Melpomene is a large, bright main-belt asteroid that was discovered by J. R. Hind on 24 June 1852, and named after Melpomenē, the Muse of tragedy in Greek mythology. Its historical symbol was a dagger over a star; it is in the pipeline for Unicode 17.0 as U+1CECB .

Atalante is a large, dark main-belt asteroid. It was discovered by the German-French astronomer H. Goldschmidt on October 5, 1855, and named by French mathematician Urbain Le Verrier after the Greek mythological heroine Atalanta. It was rendered 'Atalanta' in English sources in the 19th century. This asteroid is classified as C-type (carbonaceous), according to the Tholen classification system.

Echo is a quite large main-belt asteroid. It was discovered by James Ferguson of the United States Naval Observatory in Washington D.C., on September 14, 1860. It was his third and final asteroid discovery. It is named after Echo, a nymph in Greek mythology. James Ferguson had initially named it "Titania", not realizing that name was already used for a satellite of Uranus.

Frigga is a large, M-type, possibly metallic main-belt asteroid. It was discovered by the German-American astronomer C. H. F. Peters on November 12, 1862. The object is named after Frigg, the Norse goddess. The asteroid is orbiting the Sun with a period of 4.36 years and completes a rotation on its axis every nine hours.
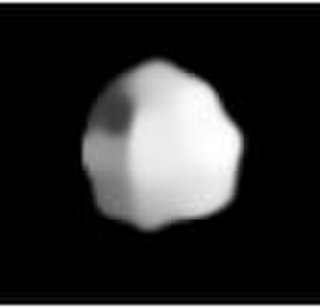
Kallisto is a fairly typical, although sizeable Main belt asteroid. It is classified as an S-type asteroid. Like other asteroids of its type, it is light in colour. It was discovered by Johann Palisa on 8 October 1879, in Pola, and was named after the same nymph Callisto in Greek mythology as Jupiter's moon Callisto.

California is an asteroid belonging to the Flora family in the Main Belt. It was discovered by Max Wolf on 25 September 1892 in Heidelberg, and is named for the U.S. state of California. This object is orbiting the Sun at a distance of 2.20 AU with a period of 3.26 yr and an eccentricity (ovalness) of 0.19. The orbital plane is inclined at an angle of 5.7° to the plane of the ecliptic.

402 Chloë is a large main-belt asteroid. It was discovered by French astronomer Auguste Charlois on 21 March 1895 from Nice. This asteroid is orbiting the Sun at a distance of 2.56 AU with a period of 4.09 years and an eccentricity of 0.11. The orbital plane is inclined at an angle of 11.8° to the plane of the ecliptic.

Galene is a typical main belt asteroid. It was discovered by the French astronomer Auguste Charlois on 27 August 1897 from Nice, and was named after Galene, one of the Nereids of Greek Mythology. This asteroid is orbiting the Sun at a distance of 2.97 AU with a period of 5.12 yr and an eccentricity of 0.12. A computer search suggests it is the most likely parent body of the impactor that generated the temporary cometary activity of 7968 Elst–Pizarro in 1996.
Pamina is a minor planet orbiting the Sun in the main belt. It is named for the heroine of Mozart's opera, The Magic Flute. This asteroid was discovered by M. Wolf in 1904 at the Heidelberg observatory in Germany. It is orbiting at a distance of 2.74 AU from the Sun, with an orbital eccentricity (ovalness) of 0.212 and a period of 4.53 yr. The orbital plane is inclined at an angle of 6.8° to the ecliptic.
678 Fredegundis is a minor planet orbiting the Sun. It was discovered 22 January 1909 from Heidelberg by German astronomer K. Wilhelm Lorenz, and was named after the French opera Frédégonde. This object is orbiting at a distance of 2.57 AU with a period of 4.13 years and an eccentricity (ovalness) of 0.22. The orbital plane is inclined at an angle of 6.1° to the plane of the ecliptic
711 Marmulla is an asteroid belonging to the Flora family in the Main Belt. It was discovered 1 March 1911 by Austrian astronomer Johann Palisa. The asteroid name may be derived from the Old High German word 'marmul', which means 'marble'. This asteroid is orbiting 2.24 AU from the Sun with a period of 3.35 yr and an eccentricity (ovalness) of 0.195. The orbital plane of 711 Marmulla is inclined at an angle of 6.1° to the plane of the ecliptic.
742 Edisona is a minor planet, specifically an asteroid orbiting in the asteroid belt that was discovered by German astronomer Franz Kaiser on February 23, 1913. It was named for inventor Thomas Edison. This asteroid is orbiting 3.01 AU with a period of 5.22 years and an eccentricity of 0.119. The orbital plane is inclined at an angle of 11.2° to the plane of the ecliptic. This is a member of the dynamic Eos family of asteroids that most likely formed as the result of a collisional breakup of a parent body.
780 Armenia is a minor planet in the asteroid belt orbiting the Sun. It is named after the Kingdom of Armenia, now Armenia. This object is orbiting at a distance of 3.11 AU with an eccentricity of 0.097 and a period of 5.50 yr. The orbital plane is inclined at an angle of 19.1° to the plane of rotation. This asteroid spans a girth of ~94 km. The long rotation period of this asteroid necessitated light curve data from more than one latitude. The overlapping data provided a solution with a period of 19.891±0.002 h and a brightness amplitude of 0.18±0.03 in magnitude.
1971 Hagihara, provisional designation 1955 RD1, is an Eoan asteroid from the outer region of the asteroid belt, approximately 12 kilometers in diameter.
5160 Camoes, provisional designation 1979 YO, is an asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 6 kilometers in diameter. The asteroid was discovered on 23 December 1979, by Belgian astronomer Henri Debehogne and Brazilian astronomer Edgar Netto at ESO's La Silla Observatory in northern Chile. It was later named for Portuguese poet Luís de Camões.

7387 Malbil (prov. designation: 1982 BS1) is an elongated background asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt. It was discovered on 30 January 1982, by American astronomer Edward Bowell at Lowell's Anderson Mesa Station in Arizona, United States. The asteroid has a rotation period of 7.5 hours and measures approximately 6 kilometers (4 miles) in diameter. It is named for American pianist Malcolm Bilson.

3169 Ostro, provisional designation 1981 LA, is a Hungaria family asteroid from the innermost regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 5 kilometers in diameter.

4001 Ptolemaeus, provisional designation 1949 PV, is a Florian asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 5 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 2 August 1949, by German astronomer Karl Reinmuth at the Heidelberg-Königstuhl State Observatory in Heidelberg, Germany. In 1991, the International Astronomical Union named the S-type asteroid after Greco-Roman astronomer Ptolemy.
1414 Jérôme, provisional designation 1937 CE, is a carbonaceous Dorian asteroid from the central region of the asteroid belt, approximately 16 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 12 February 1937 by, French astronomer Louis Boyer at Algiers Observatory, Algeria, in northern Africa, and named after his father Jérôme Boyer.
9524 O'Rourke, provisionally designated 1981 EJ5, is an asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 3 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 2 March 1981, by American astronomer Schelte Bus at the Siding Spring Observatory in New South Wales, Australia. The asteroid was named after Laurence O'Rourke, a researcher at the European Space Astronomy Centre.











