
The 2nd United States Congress, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives, met at Congress Hall in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, from March 4, 1791, to March 4, 1793, during the third and fourth years of George Washington's presidency. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the provisions of Article I, Section 2, Clause 3 of the United States Constitution. Additional House seats were assigned to the two new states of Vermont and Kentucky. Both chambers had a Pro-Administration majority.

Isaac Toucey was an American politician who served as a U.S. senator, U.S. Secretary of the Navy, U.S. Attorney General and the 33rd Governor of Connecticut.

Francis Granger was an American politician who represented Ontario County, New York, in the United States House of Representatives for three non-consecutive terms. He was a leading figure in the state and national Whig Party, particularly in its moderate-conservative faction. He served as a Whig vice presidential nominee on the party's multi-candidate 1836 ticket and, in that role, became the only person to ever lose a contingent election for the vice presidency in the U.S. Senate. He also served briefly in 1841 as United States Postmaster General in the cabinet of William Henry Harrison. In 1856, he became the final Whig Party chairman before the party's collapse, after which he joined the Constitutional Union Party.

The Connecticut State House of Representatives is the lower house in the Connecticut General Assembly, the state legislature of the U.S. state of Connecticut. The house is composed of 151 members representing an equal number of districts, with each constituency containing nearly 22,600 residents. Representatives are elected to two-year terms with no term limits. The House convenes within the Connecticut State Capitol in Hartford.

The 1826–27 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 3, 1826, and August 30, 1827. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 20th United States Congress convened on December 3, 1827. They occurred during John Quincy Adams's presidency. Elections were held for all 213 seats, representing 24 states.

The 1792–93 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between August 27, 1792, and September 6, 1793. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 3rd United States Congress convened on December 2, 1793. With the addition of the new state of Kentucky's representatives, and the congressional reapportionment based on the 1790 United States census, the size of the House increased to 105 seats.
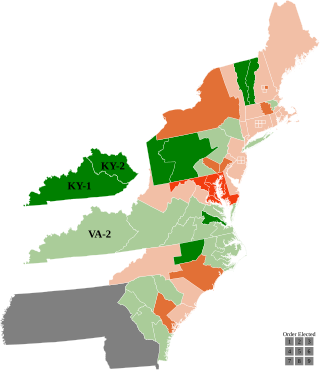
The 1790–91 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 27, 1790, and October 11, 1791. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before or after the first session of the 2nd United States Congress convened on October 24, 1791. This was the first midterm election cycle, which took place in the middle of President George Washington's first term. The size of the House increased to 67 seats after the new state of Vermont elected its first representatives.
Joshua Coit was an eighteenth-century American lawyer and politician. He served as a United States Representative from Connecticut.
Amasa Learned was an American preacher, lawyer, and politician from New London, Connecticut. He served in the state's House of Representatives and represented Connecticut in the U.S. House from 1791 until 1795.
James Davenport was an eighteenth-century American lawyer, politician and judge. He served as a U.S. Representative from Connecticut.

Thomson Joseph Skinner was an American politician from Williamstown, Massachusetts. In addition to service as a militia officer during the American Revolution, he served as a county judge and sheriff, member of both houses of the Massachusetts legislature, U.S. Marshal, and member of the United States House of Representatives. He served for two years as Treasurer and Receiver-General of Massachusetts, and after his death an audit showed his accounts to be deficient for more than the value of his estate, which led to those who had posted bonds on his behalf having to pay the debt.
Samuel Lyman was a United States representative from Massachusetts.

Thomas Ruggles Gold was a United States representative from New York.
Massachusetts's at-large congressional seat is an obsolete construct only used during the 1792–1793 United States House of Representatives elections in Massachusetts. In that election, one of the state's then-14 representatives to the U.S. House was elected statewide at-large. At that time, the U.S. state of Massachusetts included the District of Maine.

Various kinds of elections in Connecticut occurs annually in each of the state's cities and towns, the exact type of which is dependent on the year. Elections for federal and statewide offices occur in even-numbered years, while municipal elections occur in odd-numbered ones. The office of the Connecticut Secretary of State oversees the election process, including voting and vote counting. In a 2020 study, Connecticut was ranked as the 20th easiest state for citizens to vote in.

The 1792–93 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states, coinciding with President George Washington's unanimous re-election. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1792 and 1793, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the ten senators in Class 2.
Three special elections were held in Connecticut's at-large congressional district in 1793 to fill vacancies caused by the resignation, prior to the start of the 3rd Congress, of three representatives-elect.

The 1792 United States elections elected the members of the 3rd United States Congress. Congress was broadly divided between a Pro-Administration faction supporting the policies of George Washington's administration and an Anti-Administration faction opposed to those policies. Due to this, the Federalist Party and the Democratic-Republican Party were starting to emerge as the distinct political parties of the First Party System. In this election, the Pro-Administration faction maintained control of the Senate, but lost its majority in the House.

The 2016 United States House of Representatives elections in Connecticut were held on Tuesday, November 8, 2016 to elect the five U.S. representatives from the state of Connecticut, one from each of the state's five congressional districts. The elections coincided with the 2016 U.S. presidential election, as well as other elections to the House of Representatives, elections to the United States Senate and various state and local elections. The primaries were held on August 9.













