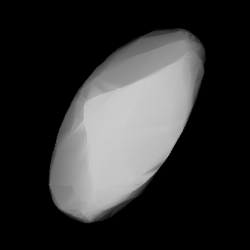
 Shape model of Annette from its lightcurve | |
| Discovery [1] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | C. W. Tombaugh |
| Discovery site | Lowell Obs. |
| Discovery date | 5 October 1929 |
| Designations | |
| (2839) Annette | |
Named after | Annette Tombaugh (discoverer's daughter) [2] |
| 1929 TP ·1937 AB1 1939 UL ·1962 TE 1970 BB ·1972 XF1 1982 VP | |
| main-belt · Flora [3] | |
| Orbital characteristics [1] | |
| Epoch 4 September 2017 (JD 2458000.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 0 | |
| Observation arc | 87.67 yr (32,023 days) |
| Aphelion | 2.5493 AU |
| Perihelion | 1.8838 AU |
| 2.2166 AU | |
| Eccentricity | 0.1501 |
| 3.30 yr (1,205 days) | |
| 200.55° | |
| 0° 17m 55.32s / day | |
| Inclination | 4.8085° |
| 44.569° | |
| 6.8264° | |
| Physical characteristics | |
| 5.41±0.86 km [4] 7.313±0.150 km [5] 7.562±0.122 km [6] | |
| 10.457±0.003 h [7] 10.4595±0.0001 h [8] | |
| 0.0563±0.0118 [6] 0.060±0.005 [5] 0.24 (assumed) [3] 0.47±0.22 [4] | |
| S [3] | |
| 12.9 [1] ·12.92 [4] ·14.35 [3] [6] [8] | |
2839 Annette (prov. designation: 1929 TP) is a bright Flora asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt. It was discovered on 5 October 1929, by American astronomer Clyde Tombaugh at Lowell Observatory during his search for Pluto. [9] The presumed S-type asteroid has a rotation period of 10.5 hours and measures approximately five kilometers (three miles) in diameter. It was named after the discoverer's daughter. [2]
