
Nemausa is a large main-belt asteroid that was discovered on January 22, 1858, by Joseph Jean Pierre Laurent. Laurent made the discovery from the private observatory of Benjamin Valz in Nîmes, France. The house, at 32 rue Nationale in Nîmes, has a plaque commemorating the discovery. With Laurent's permission, Valz named the asteroid after the Celtic god Nemausus, the patron god and namesake of Nîmes during Roman times.
Metis is one of the larger main-belt asteroids. It is composed of silicates and metallic nickel-iron, and may be the core remnant of a large asteroid that was destroyed by an ancient collision. Metis is estimated to contain just under half a percent of the total mass of the asteroid belt.

Laetitia is a large main-belt asteroid that was discovered by French astronomer Jean Chacornac on 9 February 1856 and named after Laetitia, a minor Roman goddess of gaiety. The spectrum matches an S-type, indicating a stony (silicate) composition. It is orbiting the Sun with a period of 4.61 years and is spinning on its axis once every 5.1 hours.
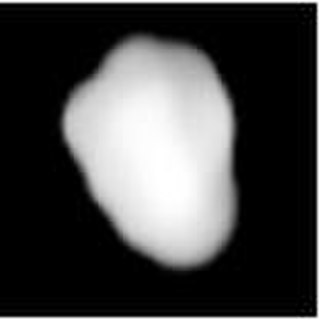
Daphne is a large asteroid from the asteroid belt. It is a dark-surfaced body 174 km in diameter is probably composed of primitive carbonaceous chondrites. The spectra of the asteroid displays evidence of aqueous alteration. It was discovered by H. Goldschmidt on May 22, 1856, and named after Daphne, the nymph in Greek mythology who was turned into a laurel tree. Incorrect orbital calculations initially resulted in 56 Melete being mistaken for a second sighting of Daphne. Daphne was not sighted again until August 31, 1862.
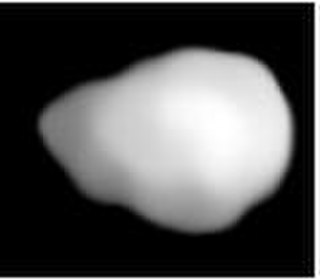
Doris is one of the largest main belt asteroids. It was discovered on 19 September 1857 by Hermann Goldschmidt from his balcony in Paris.

Aurora is one of the largest main-belt asteroids. With an albedo of only 0.04, it is darker than soot, and has a primitive composition consisting of carbonaceous material. It was discovered by J. C. Watson on September 6, 1867, in Ann Arbor, and named after Aurora, the Roman goddess of the dawn.

Arethusa is a large main-belt asteroid. It was discovered by German astronomer Robert Luther on 23 November 1867, and named after one of the various Arethusas in Greek mythology. Arethusa has been observed occulting a star three times: first on 2 February 1998, and twice in January 2003.
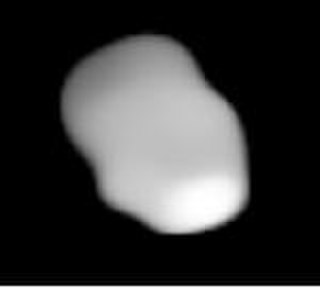
Miriam is a moderately large, very dark main belt asteroid. It was discovered by C. H. F. Peters on August 22, 1868, from the Litchfield Observatory.

Ate is a main-belt asteroid discovered by the German-American astronomer C. H. F. Peters on August 14, 1870, and named after Ate, the goddess of mischief and destruction in Greek mythology. In the Tholen classification system, it is categorized as a carbonaceous C-type asteroid, while the Bus asteroid taxonomy system lists it as an Ch asteroid.

Lachesis is a large main-belt asteroid. It was discovered by French astronomer Alphonse Borrelly on April 10, 1872, and independently by German-American astronomer Christian Heinrich Friedrich Peters on April 11, 1872, then named after Lachesis, one of the Moirai, or Fates, in Greek mythology. A Lachesean occultation of a star occurred in 1999 and was confirmed visually by five observers and once photoelectrically, with the chords yielding an estimated elliptical cross-section of 184 × 144 km.

163 Erigone is an asteroid from the asteroid belt and the namesake of the Erigone family of asteroids that share similar orbital elements and properties. It was discovered by French astronomer Henri Joseph Perrotin on April 26, 1876, and named after one of the two Erigones in Greek mythology. This asteroid is orbiting the Sun at a distance of 2.37 AU with a period of 3.643 years and an eccentricity (ovalness) of 0.19. The orbital plane is inclined at an angle of 4.8° to the plane of the ecliptic.

Prokne is a main-belt asteroid that was discovered by German-American astronomer C. H. F. Peters on March 21, 1879, in Clinton, New York, and named after Procne, the sister of Philomela in Greek mythology. Stellar occultations by Prokne have been observed twice, in 1984 from Italy and again in 1999 from Iowa.

Dynamene is a large dark main-belt asteroid that was discovered by German-American astronomer Christian Heinrich Friedrich Peters on July 27, 1879, in Clinton, New York. The name derives from Dynamene, one of the fifty Nereids in Greek mythology. Based upon its spectrum, 200 Dynamene is classified as a C-type asteroid, indicating that it probably has a primitive composition similar to the carbonaceous chondrite meteorites. The spectra of the asteroid displays evidence of aqueous alteration.

Hypatia is a very large main-belt asteroid that was discovered by Russian astronomer Viktor Knorre on July 1, 1884, in Berlin. It was the third of his four asteroid discoveries. The name was given in honour of philosopher Hypatia of Alexandria. Based upon the spectrum, it is classified as a C-type asteroid and is probably composed of primitive carbonaceous material. Like many asteroids of this type, its surface is very dark in colour.

Eukrate is a rather large main-belt asteroid. It is dark and probably a primitive carbonaceous body. The asteroid was discovered by Robert Luther on March 14, 1885, in Düsseldorf. It was named after Eucrate, a Nereid in Greek mythology.

Chicago is a very large main-belt asteroid. It is classified as a C-type asteroid and is probably composed of carbonaceous material.

Ornamenta is a relatively large main-belt asteroid, measuring 118 km in diameter. It is classified as a C-type asteroid and is probably composed of carbonaceous material.
Liguria is a very large main-belt asteroid that was discovered by Auguste Charlois on January 21, 1893, in Nice. It is one of seven of Charlois's discoveries that was expressly named by the Astromomisches Rechen-Institut, and was named for the Italian region.
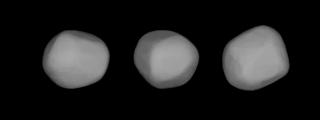
Diotima is one of the larger main-belt asteroids. It is classified as a C-type asteroid and is probably composed of primitive carbonaceous material.
Gyptis, minor planet designation: 444 Gyptis, is a main-belt asteroid that was discovered by J. Coggia on March 31, 1899, in Marseilles. It is classified as a C-type asteroid and is probably composed of carbonaceous material. The spectra of the asteroid displays evidence of aqueous alteration.


















