| UTC time | 1918-08-15 12:18:21 |
|---|---|
| ISC event | 913230 |
| USGS-ANSS | ComCat |
| Local date | August 15, 1918 |
| Local time | 20:18 |
| Duration | >3 minutes [1] |
| Magnitude | 8.3 Mw [2] |
| Depth | 20 km (12 mi) [2] |
| Epicenter | 5°32′17″N123°59′38″E / 5.538°N 123.994°E [2] |
| Max. intensity | MMI X (Extreme) |
| Tsunami | Yes |
| Landslides | Yes |
| Casualties | 52 |
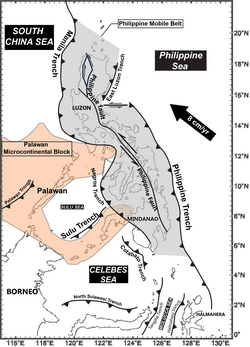
The 1918 Celebes Sea earthquake occurred on August 15 at 12:18 UTC near the Moro Gulf coast of Mindanao. [1] It had a magnitude of 8.3 on the moment magnitude scale [3] and a maximum perceived intensity of X (Extreme) on the Mercalli intensity scale, making it the strongest earthquake in history to hit the Philippines. It triggered a tsunami of up to 7 m in height and the combined effects of the earthquake and tsunami led to the deaths of 52 people.


