In seismology, an aftershock is a smaller earthquake that follows a larger earthquake, in the same area of the main shock, caused as the displaced crust adjusts to the effects of the main shock. Large earthquakes can have hundreds to thousands of instrumentally detectable aftershocks, which steadily decrease in magnitude and frequency according to a consistent pattern. In some earthquakes the main rupture happens in two or more steps, resulting in multiple main shocks. These are known as doublet earthquakes, and in general can be distinguished from aftershocks in having similar magnitudes and nearly identical seismic waveforms.

Arkalochori is a town and a former municipality in the Heraklion regional unit, Crete, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Minoa Pediada, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 237.589 km2 (91.734 sq mi).
The 1999 Hector Mine earthquake occurred in Southern California, United States, on October 16 at 02:46:50 PDT. Its moment magnitude was 7.1 and the earthquake was preceded by 12 foreshocks, the largest of which had a magnitude of 3.8. The event is thought to have been triggered by the 1992 Landers earthquake which occurred seven years earlier. It also deformed nearby faults vertically and horizontally. The earthquake's hypocenter was at a depth of 20 kilometers and its epicenter at 34.603° N 116.265° W.
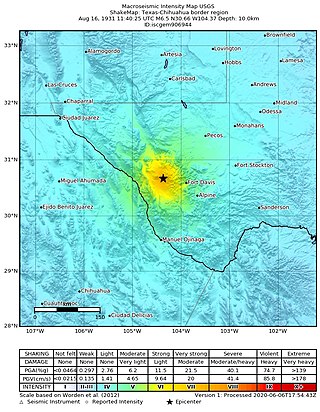
In the early morning hours of August 16, 1931, a powerful earthquake occurred in West Texas with a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe). Estimates of its magnitude range between 5.8 and 6.4 mb, making it the most powerful earthquake ever recorded in Texas history. Its epicenter was near the town of Valentine, Texas; there, the earthquake caused damage to many homes and buildings. The earthquake may have been caused by movement along oblique-slip faulting in West Texas, the most seismically active region in the state. Shaking from the earthquake was perceptible within a 400 mi (640 km) radius of the epicenter, affecting four U.S. states and northern Mexico. Several foreshocks and aftershocks accompanied the primary temblor, with the aftershocks continuing until at least November 3, 1931. The main earthquake caused no fatalities, though several people sustained minor injuries; the damage in Valentine amounted to $50,000–$75,000.
The 1303 Crete earthquake occurred at about dawn on 8 August. It had an estimated magnitude of about 8, a maximum intensity of IX (Violent) on the Mercalli intensity scale, and triggered a major tsunami that caused severe damage and loss of life on Crete and at Alexandria. It badly damaged the Lighthouse of Alexandria.

The 2016 Kumamoto earthquakes were a series of earthquakes, including a magnitude 7.0 mainshock which struck at 01:25 JST on April 16, 2016 beneath Kumamoto City of Kumamoto Prefecture in Kyushu Region, Japan, at a depth of about 10 kilometres, and a foreshock earthquake with a magnitude 6.2 at 21:26 JST (12:26 UTC) on April 14, 2016, at a depth of about 11 kilometres.

On May 4, 2018, an earthquake with a magnitude of 6.9 struck Hawaii island in the Hawaii archipelago at around 12:33 p.m. local time. The earthquake's epicenter was near the south flank of Kīlauea, which has been the site of seismic and volcanic activity since late April of that year. According to the United States Geological Survey the quake was related to the new lava outbreaks at the volcano, and it resulted in the Hilina Slump moving about two feet. It was the largest earthquake to affect Hawaii since the 1975 earthquake, which affected the same region, killing two people and injuring another 28.

