
Earthquakes are caused by movements within the Earth's crust and uppermost mantle. They range from weak events detectable only by seismometers, to sudden and violent events lasting many minutes which have caused some of the greatest disasters in human history. Below, earthquakes are listed by period, region or country, year, magnitude, cost, fatalities, and number of scientific studies.
The 2005 Hindu Kush earthquake hit northeastern Afghanistan with a magnitude of 6.5 on December 12 at 21:47 (UTC). According to the United States Geological Survey, the maximum Mercalli intensity was V (Moderate) at Chitral. Five people were killed in the Hindu Kush region and landslides blocked several roads near Bagh, Kashmir. The earthquake occurred some 65 miles away from Faizabad, a city in the Hindu Kush mountains, but it could be felt in many neighboring areas. It could even be felt about 200 miles away in Islamabad, Pakistan. The quake was strong enough to trigger panic among survivors of October's devastating earthquake, who came out from their makeshift shelters in freezing temperatures. Although magnitude–6 earthquakes typically cause severe damage, this quake caused relatively little due to the fact that it occurred deep underground.
The 1976 Songpan–Pingwu earthquake that struck Songpan and Pingwu counties in Sichuan, China consisted of three mainshocks on the 16th, 21st, and 23rd (UTC) of August. A 1984 report gave the magnitudes as 7.2, 6.7, and 7.2, respectively. The magnitudes were subsequently recalculated as 6.7, 6.3, and 6.4 on the scale, and 7.0, 6.6, and 6.7 on the scale. These were preceded by an earthquake swarm lasting three years. During the period from August 16 to August 31 there were over 400 aftershocks of magnitude 3.0 or greater.
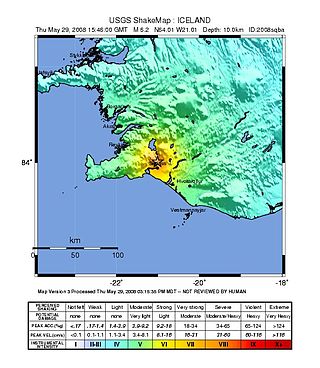
The 2008 Iceland earthquake was a doublet earthquake that struck on 29 May at 15:46 UTC in southwestern Iceland. The recorded magnitudes of the two main quakes were 5.9 and 5.8 Mw , respectively, giving a composite magnitude of 6.1 Mw . There were no human fatalities, but injuries were reported and a number of sheep were killed. The epicenter of the earthquake was between the towns of Hveragerði and Selfoss, about 45 kilometers (28 mi) east-southeast of the capital, Reykjavík. It was the strongest earthquake to hit Iceland since the summer of 2000.

The 1976 Moro Gulf earthquake and tsunami occurred on near the islands of Mindanao and Sulu, in the Philippines. It measured 8.0 on the moment magnitude scale occurring at a depth of 20 km (12 mi). The earthquake was accompanied by a destructive tsunami that resulted in a majority of the estimated 5,000 to 8,000 fatalities. It was the deadliest and strongest earthquake in the Philippines in 58 years since the 1918 Celebes Sea earthquake.

The 2009 West Papua earthquakes occurred on January 4 local time in Indonesia's Tambrauw Regency in Southwest Papua. The very large earthquake doublet comprised a 7.6 initial shock that had a maximum Mercalli intensity of VI (Strong) and a second event measuring Mw 7.4 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VII. The events took place less than three hours apart to the east-northeast of Sorong on the Bird's Head Peninsula and left at least four people dead and dozens injured.
The 1951 East Rift Valley earthquakes were a series of earthquakes which struck eastern Taiwan from 22 October 1951 to 5 December 1951, four of which registered at 7 or greater on the moment magnitude scale, the largest of those being magnitude 7.3 and 7.8 quakes on November 24. Altogether the quakes killed 85 people.

