Related Research Articles
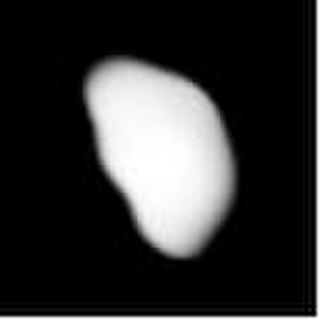
Victoria is a large main-belt asteroid, orbiting the Sun with a period of 3.56 years and an eccentricity of 0.221. It is a stony (S-type) asteroid, about 112–124 km across with an albedo of 0.18 and a rotation period of 8.66 hours. Victoria has been observed to occult a star three times since its discovery. Radar and speckle interferometry observations show that the shape of Victoria is elongated, and it is suspected to be a binary asteroid, with a moon of irregular shape.

Lachesis is a large main-belt asteroid. It was discovered by French astronomer Alphonse Borrelly on April 10, 1872, and independently by German-American astronomer Christian Heinrich Friedrich Peters on April 11, 1872, then named after Lachesis, one of the Moirai, or Fates, in Greek mythology. A Lachesean occultation of a star occurred in 1999 and was confirmed visually by five observers and once photoelectrically, with the chords yielding an estimated elliptical cross-section of 184 × 144 km.
Zähringia, provisional designation 1896 CZ, is a stony asteroid from the intermediate asteroid belt, approximately 14 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 7 September 1896, by astronomer Max Wolf at Heidelberg Observatory in Germany. The asteroid was named for the House of Zähringen, a medieval noble family that ruled parts of Swabia and Switzerland.

Taurinensis, provisional designation 1903 LV, is a stony asteroid and large Mars-crosser on an eccentric orbit from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 20 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 23 June 1903, by astronomer Max Wolf at the Heidelberg-Königstuhl State Observatory in southwest Germany. The asteroid was named after the Italian city of Turin. It is the 4th-largest Mars-crossing asteroid.
820 Adriana, provisional designation 1916 ZB, is an exceptionally dark asteroid from the outer region of the asteroid belt, about 59 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered by German astronomer Max Wolf at Heidelberg Observatory in southern Germany, on 30 March 1916.
858 El Djezaïr is a stony asteroid from the asteroid belt, about 24 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on May 26, 1916, by French astronomer Frédéric Sy at the Algiers Observatory in Algeria, North Africa, and given the provisional designation 1916 a.
2099 Öpik, provisional designation 1977 VB, is a dark and eccentric asteroid and Mars-crosser from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 5.1 kilometers in diameter.
Sirene, provisional designation 1923 PE, is an eccentric asteroid and sizable Mars-crosser from the central regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 5 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered by German astronomer Karl Reinmuth at the Heidelberg-Königstuhl State Observatory on 31 October 1923. The asteroid was named after the Siren from Greek mythology.
1134 Kepler, provisional designation 1929 SA, is a stony asteroid and eccentric Mars-crosser from the asteroid belt, approximately 4 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 25 September 1929, by German astronomer Max Wolf at Heidelberg Observatory in southwest Germany. It is named after Johannes Kepler.
2244 Tesla, provisional designation 1952 UW1, is a carbonaceous asteroid from the central region of the asteroid belt, approximately 25 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 22 October 1952, by Serbian astronomer Milorad Protić at the Belgrade Observatory, then Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia, now Serbia. It is named after the inventor Nikola Tesla.

1905 Ambartsumian, provisional designation 1972 JZ, is an asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 8 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 14 May 1972, by Russian astronomer Tamara Smirnova at the Crimean Astrophysical Observatory, Nauchnyj, on the Crimean peninsula. The asteroid was named after theoretical astrophysicist Victor Ambartsumian.
1818 Brahms, provisional designation 1939 PE, is an asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 6 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 15 August 1939, by German astronomer Karl Reinmuth at Heidelberg Observatory in southern Germany. The asteroid was named after composer Johannes Brahms.
3034 Climenhaga is a stony Florian asteroid and synchronous binary asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 7.8 kilometers in diameter. The asteroid was discovered on 24 September 1917 by German astronomer Max Wolf at Heidelberg Observatory in southwest Germany and assigned provisional designation A917 SE. It was later named after Canadian astrophysicist John Climenhaga. Its minor-planet moon has a period of nearly 19 hours.
6141 Durda, provisional designation 1992 YC3 is a stony Hungaria asteroid, classified as slow rotator and Mars-crosser from the innermost region of the asteroid belt, approximately 3.2 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 26 December 1992, by Spacewatch at Kitt Peak National Observatory in Arizona, United States.
9069 Hovland, provisional designation 1993 OV, is a stony binary Hungaria asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 3 kilometers in diameter.
3040 Kozai, provisional designation 1979 BA, is a stony asteroid and Mars-crosser on a tilted orbit from the innermost regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 4 kilometers in diameters.
1921 Pala, provisional designation 1973 SE is a background asteroid in an unstable orbit located in the outer region of asteroid belt, approximately 8.2 kilometers in diameter. It is one of very few bodies located in the 2 : 1 mean motion resonance with Jupiter. It was discovered by Dutch–American astronomer Tom Gehrels at Palomar Observatory on 20 September 1973.
1857 Parchomenko, provisional designation 1971 QS1, is a stony asteroid and suspected binary from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 8 kilometers in diameter.
2044 Wirt, provisional designation 1950 VE, is a binary Phocaea asteroid and Mars-crosser, approximately 6.7 kilometers in diameter. The minor-planet moon has an estimated diameter of 1.89 kilometer.
2661 Bydžovský, provisional designation 1982 FC1, is an asteroid from the outer region of the asteroid belt, approximately 30 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 23 March 1982, by Czech astronomer Zdeňka Vávrová at the South Bohemian Kleť Observatory in the Czech Republic. The asteroid was named after mathematician Bohumil Bydžovský.
References
- ↑ "Selene". Lexico UK English Dictionary. Oxford University Press. Archived from the original on 22 March 2020.
- ↑ "580 Selene (1905 SE)". JPL Small-Body Database . NASA/Jet Propulsion Laboratory . Retrieved 5 May 2016.
- ↑ Schmadel, Lutz D. (2003). "(580) Selene". Dictionary of Minor Planet Names – (580) Selene. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. p. 160. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-29925-7_581. ISBN 978-3-540-29925-7.
- ↑ Antonini, Pierre (16 May 2005). "Courbes de rotation d'astéroïdes et de comètes" (in French). Observatoire de Genève. Archived from the original on 8 July 2006. Retrieved 12 June 2006.
- ↑ "Occultation by (580) Selene". RASNZ Occultation Section. 18 January 2005. Archived from the original on 21 December 2005. Retrieved 12 June 2006.