The 1801 Rhode Island gubernatorial election was an uncontested election held on April 1, 1801 to elect the Governor of Rhode Island. Arthur Fenner, the incumbent Governor, was the sole candidate and so won with 100% of the vote.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1801, in 13 states.
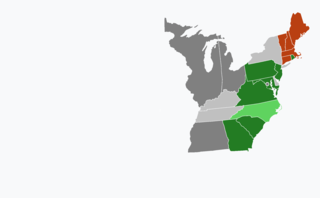
United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1802, in 12 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1803, in 12 states.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1804, in 13 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1810, in 13 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1806, in 10 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections.
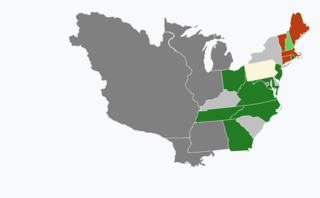
United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1805, in 13 states.

The 1800 New Hampshire gubernatorial election took place on March 11, 1800. Incumbent Federalist Governor John Taylor Gilman won re-election to a seventh term, defeating Democratic-Republican candidate Timothy Walker.

The 1799 New Hampshire gubernatorial election took place on March 12, 1799. Incumbent Federalist Governor John Taylor Gilman won re-election to a sixth term.

The 1797 New Hampshire gubernatorial election took place on March 14, 1797. Incumbent Federalist Governor John Taylor Gilman won re-election to a fourth term.

The 1798 New Hampshire gubernatorial election took place on March 13, 1798. Incumbent Federalist Governor John Taylor Gilman won re-election to a fifth term, easily defeating various minor candidates.

The 1800 Connecticut gubernatorial election took place on April 10, 1800. Incumbent Federalist Governor Jonathan Trumbull Jr. won re-election to a third full term, effectively unopposed.

The 1802 Connecticut gubernatorial election took place on April 8, 1802. Incumbent Federalist Governor Jonathan Trumbull Jr. won re-election to a fifth full term, defeating Democratic-Republican candidate Ephraim Kirby.

The 1804 Connecticut gubernatorial election took place on April 12, 1804. Incumbent Federalist Governor Jonathan Trumbull Jr. won re-election to a seventh full term, defeating Democratic-Republican candidate William Hart.

The 1807 Connecticut gubernatorial election took place on April 9, 1807. Incumbent Federalist Governor Jonathan Trumbull Jr. won re-election to a tenth full term, defeating Democratic-Republican candidate William Hart in a re-match of the previous year's election.

The 1820 Massachusetts gubernatorial election was held on April 3, 1820.
The 1807 Massachusetts gubernatorial election was held on April 6, 1807.

The 1810 Connecticut gubernatorial election took place on April 9, 1810.
The 1814 Connecticut gubernatorial election took place on April 11, 1814.