The 2002 Mindanao earthquake struck the Philippines at 05:16 Philippine Standard Time on March 6. The world's sixth most powerful earthquake of the year, it registered a magnitude of 7.5 and was a megathrust earthquake. It originated near the Cotabato Trench, a zone of deformation situated between the Philippine Sea plate and the Sunda plate, and occurred very near to the Philippines' strongest earthquake for the 20th century, the 1918 Celebes Sea earthquake.
The 2010 Oaxaca earthquake struck Oaxaca, Mexico on June 30, 2010, with an magnitude of 6.3. Many people in different cities left their beds and ran into the street, as the quake struck at 2:22 am.
The 1967 Mudurnu earthquake or more correctly, the 1967 Mudurnu Valley earthquake occurred at about 18:57 local time on 22 July near Mudurnu, Bolu Province, north-western Turkey. The magnitude 7.4 earthquake was one of a series of major and intermediate quakes that have occurred in modern times along the North Anatolian Fault since 1939.
The 1997 Harnai earthquake occurred on February 27 at 21:08 UTC near Harnai, Pakistan, and felt throughout much of central Balochistan, with a magnitude estimated at 7.0 on the scale. A 2016 study determined that this was a doublet earthquake, the Mw 6.8 shock that hit 19 seconds later being a continuation of the initial main shock. The largest aftershock was an 6.4 shock that hit 22 minutes after the main shock. The earthquake was caused by the collision between the Indian plate and the Eurasian plate.

The 1990 Vrancea earthquakes were three earthquakes on 30 and 31 May 1990 with magnitudes of 7.0 and 6.2 Mw that struck the Romanian county of Vrancea, on two consecutive days. Severe damage in the Bucharest-Brăila-Brașov area was reported and dozens of casualties in Romania and neighbouring Moldova, Ukraine and Bulgaria.

The 1918 Celebes Sea earthquake occurred on August 15 at 12:18 UTC near the Moro Gulf coast of Mindanao. It had a magnitude of 8.3 on the moment magnitude scale and a maximum perceived intensity of X (Extreme) on the Mercalli intensity scale. It triggered a tsunami of up to 7 m in height and the combined effects of the earthquake and tsunami led to the deaths of 52 people.
The 1976 Longling earthquake in Yunnan Province, People's Republic of China, was a doublet earthquake, with two main shocks striking just east of Longling at 12:23:20 and 14:00:22 UTC. The magnitudes were estimated at 6.7 and 6.6, respectively, on the (GCMT) scale, and 6.9 and 7.0 on the scale; Chinese sources put these at 7.4 and 7.3 on the scale. The region is noted for the quantity and intensity of its earthquakes, and the complexity of its tectonics, which are closely related to the collision between the Indian and Eurasian tectonic plates.
The 1982 Ometepec earthquake that struck Mexico's southwestern coast near Ometepec (Guerrero) on 7 June was a doublet earthquake that ruptured in two steps. The first happened at 06:52 UTC, the second five hours later at 10:59 UTC. Estimated magnitudes are 6.9 and 7.0 on the scale, and 5.8 and 6.0 on the scale. The maximum Mercalli intensities were VII and VIII, respectively.
On 4 May 2000 at 12:21 WITA, a 7.5 earthquake struck off the coast of Banggai Islands Regency, Central Sulawesi, Indonesia, which was followed by a damaging local tsunami. The earthquake and tsunami killed at least 54 people and injured 270 others, with most of the damage and casualties occurring in the Banggai Islands.
The 2019 Cotabato earthquakes were an earthquake swarm which struck the province of Cotabato on the island of Mindanao in the Philippines in October 2019. Three of these earthquakes were above 6.0 on the moment magnitude scale with a Mercalli intensity of VIII. More than 40 people have been reported dead or missing and nearly 800 were injured as a result of these events.
At 14:11 PST on December 15, 2019, the province of Davao del Sur on the island of Mindanao in the Philippines was struck by an earthquake measuring 6.8 . It had a maximum perceived intensity of VII on the Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale. At least 13 people were killed and another 210 injured.








