
Avezzano is a city in the Abruzzo region, province of L'Aquila, Italy. It is the second most populous municipality in the province and the sixth in the region. It is the main commercial, industrial and agricultural centre of the Marsica area, with important high-tech industries and the Fucino Space Centre.

Pescina is a township and comune in the province of L'Aquila, Abruzzo, central Italy. It is a part of the mountain community Valle del Giovenco.

The Fucine Lake was a large endorheic karst lake between 650 and 680 m above sea level and surrounded by the Monte Sirente-Monte Velino mountain ranges to the north-northeast, Mount Salviano to the west, Vallelonga to the south, and the Valle del Giovenco to the east-southeast. Located in western Abruzzo in central Italy, the town of Avezzano lies to the northwest, Ortucchio to the southeast, and Trasacco to the southwest of the historic lake. Once the third largest lake in Italy after Lake Garda and Lake Maggiore, it was finally drained in 1878.
Two earthquakes hit the Italian regions of Molise and Apulia on 31 October at 10:32:58 (UTC) and 1 November at 15:09:00 (UTC). The shocks had magnitudes of 5.9 and 5.8 respectively. Most of the victims were killed and injured when a school collapsed in the town of San Giuliano di Puglia: 26 of the 51 schoolchildren died, together with one of their teachers. In particular, none of the nine children in the school's 4th Year survived.
The 1989 Malawi earthquake occurred on 10 March in central Malawi, with a moment magnitude of 6.3 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe). It was preceded by a number of foreshocks, the largest being a 5.7 shock on the previous day. The earthquake was felt strongly throughout central Malawi, and also felt in parts of Mozambique and Zambia. Nine people were killed, with many others injured or left homeless.

The 1915 Pleasant Valley earthquake occurred at in north-central Nevada. With a moment magnitude of 6.8, a surface wave magnitude of 7.7, and a maximum Mercalli intensity of X (Extreme), it was the strongest earthquake ever recorded in the state.
Striking southern Italy on 8 September, the 1905 Calabria earthquake had a moment magnitude of 7.2 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of XI (Extreme). The first major earthquake of the 20th century, it severely damaged parts of Lipari, Messina Province and a large area between Cosenza and Nicotera and killed between 557 and 2,500 people.
The 1694 Irpinia–Basilicata earthquake occurred on 8 September. It caused widespread damage in the Basilicata and Apulia regions of what was then the Kingdom of Naples, resulting in more than 6,000 casualties. The earthquake occurred at 11:40 UTC and lasted between 30 and 60 seconds.
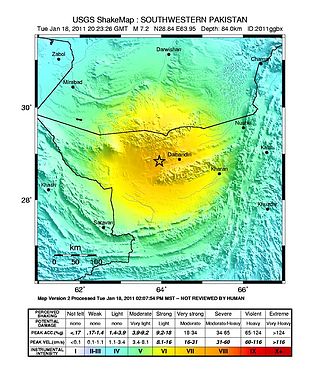
The 2011 Dalbandin earthquake occurred on with a moment magnitude of 7.2 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VII. The shock occurred in a sparsely populated area of Balochistan, caused moderate damage, three deaths, and some injuries.

The 2011 Lorca earthquake was a moderate 5.1 earthquake that occurred 6:47 p.m. CEST on 11 May 2011, near the town of Lorca, causing significant localized damage in the Region of Murcia, Spain, and panic among locals, and displacing many from their homes. The quake was preceded by a magnitude 4.4 foreshock at 17:05, that inflicted substantial damage to many older structures in the area, including the historical Espolón Tower of Lorca Castle, the Hermitage of San Clemente and the Convent of Virgen de Las Huertas. Three people were killed by a falling cornice. A total of nine deaths have been confirmed, while dozens are reported injured. The earthquake was the worst to hit the region since a 5.0 Mw tremor struck west of Albolote, Granada in 1956.

In May 2012, two major earthquakes struck Northern Italy, causing 27 deaths and widespread damage. The events are known in Italy as the 2012 Emilia earthquakes, because they mainly affected the Emilia region.
The 1990 Upland earthquake occurred at on February 28 with a moment magnitude of 5.7 and a maximum Mercalli Intensity of VII. This left-lateral strike-slip earthquake occurred west of the San Andreas Fault System and injured thirty people, with total losses of $12.7 million. Many strong motion instruments captured the event, with an unexpectedly high value seen on water tank near the epicentral area.

An earthquake, measuring 6.2 ± 0.016 on the moment magnitude scale, hit Central Italy on 24 August 2016 at 03:36:32 CEST. Its epicentre was close to Accumoli, with its hypocentre at a depth of 4 ± 1 km, approximately 75 km (47 mi) southeast of Perugia and 45 km (28 mi) north of L'Aquila, in an area near the borders of the Umbria, Lazio, Abruzzo and Marche regions. As of 15 November 2016, 299 people had been killed.
On December 5, 1456, the largest earthquake to occur on the Italian Peninsula in historical times struck the Kingdom of Naples. The earthquake had an estimated moment magnitude of Mw 7.19–7.4, and was centred near the town of Pontelandolfo in the present-day Province of Benevento, southern Italy. Earning a level of XI (Extreme) on the Modified Mercalli intensity scale, the earthquake caused widespread destruction in central and southern Italy. Estimates of the death toll range greatly with up to 70,000 deaths reported. It was followed by two strong Mw 7.0 and 6.0 earthquakes to the north on December 30. The earthquake sequence is considered the largest in Italian history, and one of the most studied.
The second shock in the 1962 Irpinia earthquake sequence was the largest and most destructive in a series of earthquakes in the southern Apennines. It occurred on 21 August at 18:19 CET, measuring 6.15 and assigned a maximum intensity of IX (Violent). It was preceded by an Mw 5.68 foreshock, and followed by a 5.34 aftershock. The earthquakes resulted in nearly 20 fatalities and significant property losses.
The 1706 Abruzzo earthquake, also known as the Maiella earthquake, occurred on November 3 at 13:00 CEST. The earthquake with a possible epicenter in the Central Apennine Mountains (Maiella), Abruzzo had an estimated moment magnitude of 6.6–6.84 Mw . It was assigned a maximum Mercalli intensity of XI (Extreme), causing tremendous destruction in Valle Peligna. At least 2,400 people were killed.

The 1917 San Salvador earthquake occurred on June 7 at 18:55 local time near the Salvadoran capital. The hypocenter of the Mw 6.7 was at a shallow depth of 15 km (9.3 mi), and occurred along a shallow crustal fault near San Salvador. The earthquake caused significant destruction of the city and left approximately 1,050 dead. It was followed by an eruption on San Salvador that killed another 1,100. Only behind the earthquake of 1986, it is the second deadliest in El Salvador's history.
The Medal of Merit for the Avezzano Earthquake of 1915 was a medal established by the Kingdom of Italy in 1915 to recognize service in support of relief efforts related to the 1915 Avezzano earthquake. In 1916, a certificate of honorable mention was established to recognize relief service in connection with the earthquake which did not rise to a level meeting the criteria for the medal itself.