On 18 August 2020, at 8:03 PST, a 6.6 magnitude earthquake struck the island province of Masbate in the Philippines, leaving at least 2 dead and 170 injured.
The 1968 Borrego Mountain earthquake occurred on April 8, at 18:28 PST in the geologically active Salton Trough of Southern California. The Salton Trough represents a pull-apart basin formed by movements along major faults. This region is dominated by major strike-slip faults one of them being the San Jacinto Fault which produced the 1968 earthquake. The mainshock's epicenter was near the unincorporated community of Ocotillo Wells in San Diego County. The moment magnitude (Mw ) 6.6 strike-slip earthquake struck with a focal depth of 11.1 km (6.9 mi). The zone of surface rupture was assigned a maximum Modified Mercalli intensity (MMI) of VII.
The 1856 Heraklion earthquake, also known as the Crete earthquake or Rhodes earthquake, occurred on the morning of October 12 at 02:45 am local time. This extremely catastrophic earthquake had an estimated magnitude of 7.7 to 8.3 at a depth of approximately 61 to 100 km. The earthquake was felt over a very wide area extending from Sicily, Italy to the Levant and North Africa. On the Greek island of Crete, the effects of the earthquake were cataclysmic, over 500 bodies were recovered in the city of Heraklion. Shockwaves from the earthquake were felt intensely, covering all of the Ottoman Empire; present-day Turkey, Cyprus and the Middle East where damage and human losses were reported. In Malta, the Għajn Ħadid Tower—a coastal watchtower built around the year 1638—was severely damaged in the earthquake, when its upper floor collapsed. In Cairo, Egypt, the earthquake destroyed buildings, created seiches in canals, and killed several people. Off the Egyptian and Italian coasts, sailors reported feeling a seaquake.
The 1986 Kalamata earthquake struck the southern Peloponnese Region of Greece on September 13 at 20:24 local time. The 12.5 km (7.8 mi) deep moment magnitude (Mw ) 5.9 earthquake had an epicenter near the coastal city of Kalamata and was assigned X (Extreme) on the Mercalli intensity scale. The earthquake was the result of normal faulting along a northwest-dipping fault and produced surface ruptures. Extensive damage was reported in Kalamata and Elaiochori. At least 20 people died and 330 were injured. Survivors sought refuge at campsites and reconstruction work lasted five years.
The 1995 Menglian earthquake or 1995 Myanmar–China earthquake occurred on 12 July at 05:46:43 local time in the Myanmar–China border region. The earthquake had an epicenter on the Myanmar side of the border, located in the mountainous region of Shan State. It registered 7.3 on the Chinese surface-wave magnitude scale (Ms ) and 6.8 on the moment magnitude scale (Mw ). With a maximum Mercalli intensity assigned at VIII, it killed 11 people and left another 136 injured. Over 100,000 homes in both countries were destroyed and 42,000 seriously damaged. Some damage to structures were also reported in Chiang Mai and Chiang Rai, Thailand. The low death toll from this earthquake was attributed to an early warning issued prior to it happening. Precursor events including foreshocks and some seismic anomalies led to an evacuation of the area before the mainshock struck. It is thought to be one of the few successfully predicted earthquakes in history.
The 1941 Sa'dah earthquake or the Jabal Razih earthquake occurred on January 11 in Razih District of the Mutawakkilite Kingdom of Yemen. The earthquake had a surface-wave magnitude of 5.8–6.5 and a shallow focal depth. Despite the moderate size of this earthquake, an estimated 1,200 people perished and at least 200 injured. With a maximum MSK-64 intensity assigned at VIII, it destroyed many villages and collapsed homes in the region of North Yemen.
The 2021 South Sandwich Islands earthquakes were a pair of powerful earthquakes, followed by many strong aftershocks which struck along the South Sandwich Trench in August 2021. The quakes measured 7.5 and 8.1 on the moment magnitude scale, according to the United States Geological Survey. The mainshock is tied with another event in 1929 as the largest earthquake ever recorded in the South Atlantic region, and is tied with the 2021 Kermadec Islands earthquake as the second largest earthquake of 2021.
On February 7, 2021, at 12:22 PM PST, an earthquake measuring Mww 6.0 struck Davao del Sur and Cotabato. The event registered a Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale (MMI) of VIII (Severe) with VII on the PHIVOLCS Earthquake Intensity Scale (PEIS).

On March 3, 2021, 12:16:09 the 2021 Larissa earthquake had a magnitude of 6.3 with an intensity of VIII (Severe) on the Mercalli Scale 9 kilometers west of Týrnavos, Greece. One person was confirmed dead with eleven other people injured. Light shaking was also felt as far as Albania, North Macedonia, Kosovo and Montenegro.
The 2021 Lasithi earthquake was a magnitude 6.4 earthquake with a maximum intensity of VIII (Severe) on the Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale which occurred on 12 October 2021, 12:24 (UTC+3:30) off the island of Crete. The quake was also felt at low intensity as far as Cairo and Istanbul.
The 1954 Sofades earthquake struck central Greece on 30 April 1954, at 16:02 (UTC+3). It was estimated to be 6.7–7.0 Mw and had a maximum Modified Mercalli intensity of X (Extreme). More than 25 people died, 717 were injured and about 28,000 structures were damaged or destroyed.
An earthquake struck Western Greece near the coastal city of Aigio at on 15 June 1995. The second destructive earthquake to strike Greece in a month, it measured 6.4–6.5 on the moment magnitude scale (Mw ). It was assigned a maximum Modified Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe) and EMS-98 intensity of IX (Destructive). The horizontal peak ground acceleration reached 0.54 g and ground velocity peaked at 52 cm/s (20 in/s)—the strongest ground motion ever recorded in Greece. Fifteen minutes after the mainshock, a large aftershock struck, causing further damage to Aigio. Faulting occurred on either the Aigion fault or an unnamed offshore fault. Other faults in the region have the potential to produce earthquakes up to Mw 6.9, which poses a risk to Aigio and the surrounding Gulf of Corinth.