
The Peloponnesian War was an ancient Greek war fought by the Delian League led by Athens against the Peloponnesian League led by Sparta. Historians have traditionally divided the war into three phases. In the first phase, the Archidamian War, Sparta launched repeated invasions of Attica, while Athens took advantage of its naval supremacy to raid the coast of the Peloponnese and attempt to suppress signs of unrest in its empire. This period of the war was concluded in 421 BC, with the signing of the Peace of Nicias. That treaty, however, was soon undermined by renewed fighting in the Peloponnese. In 415 BC, Athens dispatched a massive expeditionary force to attack Syracuse, Sicily; the attack failed disastrously, with the destruction of the entire force in 413 BC. This ushered in the final phase of the war, generally referred to either as the Decelean War, or the Ionian War. In this phase, Sparta, now receiving support from the Achaemenid Empire, supported rebellions in Athens's subject states in the Aegean Sea and Ionia, undermining Athens's empire, and, eventually, depriving the city of naval supremacy. The destruction of Athens's fleet in the Battle of Aegospotami effectively ended the war, and Athens surrendered in the following year. Corinth and Thebes demanded that Athens should be destroyed and all its citizens should be enslaved, but Sparta refused.
Year 404 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Tribunate of Volusus, Cossus, Fidenas, Ambustus, Maluginensis and Rutilus. The denomination 404 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
This article concerns the period 409 BC – 400 BC.
This decade witnessed the continuing decline of the Achaemenid Empire, fierce warfare amongst the Greek city-states during the Peloponnesian War, the ongoing Warring States period in Zhou dynasty China, and the closing years of the Olmec civilization in modern-day Mexico.

Lysander was a Spartan admiral who commanded the Spartan fleet in the Hellespont which defeated the Athenians at Aegospotami in 405 BC. The following year, he was able to force the Athenians to capitulate, bringing the Peloponnesian War to an end. He then played a key role in Sparta's domination of Greece for the next decade until his death at the Battle of Haliartus.

Thrasybulus was an Athenian general and democratic leader. In 411 BC, in the wake of an oligarchic coup at Athens, the pro-democracy sailors at Samos elected him as a general, making him a primary leader of the ultimately successful democratic resistance to the coup. As general, he was responsible for recalling the controversial nobleman Alcibiades from exile, and the two worked together extensively over the next several years. In 411 and 410, Thrasybulus was in command along with Alcibiades and others at several critical Athenian naval victories.

Alcibiades, son of Cleinias /ˌælsəˈbaɪədiz/ Ancient Greek: Ἀλκιβιάδης, romanized:Alkibiádēs, [alkibiádɛːs];, from the deme of Scambonidae, was a prominent Athenian statesman, orator, and general. He was the last famous member of his mother's aristocratic family, the Alcmaeonidae, which fell from prominence after the Peloponnesian War. He played a major role in the second half of that conflict as a strategic advisor, military commander, and politician.
Year 410 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Mamercinus and Volusus. The denomination 410 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Theramenes was an Athenian statesman, prominent in the final decade of the Peloponnesian War. He was particularly active during the two periods of oligarchic government at Athens, as well as in the trial of the generals who had commanded at Arginusae in 406 BC. A moderate oligarch, he often found himself caught between the democrats on the one hand and the extremist oligarchs on the other. Successful in replacing a narrow oligarchy with a broader one in 411 BC, he failed to achieve the same end in 404 BC, and was executed by the extremists whose policies he had opposed.
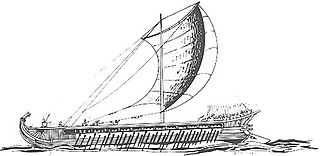
The naval Battle of Cyzicus took place in 410 BC during the Peloponnesian War. In the battle, an Athenian fleet commanded by Alcibiades, Thrasybulus, and Theramenes routed and completely destroyed a Spartan fleet commanded by Mindarus. The victory allowed Athens to recover control over a number of cities in the Hellespont over the next year. In the wake of their defeat, the Spartans made a peace offer, which the Athenians rejected.

