
An earthquake – also called a quake, tremor, or temblor – is the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they cannot be felt, to those violent enough to propel objects and people into the air, damage critical infrastructure, and wreak destruction across entire cities. The seismic activity of an area is the frequency, type, and size of earthquakes experienced over a particular time. The seismicity at a particular location in the Earth is the average rate of seismic energy release per unit volume.
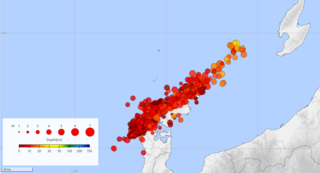
In seismology, an earthquake swarm is a sequence of seismic events occurring in a local area within a relatively short period. The time span used to define a swarm varies, but may be days, months, or years. Such an energy release is different from the situation when a major earthquake is followed by a series of aftershocks: in earthquake swarms, no single earthquake in the sequence is obviously the main shock. In particular, a cluster of aftershocks occurring after a mainshock is not a swarm.

The Aleutian Trench is an oceanic trench along a convergent plate boundary which runs along the southern coastline of Alaska and the Aleutian islands. The trench extends for 3,400 kilometres (2,100 mi) from a triple junction in the west with the Ulakhan Fault and the northern end of the Kuril–Kamchatka Trench, to a junction with the northern end of the Queen Charlotte Fault system in the east. It is classified as a "marginal trench" in the east as it runs along the margin of the continent. The subduction along the trench gives rise to the Aleutian Arc, a volcanic island arc, where it runs through the open sea west of the Alaska Peninsula. As a convergent plate boundary, the trench forms part of the boundary between two tectonic plates. Here, the Pacific plate is being subducted under the North American plate at a dip angle of nearly 45°. The rate of closure is 7.5 centimetres (3 in) per year.

An earthquake occurred on November 27, 2005, at 13:52 IRST on the sparsely populated Qeshm Island off Southern Iran, killing 13 people and devastating 13 villages. It was Iran's second major earthquake of 2005, following the one at Zarand in February. The epicenter was about 1,500 kilometers (930 mi) south of Tehran, close to Iran's southern borders. Initial measurements showed that the earthquake registered about 6.0 on the moment magnitude scale, although that was reduced to 5.8 after further analysis. More than 400 minor aftershocks followed the main quake, 36 of which were greater than magnitude 2.5. The earthquake occurred in a remote area during the middle of the day, limiting the number of fatalities. Iranian relief efforts were effective and largely adequate, leading the country to decline offers of support from other nations and UNICEF.

The 1999 İzmit earthquake had a moment magnitude of 7.6 and struck Kocaeli Province, Turkey on 17 August. Between 17,127 and 18,373 people died as a result, and the damage was estimated at US$6.5 billion. It was named for the epicenter's proximity to the northwestern city of İzmit. The earthquake occurred at 03:01 local time at a shallow depth of 15 km (9.3 mi). A maximum Mercalli intensity of X (Extreme) was observed. The earthquake lasted for 37 seconds, causing seismic damage, and is widely remembered as one of the deadliest natural disasters in modern Turkish history.

The 1927 Gulang earthquake occurred at 06:32 a.m. on 23 May. This 7.6 magnitude event had an epicenter near Gulang, Gansu in the Republic of China. There were 40,912 deaths. It was felt up to 700 km (435 mi) away.
The 1762 Arakan earthquake occurred at about 17:00 local time on 2 April, with an epicentre somewhere along the coast from Chittagong to Arakan in modern Myanmar. It had an estimated moment magnitude between 8.5 and 8.8 and a maximum estimated intensity of XI (Extreme). It triggered a local tsunami in the Bay of Bengal and caused at least 200 deaths. The earthquake was associated with major areas of both uplift and subsidence. It is also associated with a change in course of the Brahmaputra River to from east of Dhaka to 150 kilometres (93 mi) to the west via the Jamuna River.

The 1819 Rann of Kutch earthquake occurred at about 18:45 to 18:50 local time on 16 June 1819. It had an estimated magnitude ranging from 7.7 to 8.2 on the moment magnitude scale and a maximum perceived intensity of XI (Extreme) on the Mercalli intensity scale. It triggered a tsunami and caused at least 1,543 deaths. The earthquake caused an area of subsidence that formed the Sindri Lake and a local zone of uplift to the north about 80 km (50 mi) long, 6 km (3.7 mi) wide and 6 m (20 ft) high that dammed the Koree / Kori / Puran / Nara river. This natural dam was known as the Allah Bund.

