Related Research Articles

Aluminium is a chemical element; it has symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. It has a great affinity towards oxygen, forming a protective layer of oxide on the surface when exposed to air. Aluminium visually resembles silver, both in its color and in its great ability to reflect light. It is soft, nonmagnetic, and ductile. It has one stable isotope, 27Al, which is highly abundant, making aluminium the twelfth-most common element in the universe. The radioactivity of 26Al, a more unstable isotope, leads to it being used in radiometric dating.

An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which in most cases at least one is a metallic element, although it is also sometimes used for mixtures of elements; herein only metallic alloys are described. Most alloys are metallic and show good electrical conductivity, ductility, opacity, and luster, and may have properties that differ from those of the pure elements such as increased strength or hardness. In some cases, an alloy may reduce the overall cost of the material while preserving important properties. In other cases, the mixture imparts synergistic properties such as corrosion resistance or mechanical strength.

Duralumin is a trade name for one of the earliest types of age-hardenable aluminium–copper alloys. The term is a combination of Dürener and aluminium. Its use as a trade name is obsolete. Today the term mainly refers to aluminium-copper alloys, designated as the 2000 series by the international alloy designation system (IADS), as with 2014 and 2024 alloys used in airframe fabrication.
Aluminium–silicon alloys or Silumin is a general name for a group of lightweight, high-strength aluminium alloys based on an aluminum–silicon system (AlSi) that consist predominantly of aluminum - with silicon as the quantitatively most important alloying element. Pure AlSi alloys cannot be hardened, the commonly used alloys AlSiCu and AlSiMg can be hardened. The hardening mechanism corresponds to that of AlCu and AlMgSi.

Aluminium bronze is a type of bronze in which aluminium is the main alloying metal added to copper, in contrast to standard bronze or brass. A variety of aluminium bronzes of differing compositions have found industrial use, with most ranging from 5% to 11% aluminium by weight, the remaining mass being copper; other alloying agents such as iron, nickel, manganese, and silicon are also sometimes added to aluminium bronzes.
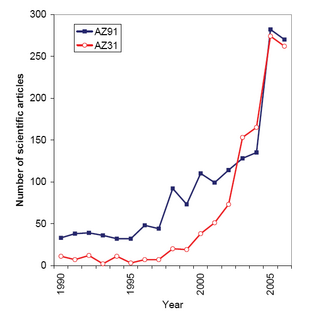
Magnesium alloys are mixtures of magnesium with other metals, often aluminium, zinc, manganese, silicon, copper, rare earths and zirconium. Magnesium alloys have a hexagonal lattice structure, which affects the fundamental properties of these alloys. Plastic deformation of the hexagonal lattice is more complicated than in cubic latticed metals like aluminium, copper and steel; therefore, magnesium alloys are typically used as cast alloys, but research of wrought alloys has been more extensive since 2003. Cast magnesium alloys are used for many components of modern cars and have been used in some high-performance vehicles; die-cast magnesium is also used for camera bodies and components in lenses.

Aluminium recycling is the process in which secondary commercial aluminium is created from scrap or other forms of end-of-life or otherwise unusable aluminium. It involves re-melting the metal, which is cheaper and more energy-efficient than the production of virgin aluminium by electrolysis of alumina (Al2O3) refined from raw bauxite by use of the Bayer and Hall–Héroult processes.

An aluminium alloy (UK/IUPAC) or aluminum alloy is an alloy in which aluminium (Al) is the predominant metal. The typical alloying elements are copper, magnesium, manganese, silicon, tin, nickel and zinc. There are two principal classifications, namely casting alloys and wrought alloys, both of which are further subdivided into the categories heat-treatable and non-heat-treatable. About 85% of aluminium is used for wrought products, for example rolled plate, foils and extrusions. Cast aluminium alloys yield cost-effective products due to the low melting point, although they generally have lower tensile strengths than wrought alloys. The most important cast aluminium alloy system is Al–Si, where the high levels of silicon (4–13%) contribute to give good casting characteristics. Aluminium alloys are widely used in engineering structures and components where light weight or corrosion resistance is required.
Aluminium–lithium alloys are a set of alloys of aluminium and lithium, often also including copper and zirconium. Since lithium is the least dense elemental metal, these alloys are significantly less dense than aluminium. Commercial Al–Li alloys contain up to 2.45% lithium by mass.
6061 aluminium alloy is a precipitation-hardened aluminium alloy, containing magnesium and silicon as its major alloying elements. Originally called "Alloy 61S", it was developed in 1935. It has good mechanical properties, exhibits good weldability, and is very commonly extruded. It is one of the most common alloys of aluminium for general-purpose use.
7075 aluminium alloy (AA7075) is an aluminium alloy with zinc as the primary alloying element. It has excellent mechanical properties and exhibits good ductility, high strength, toughness, and good resistance to fatigue. It is more susceptible to embrittlement than many other aluminium alloys because of microsegregation, but has significantly better corrosion resistance than the alloys from the 2000 series. It is one of the most commonly used aluminium alloys for highly stressed structural applications and has been extensively used in aircraft structural parts.
Sustained load cracking, or SLC, is a metallurgical phenomenon that occasionally develops in pressure vessels and structural components under stress for sustained periods of time.
2014 aluminium alloy (aluminum) is an aluminium-based alloy often used in the aerospace industry.
7068 aluminium alloy is one of the strongest commercially available aluminium alloys, with a tensile strength comparable to that of some steels. This material, also known as an aircraft alloy, is heat treatable.
5005 aluminium alloy is an aluminium–magnesium alloy with good resistance to atmospheric corrosion. It is used in decorative and architectural applications.
2195 aluminium alloy is an alloy in the wrought aluminium-copper family. It is one of the Weldalite family of Aluminium–lithium alloys. It is one of the most complex grades in the 2000 series, with at least 91.9% aluminium by weight. 2195 aluminium can be alternately referred to by the UNS designation A92195.
5182 Aluminium alloy has magnesium and manganese as minor elements. 5182 Aluminium alloy is used in the automobile industry for making various parts of vehicles.
1070 is a pure aluminium alloy. It is a wrought alloy with a high corrosion resistance and an excellent brazing ability.
1200 Aluminium alloy has aluminium as the major element, and has silicon, zinc, copper, titanium and manganese as minor elements.
2090 Aluminium alloy consists of copper, lithium, zirconium as minor elements and other impurity alloying elements.
References
- 1 2 3 "2017 Aluminium alloy". 6 May 2013. Archived from the original on 2015-10-27.
- ↑ "2017 Aluminium alloy properties". Archived from the original on 2004-05-15.