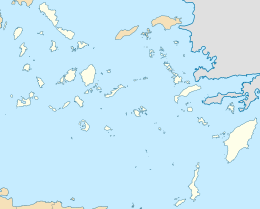
The Cyclades are an island group in the Aegean Sea, southeast of mainland Greece and a former administrative prefecture of Greece. They are one of the island groups which constitute the Aegean archipelago. The name refers to the archipelago forming a circle around the sacred island of Delos. The largest island of the Cyclades is Naxos, however the most populated is Syros.

Santorini, officially Thira or Thera, is a Greek island in the southern Aegean Sea, about 200 km (120 mi) southeast from the mainland. It is the largest island of a small, circular archipelago formed by the Santorini caldera. It is the southernmost member of the Cyclades group of islands, with an area of approximately 73 km2 (28 sq mi) and a 2021 census population of 15,480. The municipality of Santorini includes the inhabited islands of Santorini and Therasia, and the uninhabited islands of Nea Kameni, Palaia Kameni, Aspronisi, Anydros, and Christiana. The total land area is 91 km2 (35 sq mi). Santorini is part of the Thira regional unit.

The Cascadia subduction zone is a 960 km (600 mi) fault at a convergent plate boundary, about 100–200 km (70–100 mi) off the Pacific coast, that stretches from northern Vancouver Island in Canada to Northern California in the United States. It is capable of producing 9.0+ magnitude earthquakes and tsunamis that could reach 30 m (98 ft). The Oregon Department of Emergency Management estimates shaking would last 5–7 minutes along the coast, with strength and intensity decreasing further from the epicenter. It is a very long, sloping subduction zone where the Explorer, Juan de Fuca, and Gorda plates move to the east and slide below the much larger mostly continental North American plate. The zone varies in width and lies offshore beginning near Cape Mendocino, Northern California, passing through Oregon and Washington, and terminating at about Vancouver Island in British Columbia.

Firá is the modern capital of the Greek Aegean island of Santorini (Thera). A traditional settlement, "Firá" derives its name from an alternative pronunciation of "Thíra", the ancient name of the island itself.

Anafi or Anaphe is a Greek island community in the Cyclades. In 2021, it had a population of 293. Its land area is 40.370 square kilometres. It lies east of the island of Thíra (Santorini). Anafi is part of the Thira regional unit.

Anydros is an uninhabited Greek islet in the municipality of Santorini, which is a group of islands in the Cyclades. It is north of the island Anafi, and southwest of Amorgos. The island hosts a seismometer, part of the Greek national network, installed in 2025.
A slow earthquake is a discontinuous, earthquake-like event that releases energy over a period of hours to months, rather than the seconds to minutes characteristic of a typical earthquake. First detected using long term strain measurements, most slow earthquakes now appear to be accompanied by fluid flow and related tremor, which can be detected and approximately located using seismometer data filtered appropriately. That is, they are quiet compared to a regular earthquake, but not "silent" as described in the past.
The 2008 Peloponnese earthquake killed two people, injured more than 220 and left at least 2,000 people homeless in north western Peloponnese, Greece, on June 8. The earthquake hit the area at 1525 EET, with a moment magnitude of 6.5, according to the Athens Geodynamic Institute. It was strongly felt as far away as in Athens and in parts of southern Italy. The US Geological Survey reported that the quake had a magnitude of 6.4. The epicenter of the tremor was located about 15 miles (32 km) southwest of the Greek port city of Patras, at a depth of 16 km. Interior Minister Prokopis Pavlopoulos dispatched rescue and recovery teams, the Red Cross and units of the army in order to assess the damage and the needs of survivors in the earthquake affected areas.

The Aegean Sea plate is a small tectonic plate located in the Eastern Mediterranean under Southern Greece and western Turkey. Its southern edge is the Hellenic subduction zone south of Crete, where the African plate is being swept under the Aegean Sea plate. Its northern margin is a divergent boundary with the Eurasian plate.
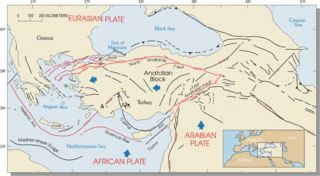
The Hellenic arc or Aegean arc is an arcuate mountain chain of the southern Aegean Sea located on the southern margin of the Aegean Sea plate. Geologically it results from the subduction of the African plate under it along the Hellenic subduction zone. The Hellenic Trench trends parallel to its southern side. The Aegean Sea plate, a microplate, is often considered part of the Eurasian plate from which it is in the process of diverging. The arc itself is mainly marine, the mountaintops appearing as islands in the Ionian Sea, Crete and its environs, or in the Dodecanese group. It encroaches on mainland terrain in the Peloponnesus, on Crete, on Rhodes, and on the southern coast of Anatolia, thus being encompassed by both Greece and Turkey.
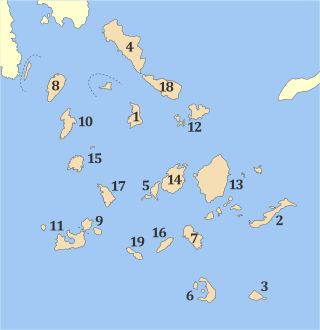
Thira is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of South Aegean. The regional unit covers the islands of Thira (Santorini), Anafi, Folegandros, Ios, Sikinos and several smaller islands in the Aegean Sea.
The 1956 Amorgos earthquake occurred at 03:11 UTC on July 9. It had a magnitude of 7.7 on the moment magnitude scale and a maximum perceived intensity of IX on the Mercalli intensity scale. The epicentre was to the south of the island of Amorgos, the easternmost island of the Cyclades in the Aegean Sea. There was significant damage on Amorgos and the neighbouring island of Santorini. It was the largest earthquake in Greece in the 20th century. It was followed 13 minutes later by a magnitude 7.2 earthquake near Santorini. It triggered a major tsunami with a maximum run-up of 30 m. The combined effects of the earthquake shaking and the tsunami caused the deaths of 53 people with a further 100 injured.

