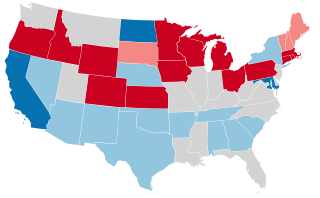
United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1938, in 33 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 8, 1938. Elections took place on September 12 in Maine.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1930, in 33 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 4, 1930. Elections took place on September 8 in Maine.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1928, in 35 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 6, 1928. Elections took place on September 10 in Maine.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1926, in 33 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 2, 1926. Elections took place on October 5 in Arkansas, and September 13 in Maine.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1924, in 36 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 4, 1924. Elections took place on October 7, 1924 in Arkansas, and September 8, 1924 in Maine.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1922, in 33 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 7, 1922. Elections took place on October 3 in Arkansas, and September 11 in Maine.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1920, in 35 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 2, 1920. Elections took place on September 13 in Maine.
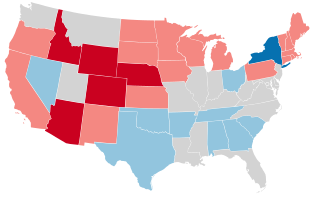
United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1918, in 32 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 5, 1918. Elections took place on September 9 in Maine.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1916, in 36 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 7, 1916. Elections took place on September 11 in Maine.
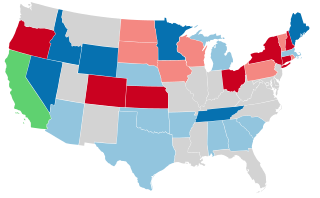
United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1914, in 31 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 3, 1914.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1912, in 33 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 5, 1912. In addition, there was a special election in Georgia on January 10, 1912.

United States gubernatorial elections were held 31 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 8, 1910.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1908, in 33 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 3, 1908.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1906, in 28 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 6, 1906.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1902, in 27 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 4, 1902.