
The Twelfth Amendment to the United States Constitution provides the procedure for electing the president and vice president. It replaced the procedure in Article II, Section 1, Clause 3, under which the Electoral College originally functioned. The amendment was proposed by Congress on December 9, 1803, and was ratified by the requisite three-fourths of state legislatures on June 15, 1804. The new rules took effect for the 1804 presidential election and have governed all subsequent presidential elections.

Voting is a method by which a group, such as a meeting or an electorate, convenes together for the purpose of making a collective decision or expressing an opinion usually following discussions, debates or election campaigns. Democracies elect holders of high office by voting. Residents of a jurisdiction represented by an elected official are called "constituents", and the constituents who choose to cast a ballot for their chosen candidate are called "voters." There are different systems for collecting votes, but while many of the systems used in decision-making can also be used as electoral systems, any which cater to proportional representation can only be used in elections.

Eugene Talmadge was an attorney and American politician who served three terms as the 67th governor of Georgia, from 1933 to 1937, and then again from 1941 to 1943. Elected to a fourth term in November 1946, he died before his inauguration, scheduled for January 1947. Only Talmadge and Joe Brown, in the mid-19th century, have been elected four times as governor of Georgia.

In electoral systems which use ranked voting, a donkey vote is a cast ballot where the voter ranks the candidates based on the order they appear on the ballot itself. The voter that votes in this manner is referred to as a donkey voter.
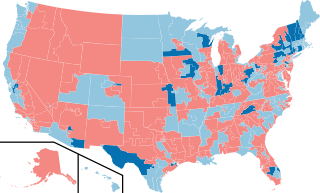
The 2006 United States House of Representatives elections were held on November 7, 2006, to elect members to the United States House of Representatives. It took place in the middle of President George W. Bush's second term in office. All 435 seats of the House were up for election. Those elected served in the 110th United States Congress from January 3, 2007, until January 3, 2009. The incumbent majority party, the Republicans, had won majorities in the House consecutively since 1994, and were defeated by the Democrats who won a majority in the chamber, ending 12 years of Republican control in the House.

The 1822–23 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 1, 1822, and August 14, 1823. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 18th United States Congress convened on December 1, 1823. They occurred during President James Monroe's second term.

The 1806–07 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 29, 1806 and August 4, 1807. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 10th United States Congress convened on October 26, 1807. They occurred during Thomas Jefferson's second term. Elections were held for all 142 seats, representing 17 states.
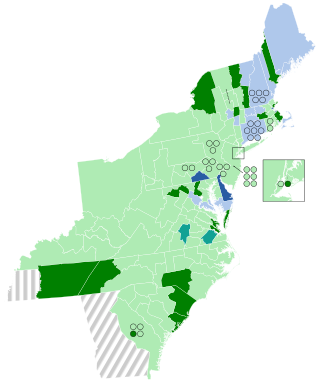
The 1804–05 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 24, 1804 and August 5, 1805. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 9th United States Congress convened on December 2, 1805. The elections occurred at the same time as President Thomas Jefferson's re-election. Elections were held for all 142 seats, representing 17 states.

The 1800–01 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 29, 1800, and August 1, 1801. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 7th United States Congress convened on December 7, 1801. They were held at the same time as the 1800 presidential election, in which Vice President Thomas Jefferson, a Democratic Republican, defeated incumbent President John Adams, a Federalist. Elections were held for all 105 seats, representing 15 states.

The 1792–93 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between August 27, 1792, and September 6, 1793. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 3rd United States Congress convened on December 2, 1793. With the addition of the new state of Kentucky's representatives, and the congressional reapportionment based on the 1790 United States census, the size of the House increased to 105 seats.
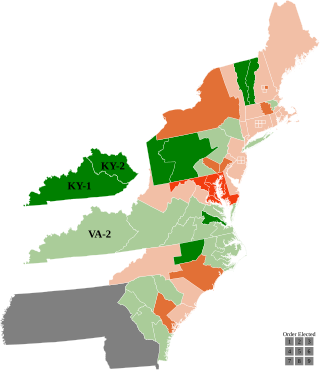
The 1790–91 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 27, 1790, and October 11, 1791. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before or after the first session of the 2nd United States Congress convened on October 24, 1791. This was the first midterm election cycle, which took place in the middle of President George Washington's first term. The size of the House increased to 67 seats after the new state of Vermont elected its first representatives.

The Tibetan Parliament in Exile (TPiE), officially the Parliament of the Central Tibetan Administration, is the unicameral and highest legislative organ of the Central Tibetan Administration, the government-in-exile of the Tibet Autonomous Region of China. It was established and is based in Dharamshala, India. The creation of this democratically elected body has been one of the major changes that the 14th Dalai Lama brought about in his efforts to introduce a democratic system of administration.

The 2008 United States presidential election in Connecticut took place on November 4, 2008, and was part of the 2008 United States presidential election. Voters chose seven representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 2000 United States presidential election in Connecticut took place on November 7, 2000, and was part of the 2000 United States presidential election. Voters chose eight representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 1802 United States House of Representatives elections in New York were held from April 27 to 29, 1802, to elect 17 U.S. Representatives to represent the State of New York in the United States House of Representatives of the 8th United States Congress.

The 83rd New York State Legislature, consisting of the New York State Senate and the New York State Assembly, met from January 3 to April 17, 1860, during the second year of Edwin D. Morgan's governorship, in Albany.

The three governors controversy was a political crisis in the U.S. state of Georgia from 1946 to 1947. On December 21, 1946, Eugene Talmadge, the governor-elect of Georgia, died before taking office. The state constitution did not specify who would assume the governorship in such a situation, so three men made claims to the governorship: Ellis Arnall, the outgoing governor; Melvin E. Thompson, the lieutenant governor-elect; and Herman Talmadge, Eugene Talmadge's son. Eventually a ruling by the Supreme Court of Georgia settled the matter in favor of Thompson. Georgia's Secretary of State Ben Fortson hid the state seal in his wheelchair so no official business could be conducted until the controversy was settled.

The 1948 Georgia gubernatorial special election took place on November 2, 1948, in order to elect the Governor of Georgia.
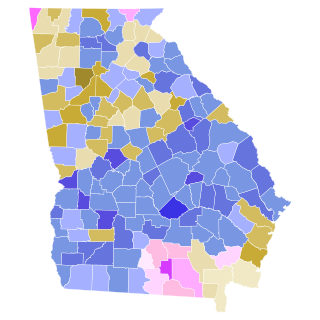
The 1946 Georgia gubernatorial election took place on November 5, 1946, in order to elect the Governor of Georgia.

The 1934 Georgia gubernatorial election took place on November 6, 1934, in order to elect the Governor of Georgia.




















