
Honorius was Roman emperor from 393 to 423. He was the younger son of emperor Theodosius I and his first wife Aelia Flaccilla. After the death of Theodosius in 395, Honorius, under the regency of Stilicho, ruled the western half of the empire while his brother Arcadius ruled the eastern half. His reign over the Western Roman Empire was notably precarious and chaotic. In 410, Rome was sacked for the first time since the Battle of the Allia almost 800 years prior.

The Visigoths were a Germanic people united under the rule of a king and living within the Roman Empire during late antiquity. The Visigoths first appeared in the Balkans, as a Roman-allied barbarian military group united under the command of Alaric I. Their exact origins are believed to have been diverse but they probably included many descendants of the Thervingi who had moved into the Roman Empire beginning in 376 and had played a major role in defeating the Romans at the Battle of Adrianople in 378. Relations between the Romans and Alaric's Visigoths varied, with the two groups making treaties when convenient, and warring with one another when not. Under Alaric, the Visigoths invaded Italy and sacked Rome in August 410.
The 400s decade ran from January 1, 400, to December 31, 409.

Year 410 (CDX) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year after the Consulship of Honorius and Theodosius. The denomination 410 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The 470s decade ran from January 1, 470, to December 31, 479.
The 500s decade ran from January 1, 500, to December 31, 509.
The 580s decade ran from January 1, 580, to December 31, 589.
The 480s decade ran from January 1, 480, to December 31, 489.
The 420s decade ran from January 1, 420, to December 31, 429.

Year 451 (CDLI) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Marcianus and Adelfius. The denomination 451 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
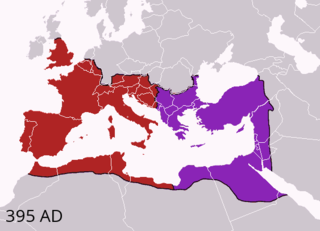
Year 395 (CCCXCV) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Olybrius and Probinus. The denomination 395 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 408 (CDVIII) was a leap year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Bassus and Philippus. The denomination 408 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 396 (CCCXCVI) was a leap year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Augustus and Augustus. The denomination 396 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The 390s decade ran from January 1, 390 to December 31, 399
The 410s decade ran from January 1, 410, to December 31, 419.
The 460s decade ran from January 1, 460, to December 31, 469.

Year 466 (CDLXVI) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Leo and Tatianus. The denomination 466 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 423 (CDXXIII) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known in Rome as the Year of the Consulship of Marinianus and Asclepiodotus. The denomination 423 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Constans II was the son of Western Roman emperor Constantine III, and served as his co-emperor from 409 to 411. Constans was a monk prior to his father being acclaimed emperor by the army in Britain in early 407, an act of rebellion against the ruling emperor Honorius. He was summoned to Gaul, appointed to the position of caesar (heir) and swiftly married so that a dynasty could be founded. In Hispania, Honorius's relatives rose in 408 and expelled Constantine's administration. An army under the generals Constans and Gerontius was sent to deal with this and Constantine's authority was re-established. Honorius acknowledged Constantine as co-emperor in early 409 and Constantine immediately raised Constans to the position of augustus (emperor), theoretically equal in rank to Honorius as well as to Constantine. Later in 409 Gerontius rebelled, proclaimed his client Maximus emperor and incited barbarian groups in Gaul to rise up. Constans was sent to quash the revolt, but was defeated and withdrew to Arles. In 410, Constans was sent to Hispania again. Gerontius had strengthened his army with barbarians and defeated Constans; the latter withdrew north and was defeated again and killed at Vienne early in 411. Gerontius then besieged Constantine in Arles and killed him.

The Visigothic Kingdom, Visigothic Spain or Kingdom of the Goths occupied what is now southwestern France and the Iberian Peninsula from the 5th to the 8th centuries. One of the Germanic successor states to the Western Roman Empire, it was originally created by the settlement of the Visigoths under King Wallia in the province of Gallia Aquitania in southwest Gaul by the Roman government and then extended by conquest over all of Hispania. The Kingdom maintained independence from the Eastern Roman or Byzantine Empire, whose attempts to re-establish Roman authority in Hispania were only partially successful and short-lived.