On 21 July 2017, a large earthquake measuring 6.6 on the moment magnitude scale struck right near Bodrum, a popular town of tourism in Turkey, killing 2 and injuring hundreds. Mostly referenced as the 2017 Bodrum–Kos earthquake, this earthquake generated a tsunami which was one of the largest tsunamis in the Mediterranean Sea region.
Northern Anatolia was struck by a large earthquake on 17 August 1668 in the late morning. It had an estimated magnitude in the range 7.8–8.0 and the maximum felt intensity was IX on the Modified Mercalli intensity scale. The epicenter of the earthquake was on the southern shore of Ladik Lake. It caused widespread damage from as far west as Bolu and as far east as Erzincan, resulting in about 8,000 deaths. It is thought to be the most powerful earthquake in Turkey.
An earthquake affected Myanmar on 5 May 1930 with a moment magnitude (Mw ) 7.4. The shock occurred 35 km (22 mi) beneath the surface with a maximum Rossi–Forel intensity of IX. The earthquake was the result of rupture along a 131 km (81 mi) segment of the Sagaing Fault—a major strike-slip fault that runs through the country. Extensive damage was reported in the southern part of the country, particularly in Bago and Yangon, where buildings collapsed and fires erupted. At least 550, and possibly up to 7,000 people were killed. A moderate tsunami struck the Burmese coast which caused minor damage to ships and a port. It was felt for over 570,000 km2 (220,000 sq mi) and as far as Shan State and Thailand. The mainshock was followed by many aftershocks; several were damaging. The December earthquake was similarly sized which also occurred along the Sagaing Fault.

An earthquake with a moment magnitude of 7.0 occurred on 30 October 2020 about 14 km (8.7 mi) northeast of the Greek island of Samos. Although Samos was closest to the epicentre, it was the large Turkish city İzmir, 70 km (43 mi) northeast that was heavily affected—more than 700 residential and commercial structures were seriously damaged or destroyed. One hundred and seventeen people died in İzmir Province while an additional 1,034 were injured. In Greece, there were two fatalities and 19 injured. The earthquake is the deadliest in the year 2020, and the third major earthquake to strike Turkey that year. It generated an unusually large tsunami. The event is called the Samos earthquake by the International Seismological Centre.
In 1914, two earthquakes shook the upper North Island of New Zealand, on Wednesday 7 October and Wednesday 28 October. They were large and shallow, with their epicentres close together northwest of Ruatoria in the Gisborne District. The earthquakes were felt strongly throughout the East Cape area, most noticeably in areas east of the epicentre such as Waipiro Bay, with a large amount of damage occurring in Tokomaru Bay in particular. One person was killed by a landslide near Cape Runaway.
The 1843 Nias earthquake off the northern coast of Sumatra, Indonesia caused severe damage when it triggered a tsunami along the coastline. The earthquake with a moment magnitude (Mw ) of 7.8 lasted nine minutes, collapsing many homes in Sumatra and Nias. It was assigned a maximum modified Mercalli intensity of XI (Extreme).
The 1983 Heze earthquake occurred near the administrative borders between the provinces of Shandong and Henan in the People's Republic of China on November 7, 1983, at 05:09 local time and date. The earthquake had a body-wave magnitude of 5.7 and a maximum intensity of VII on the Modified Mercalli intensity scale. The event caused 34 deaths and injured 2,200 people. More than 3,300 houses were destroyed.
The 1858 Prome earthquake occurred on August 24 at 15:38 local time in British Burma. The earthquake occurred with a magnitude of 7.6–8.3 on the moment magnitude scale. It had an epicenter in near the city of Pyay (Prome), Bago. The shock was felt with a maximum Modified Mercalli intensity of XI (Extreme) for about one minute. Severe damage was reported in Bago, and off the coast of Rakhine, an island sunk.
The 1979 Yapen earthquake occurred on September 12 at 05:17:51 UTC. It had an epicenter near the coast of Yapen Island in Irian Jaya, Indonesia. Measuring 7.5 on the moment magnitude scale and having a depth of 20 km (12 mi), it caused severe damage on the island. At least 115 were killed due to shaking and a moderate tsunami.
The 1968 Aegean Sea earthquake was a 7.0 earthquake that occurred in the early morning hours of February 20, 1968 local time about 57.1 km (35.5 mi) away from Myrina, Greece. This earthquake occurred between mainland Greece and Turkey, meaning both countries were impacted. 20 people died, and 39 people were injured to various degrees. It was the deadliest Greek earthquake since the 1956 Amorgos earthquake.
An earthquake struck west of Paphos, Cyprus on 11 January 2022, with a moment magnitude of 6.6. The earthquake was the largest tremor to occur in the Mediterranean Sea since the 2003 Boumerdès earthquake, and the largest to occur in Cyprus since 1996.

The 1940 Shakotan earthquake occurred on August 2 at 00:08:22 JST with a moment magnitude (Mw ) of 7.5 and maximum JMA seismic intensity of Shindo 4. The shock had an epicenter off the coast of Hokkaido, Japan. Damage from the shock was comparatively light, but the accomanying tsunami was destructive. The tsunami caused 10 deaths and 24 injuries on Hokkaido, and destroyed homes and boats across the Sea of Japan. The highest tsunami waves were recorded at the coast of Russia while along the coast of Hokkaido, waves were about 2 m.










