
The 82nd United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C., from January 3, 1951, to January 3, 1953, during the last two years of President Harry S. Truman's second term in office.

Brien McMahon was an American lawyer and politician who served in the United States Senate from 1945 to 1952. McMahon was a major figure in the establishment of the Atomic Energy Commission, through his authorship of the Atomic Energy Act of 1946.

The 1982 United States Senate elections were held on November 2, 1982. They were elections for the United States Senate following Republican gains in 1980. The 33 Senate seats of Class 1 were up for election in 1982. A total of four seats changed hands between parties, with Democrats winning seats in New Jersey and New Mexico, and Republicans taking seats in Nevada and the seat of the lone independent, Senator Harry Byrd Jr., in Virginia. Democrats made a net gain of one seat bringing them to 46 seats, while Republicans stayed at 54 seats for a majority. However, the Democratic gain in New Jersey replaced a Republican that had been appointed earlier in the year. Liberal Republicans senators in Connecticut, Rhode Island and Vermont held onto their seats, keeping the Senate in Republican hands.

The 1980 United States Senate elections were held on November 4, coinciding with Ronald Reagan's victory in the presidential election. The 34 Senate seats of Class 3 were contested in regular elections. Reagan's large margin of victory over incumbent Jimmy Carter gave a huge boost to Republican Senate candidates, allowing them to flip 12 Democratic seats and win control of the chamber for the first time since the end of the 83rd Congress in January 1955.
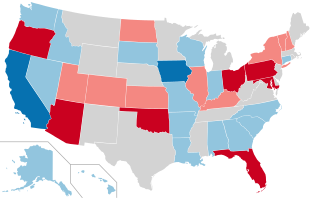
The 1968 United States Senate elections were elections for the United States Senate. Held on November 5, the 34 seats of Class 3 were contested in regular elections. They coincided with the presidential election of the same year. The Republicans picked up five net seats in the Senate. This saw Republicans win a Senate seat in Florida for the first time since Reconstruction.

The 1964 United States Senate elections were held on November 3. The 33 seats of Class 1 were contested in regular elections. Special elections were also held to fill vacancies. They coincided with the election of President Lyndon B. Johnson by an overwhelming majority, to a full term. His Democratic Party picked up a net two seats from the Republicans. As of 2023, this was the last time either party has had a two-thirds majority in the Senate, which allowed the Senate Democrats to override a veto, propose constitutional amendments, or convict and expel certain officials without any votes from Senate Republicans. However, internal divisions would have prevented the Democrats from having done so. The Senate election cycle coincided with Democratic gains in the House in the same year.

The 1952 United States Senate elections was an election for the United States Senate which coincided with the election of Dwight D. Eisenhower to the presidency by a large margin. The 32 Senate seats of Class 1 were contested in regular elections, and three special elections were held to fill vacancies. The Republicans took control of the Senate by managing to make a net gain of two seats. However, Wayne Morse (R-OR) became an independent forcing Republicans to rely on Vice President Richard Nixon's tie-breaking vote, although Republicans maintained a 48–47–1 plurality. Throughout the next Congress, Republicans were able to restore their 49–46–1 majority. This was the third time, as well as second consecutive, in which a sitting Senate leader lost his seat.

William Arthur Purtell was an American businessman and politician. A member of the Republican Party, he represented Connecticut in the United States Senate in 1952 and from 1953 to 1959.

The 81st United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C. from January 3, 1949, to January 3, 1951, during the fifth and sixth years of Harry S. Truman's presidency.
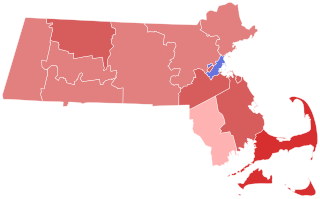
The United States Senate election of 1942 in Massachusetts was held on November 3, 1942. Republican incumbent Henry Cabot Lodge Jr. was re-elected to a second term in office over Democratic U.S. Representative Joseph E. Casey.

The 1980 United States Senate election in Pennsylvania was held on November 4, 1980. Incumbent Republican U.S. Senator Richard Schweiker decided to retire, instead of seeking a third term.
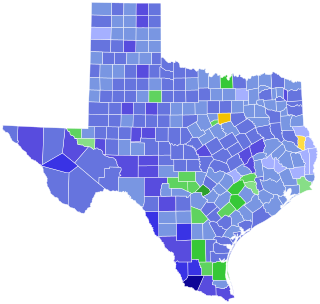
The 1934 United States Senate election in Texas was held on November 4, 1934. Incumbent Democratic U.S. Senator Tom Connally was re-elected to a second term. Connally fended off a competitive primary challenge from U.S. Representative Joseph Weldon Bailey Jr. on July 28 before facing only nominal opposition in the general election.

The 1822–23 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1822 and 1823, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 2.

The 1952 United States Senate election in Connecticut was held on November 4, 1952. Incumbent Democratic Senator William Benton, who won a special election to complete the term of retiring Senator Raymond Baldwin, was defeated by Republican William A. Purtell after serving only 2 years.

The 1982 Senate election in Maryland took place on November 2, 1982, simultaneously with other elections for seats in the U.S. Senate and House of Representatives in addition to gubernatorial openings. Incumbent Democratic Senator Paul Sarbanes won reelection to a second term in office. He defeated the Republican nominee, former Representative from Maryland's 5th district and Prince George's County Executive Lawrence Hogan.

The 1952 United States Senate election in Wisconsin was held on November 4, 1952.

The 1950 United States Senate election in Iowa took place on November 7, 1950. Incumbent Republican Senator Bourke B. Hickenlooper was re-elected to a second term in office over Democratic U.S. Undersecretary of Agriculture Albert J. Loveland.

The 1952 United States Senate special election in Connecticut was held on November 4, 1952, to fill the vacancy left by the death of Brien McMahon.

The 1922 United States Senate election in Tennessee was held on November 7, 1922. Incumbent Democratic Senator Kenneth D. McKellar was re-elected to a second term in office, defeating Republican former interim Senator Newell Sanders.

The 1944 United States Senate election in Connecticut was held on November 7, 1944.






















