
John Hardy Isakson was an American businessman and politician who served as a United States senator from Georgia from 2005 to 2019. A member of the Republican Party, he previously served in the Georgia legislature and the United States House of Representatives.

The 1932 United States Senate elections coincided with Democrat Franklin D. Roosevelt's landslide victory over incumbent Herbert Hoover in the presidential election. The 32 seats of Class 3 were contested in regular elections, and special elections were held to fill vacancies.
The 1836–37 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 4, 1836, and November 7, 1837. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives, either before or after the first session of the 25th United States Congress convened on September 4, 1837. With Arkansas and Michigan officially achieving statehood in 1836 and 1837, respectively, the size of the House was set at 242 seats.
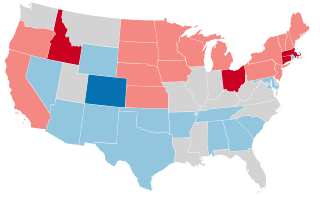
United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1946, in 34 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 5, 1946. Elections took place on September 9 in Maine.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1942, in 33 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 3, 1942. Elections took place on September 14 in Maine.
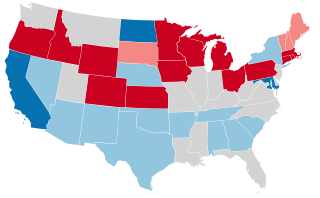
United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1938, in 33 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 8, 1938. Elections took place on September 12 in Maine.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1930, in 33 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 4, 1930. Elections took place on September 8 in Maine.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1924, in 36 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 4, 1924. Elections took place on October 7, 1924 in Arkansas, and September 8, 1924 in Maine.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1922, in 33 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 7, 1922. Elections took place on October 3 in Arkansas, and September 11 in Maine.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1920, in 35 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 2, 1920. Elections took place on September 13 in Maine.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1916, in 36 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 7, 1916. Elections took place on September 11 in Maine.
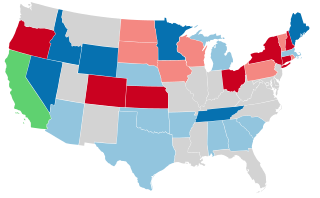
United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1914, in 31 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 3, 1914.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1912, in 33 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 5, 1912. In addition, there was a special election in Georgia on January 10, 1912.

United States gubernatorial elections were held 31 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 8, 1910.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1906, in 28 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 6, 1906.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1902, in 27 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 4, 1902.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1896, in 32 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 3, 1896.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1894, in 28 states, concurrent with the House and Senate elections, on November 6, 1894.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1888, in 26 states, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election, on November 6, 1888.

The 1926 Arkansas gubernatorial election was held on October 5, 1926.



