The History of the Peloponnesian War is a historical account of the Peloponnesian War, which was fought between the Peloponnesian League and the Delian League. It was written by Thucydides, an Athenian historian who also served as an Athenian general during the war. His account of the conflict is widely considered to be a classic and regarded as one of the earliest scholarly works of history. The History is divided into eight books.

The naval Battle of Arginusae took place in 406 BC during the Peloponnesian War near the city of Canae in the Arginusae islands, east of the island of Lesbos. In the battle, an Athenian fleet commanded by eight strategoi defeated a Spartan fleet under Callicratidas. The battle was precipitated by a Spartan victory which led to the Athenian fleet under Conon being blockaded at Mytilene; to relieve Conon, the Athenians assembled a scratch force composed largely of newly constructed ships manned by inexperienced crews. This inexperienced fleet was thus tactically inferior to the Spartans, but its commanders were able to circumvent this problem by employing new and unorthodox tactics, which allowed the Athenians to secure a dramatic and unexpected victory. Slaves and metics who participated in the battle were granted Athenian citizenship.

The Battle of Notium in 406 BC, was a Spartan naval victory in the Peloponnesian War. Prior to the battle, the Athenian commander, Alcibiades, left his helmsman, Antiochus, in command of the Athenian fleet, which was blockading the Spartan fleet in Ephesus. In violation of his orders, Antiochus attempted to draw the Spartans into battle by tempting them with a small decoy force. His strategy backfired, and the Spartans under Lysander scored a small but symbolically significant victory over the Athenian fleet. This victory resulted in the downfall of Alcibiades, and established Lysander as a commander who could defeat the Athenians at sea.
Thrasyllus was an Athenian strategos (general) and statesman who rose to prominence in the later years of the Peloponnesian War. First appearing in Athenian politics in 410 BC, in the wake of the Athenian coup of 411 BC, he played a role in organizing democratic resistance in an Athenian fleet at Samos. There, he was elected strategos by the sailors and soldiers of the fleet, and held the position until he was controversially executed several years later after the Battle of Arginusae.
Mindarus was a Spartan admiral who commanded the Peloponnesian fleet in 411 and 410 BC, during the Peloponnesian War. Successful in shifting the theatre of war into the Hellespont, he then experienced a string of defeats; in the third and final of these, he was killed and the entire Peloponnesian fleet was captured or destroyed.
The Athenian coup of 411 BC was the result of a revolution that took place during the Peloponnesian War between Athens and Sparta. The coup overthrew the democratic government of ancient Athens and replaced it with a short-lived oligarchy known as the Four Hundred.

Classical Greece was a period of around 200 years in Greek culture. This Classical period saw the annexation of much of modern-day Greece by the Persian Empire and its subsequent independence. Classical Greece had a powerful influence on the Roman Empire and on the foundations of Western civilization. Much of modern Western politics, artistic thought, scientific thought, theatre, literature and philosophy derives from this period of Greek history. In the context of the art, architecture, and culture of Ancient Greece, the Classical period corresponds to most of the 5th and 4th centuries BC. The Classical period in this sense follows the Greek Dark Ages and Archaic period and is in turn succeeded by the Hellenistic period.
Astyochus or Astyochos was a Spartan navarch who served as commander of the collective Spartan naval forces along the coast of Asia Minor from 412–411 BC. He is regarded by many contemporaries and modern scholars as a key reason for Sparta's early failures in the Ionian War. His expeditions consisting of involvements in Lesbos, Chios, Erythrae and Clazomenae all proved unsuccessful. He also refused requests for help from Chios, causing the Spartan administration to become increasingly dissatisfied with his leadership. Thucydides portrays Astyochus as timid and inept, and also depicts him often in conflict with his peers in Ionia. Toward the end of his role of commander, he exhibited great reluctance to attack the Athenians and also failed to properly pay his troops, leading to riots and violence, and eventually, his removal as commander in 412 BC, to be replaced by the Spartan Mindarus.
Phrynichus was an Athenian general (strategos) during the Peloponnesian War who supported the Athenian coup of 411 BC which briefly replaced the Athenian democracy by an oligarchy.
Peisander was an Athenian who played a prominent part in the Athenian coup of 411 BC, which briefly replaced the Athenian democracy by an oligarchy controlled by a group called the Four Hundred.









