
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosome pairs which may have different structures. The DNA in autosomes is collectively known as atDNA or auDNA.

A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. Most eukaryotic chromosomes include packaging proteins called histones which, aided by chaperone proteins, bind to and condense the DNA molecule to maintain its integrity. These chromosomes display a complex three-dimensional structure, which plays a significant role in transcriptional regulation.

XYY syndrome is a genetic condition in which a male has an extra Y chromosome. There are usually few symptoms. These may include being taller than average, acne, and an increased risk of learning problems. The person is generally otherwise typical, including typical rates of fertility.
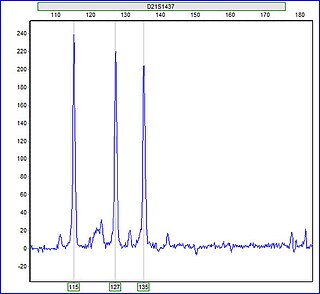
A trisomy is a type of polysomy in which there are three instances of a particular chromosome, instead of the normal two. A trisomy is a type of aneuploidy.

The XY sex-determination system is a sex-determination system used to classify many mammals, including humans, some insects (Drosophila), some snakes, some fish (guppies), and some plants. In this system, the sex of an individual is determined by a pair of sex chromosomes. Females typically have two of the same kind of sex chromosome (XX), and are called the homogametic sex. Males typically have two different kinds of sex chromosomes (XY), and are called the heterogametic sex.

The X chromosome is one of the two sex-determining chromosomes (allosomes) in many organisms, including mammals, and is found in both males and females. It is a part of the XY sex-determination system and X0 sex-determination system. The X chromosome was named for its unique properties by early researchers, which resulted in the naming of its counterpart Y chromosome, for the next letter in the alphabet, following its subsequent discovery.

Nondisjunction is the failure of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate properly during cell division. There are three forms of nondisjunction: failure of a pair of homologous chromosomes to separate in meiosis I, failure of sister chromatids to separate during meiosis II, and failure of sister chromatids to separate during mitosis. Nondisjunction results in daughter cells with abnormal chromosome numbers (aneuploidy).

Polysomy is a condition found in many species, including fungi, plants, insects, and mammals, in which an organism has at least one more chromosome than normal, i.e., there may be three or more copies of the chromosome rather than the expected two copies. Most eukaryotic species are diploid, meaning they have two sets of chromosomes, whereas prokaryotes are haploid, containing a single chromosome in each cell. Aneuploids possess chromosome numbers that are not exact multiples of the haploid number and polysomy is a type of aneuploidy. A karyotype is the set of chromosomes in an organism and the suffix -somy is used to name aneuploid karyotypes. This is not to be confused with the suffix -ploidy, referring to the number of complete sets of chromosomes.

XX male syndrome, also known as de la Chapelle syndrome, is a rare congenital intersex condition in which an individual with a 46, XX karyotype has phenotypically male characteristics that can vary among cases. Synonyms include 46,XX testicular difference of sex development, 46,XX sex reversal, nonsyndromic 46,XX testicular DSD, and XX sex reversal.

XXYY syndrome is a sex chromosome anomaly in which males have an extra X and Y chromosome. Human cells usually contain two sex chromosomes, one from the mother and one from the father. Usually, females have two X chromosomes (XX) and males have one X and one Y chromosome (XY). The appearance of at least one Y chromosome with a properly functioning SRY gene makes a male. Therefore, humans with XXYY are genotypically male. Males with XXYY syndrome have 48 chromosomes instead of the typical 46. This is why XXYY syndrome is sometimes written as 48,XXYY syndrome or 48,XXYY. It affects an estimated one in every 18,000–40,000 male births.
The short-stature homeobox gene (SHOX), also known as short-stature-homeobox-containing gene, is a gene located on both the X and Y chromosomes, which is associated with short stature in humans if mutated or present in only one copy (haploinsufficiency).
The gender taxonomy is a classification of the range of different levels at which humans vary in sexual characteristics. It is mainly used by medical specialists working in the area of sex research. John Money and Milton Diamond are probably the best known researchers in this field. Money earned his PhD for research into human hermaphroditism and pseudohermaphroditism, now known as intersex conditions. The taxonomy starts at the simplest, biological level and traces differentiations expressed at the increasingly complicated levels produced over the course of the human life cycle.

Disorders of sex development (DSDs), also known as differences in sex development, diverse sex development and variations in sex characteristics (VSC), are medical conditions involving the reproductive system. More specifically, these terms refer to "congenital conditions in which development of chromosomal, gonadal, or anatomical sex is atypical."

Cat eye syndrome or Schmid–Fraccaro syndrome, is a rare condition caused by the short arm (p) and a small section of the long arm (q) of human chromosome 22 being present three (trisomic) or four times (tetrasomic) instead of the usual two times. There is no significant reduction in life expectancy in patients who are not afflicted with one of CES' life-threatening abnormalities.

Klinefelter syndrome (KS), also known as 47,XXY is the set of symptoms that result from two or more X chromosomes in males. The primary features are infertility and small poorly functioning testicles. Often, symptoms are subtle and subjects do not realize they are affected. Sometimes, symptoms are more evident and may include weaker muscles, greater height, poor motor coordination, less body hair, breast growth, and less interest in sex. Often it is only at puberty that these symptoms are noticed. Intelligence is usually normal; however, reading difficulties and problems with speech are more common. Symptoms are typically more severe if three or more X chromosomes are present.
Sex chromosome anomalies belong to a group of genetic conditions that are caused or affected by the loss, damage or addition of one or both sex chromosomes.
The Focus Foundation, located in Davidsonville, Maryland, is a research foundation dedicated to identifying and assisting families and children who have X and Y Chromosomal Variations, dyslexia and/or developmental coordination disorder. These conditions can lead to language-based disabilities, motor planning deficits, reading dysfunction, and attention and behavioral disorders. The Focus Foundation believes that, through increased awareness, early identification, and specific and targeted treatment, children with these conditions can reach their full potential.
XXXY syndrome is a genetic condition characterized by a sex chromosome aneuploidy, where males have two extra X chromosomes.[1] Males typically have only two sex chromosomes, an X and a Y. The presence of one Y chromosome with a functioning SRY gene causes the expression of genes that determine maleness. Because of this, XXXY syndrome only affects males. The additional two X chromosomes in males with XXXY syndrome causes them to have 48 chromosomes, instead of the typical 46. XXXY syndrome is therefore often referred to as 48,XXXY. There is a wide variety of symptoms associated with this syndrome, including cognitive and behavioral problems, taurodontism, and infertility. This syndrome is usually inherited via a new mutation in one of the parents’ gametes, as those affected by it are usually infertile. It is estimated that XXXY affects one in every 50,000 male births.

XYYY syndrome, also known as 48,XYYY, is a chromosomal disorder in which a male has two extra copies of the Y chromosome. The syndrome is exceptionally rare, with only twelve recorded cases. The phenotype of the syndrome is heterogeneous, but appears to be more severe than its counterpart XYY syndrome. Common traits include borderline to mild intellectual disability, infertility, radioulnar synostosis, and in some cases tall stature.

Tetrasomy X, also known as 48,XXXX, is a chromosomal disorder in which a female has four, rather than two, copies of the X chromosome. It is associated with intellectual disability of varying severity, characteristic facial features, heart defects, and skeletal anomalies. Tetrasomy X is a rare condition, with around 100 cases recognized in the medical literature; prevalence estimates are between 1 in 85,000 and 1 in 100,000.