At 02:10 PM local time (UTC-5) on 28 January 2020, an earthquake with a magnitude of 7.7 struck the north side of the Cayman Trough, north of Jamaica and west of the southern tip of Cuba, with the epicenter being 80 miles (130 km) east-southeast of Cayman Brac, Cayman Islands, and 83 miles (134 km) north of Montego Bay, Jamaica. Schools in Jamaica, as well as corporate and public buildings in Miami, were evacuated after shaking was experienced in parts of the U.S. state of Florida, a region not typically thought of in-relation to seismic activity. Light shaking was also reported on the Yucatán Peninsula in Mexico. The quake was the largest seismic event in the Caribbean since 1946. A tsunami warning for the Caribbean Sea was initially issued by the Pacific Tsunami Warning Center, later being withdrawn.

An earthquake with a moment magnitude of 7.0 occurred on 30 October 2020 about 14 km (8.7 mi) northeast of the Greek island of Samos. Although Samos was closest to the epicentre, it was the large Turkish city İzmir, 70 km (43 mi) northeast that was heavily affected—more than 700 residential and commercial structures were seriously damaged or destroyed. One hundred and seventeen people died in İzmir Province while an additional 1,034 were injured. In Greece, there were two fatalities and 19 injured. The earthquake is the deadliest in the year 2020, and the third major earthquake to strike Turkey that year. It generated an unusually large tsunami. The event is called the Samos earthquake by the International Seismological Centre.
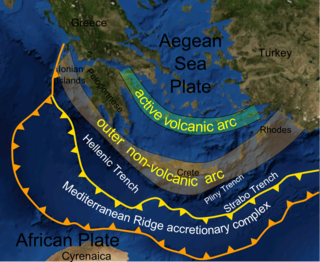
The Hellenic subduction zone (HSZ) is the convergent boundary between the African plate and the Aegean Sea plate, where oceanic crust of the African continent is being subducted north–northeastwards beneath the Aegean. The southernmost and shallowest part of the zone is obscured beneath the deformed thick sedimentary sequence that forms the Mediterranean Ridge accretionary complex. It has a well-defined Wadati–Benioff zone of seismicity, which demonstrates the relatively shallow dip of its southern part, which increases markedly to the north of the non-volcanic part of the Hellenic arc. The descending slab has been imaged using seismic tomography down to the top of the mantle transition zone at 410 km depth.
The 1856 Heraklion earthquake, also known as the Crete earthquake or Rhodes earthquake, occurred on the morning of October 12 at 02:45 am local time. This extremely catastrophic earthquake had an estimated magnitude of 7.7 to 8.3 at a depth of approximately 61 to 100 km. The earthquake was felt over a very wide area extending from Sicily, Italy to the Levant and North Africa. On the Greek island of Crete, the effects of the earthquake were cataclysmic, over 500 bodies were recovered in the city of Heraklion. Shockwaves from the earthquake were felt intensely, covering all of the Ottoman Empire; present-day Turkey, Cyprus and the Middle East where damage and human losses were reported. In Malta, the Għajn Ħadid Tower—a coastal watchtower built around the year 1638—was severely damaged in the earthquake, when its upper floor collapsed. In Cairo, Egypt, the earthquake destroyed buildings, created seiches in canals, and killed several people. Off the Egyptian and Italian coasts, sailors reported feeling a seaquake.
The 2021 Lasithi earthquake was a magnitude 6.4 earthquake with a maximum intensity of VIII (Severe) on the Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale which occurred on 12 October 2021, 12:24 (UTC+3:30) off the island of Crete. The quake was also felt at low intensity as far as Cairo and Istanbul.
Events in the year 2025 in Greece.
Starting late September 2024 and ending in early February 2025, central Ethiopia experienced a series of earthquakes, most of which were located in the Awash Fentale region, and mainly located between or around the volcanoes of Mount Fentale and Dofan, in Ethiopia's Awash National Park. The earthquakes were widely felt across much of central Ethiopia, with many of them causing localized but severe damage.