Related Research Articles

Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer in adults and is currently the most common cause of death in people with cirrhosis. HCC is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide.

Alpha-fetoprotein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AFP gene. The AFP gene is located on the q arm of chromosome 4 (4q13.3). Maternal AFP serum level is used to screen for Down syndrome, neural tube defects, and other chromosomal abnormalities.
Liver tumors are abnormal growth of liver cells on or in the liver. Several distinct types of tumors can develop in the liver because the liver is made up of various cell types. Liver tumors can be classified as benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous) growths. They may be discovered on medical imaging, and the diagnosis is often confirmed with liver biopsy. Signs and symptoms of liver masses vary from being asymptomatic to patients presenting with an abdominal mass, hepatomegaly, abdominal pain, jaundice, or some other liver dysfunction. Treatment varies and is highly specific to the type of liver tumor.
Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) is a minimally invasive procedure performed in interventional radiology to restrict a tumor's blood supply. Small embolic particles coated with chemotherapeutic drugs are injected selectively through a catheter into an artery directly supplying the tumor. These particles both block the blood supply and induce cytotoxicity, attacking the tumor in several ways.

Hepatoblastoma is a malignant liver cancer occurring in infants and children and composed of tissue resembling fetal liver cells, mature liver cells, or bile duct cells. They usually present with an abdominal mass. The disease is most commonly diagnosed during a child's first three years of life. Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) levels are commonly elevated, but when AFP is not elevated at diagnosis the prognosis is poor.

Sorafenib, sold under the brand name Nexavar, is a kinase inhibitor drug approved for the treatment of primary kidney cancer, advanced primary liver cancer, FLT3-ITD positive AML and radioactive iodine resistant advanced thyroid carcinoma.
Des-gamma carboxyprothrombin (DCP), also known as protein induced by vitamin K absence/antagonist-II (PIVKA-II), is an abnormal form of the coagulation protein, prothrombin. Normally, the prothrombin precursor undergoes post-translational carboxylation by gamma-glutamyl carboxylase in the liver prior to secretion into plasma. DCP/PIVKA-II may be detected in people with deficiency of vitamin K and in those taking warfarin or other medication that inhibits the action of vitamin K.

Fetal proteins are high levels of proteins present during the fetal stage of development. Often related proteins assume similar roles after birth or in the embryo, in which case the fetal varieties are called fetal isoforms. Sometimes, the genes coding fetal isoforms occur adjacent to their adult homologues in the genome, and in those cases a locus control region often coordinates the transition from fetal to adult forms. In other cases fetal isoforms can be produced by alternate splicing using fetal exons to produce proteins that differ in only a portion of their amino acid sequence. In some situations the continuing expression of fetal forms can reveal the presence of a disease condition or serve as a treatment for diseases such as sickle cell anemia. Some well known examples include:

Liver cancer, also known as hepatic cancer, primary hepatic cancer, or primary hepatic malignancy, is cancer that starts in the liver. Liver cancer can be primary in which the cancer starts in the liver, or it can be liver metastasis, or secondary, in which the cancer spreads from elsewhere in the body to the liver. Liver metastasis is the more common of the two liver cancers. Instances of liver cancer are increasing globally.

Glypican-3 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the GPC3 gene. The GPC3 gene is located on human X chromosome (Xq26) where the most common gene encodes a 70-kDa core protein with 580 amino acids. Three variants have been detected that encode alternatively spliced forms termed Isoforms 1 (NP_001158089), Isoform 3 (NP_001158090) and Isoform 4 (NP_001158091).

Chemokine-like factor (CKLF) is a member of the CKLF-like MARVEL transmembrane domain-containing family of proteins that in humans is encoded by the CKLF gene. This gene is located on band 22.1 in the long arm of chromosome 16.
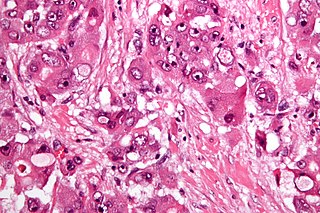
Fibrolamellar carcinoma (FLC) is a rare form of carcinoma that typically affects young adults and is characterized, under the microscope, by laminated fibrous layers interspersed between the tumor cells. It has been estimated that 200 new cases are diagnosed worldwide each year. However, in light of recent advances in our molecular understanding, this has recently been revised to suggest it may be at least ten times more common. FLC, also known as fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma, is different from the more common hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in that it afflicts young people with normal liver function and no known risk factors.

Selective internal radiation therapy (SIRT), also known as transarterial radioembolization (TARE), radioembolization or intra-arterial microbrachytherapy is a form of radionuclide therapy used in interventional radiology to treat cancer. It is generally for selected patients with surgically unresectable cancers, especially hepatocellular carcinoma or metastasis to the liver. The treatment involves injecting tiny microspheres of radioactive material into the arteries that supply the tumor, where the spheres lodge in the small vessels of the tumor. Because this treatment combines radiotherapy with embolization, it is also called radioembolization. The chemotherapeutic analogue is called chemoembolization, of which transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) is the usual form.
Ramucirumab, sold under the brand name Cyramza, is a fully human monoclonal antibody (IgG1) used for the treatment of cancer. Ramucirumab is a human vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) antagonist. Ramucirumab was developed by ImClone Systems. It was isolated from a native phage display library from Dyax.
Lenvatinib, sold under the brand name Lenvima among others, is an anti-cancer medication for the treatment of certain kinds of thyroid cancer and for other cancers as well. It was developed by Eisai Co. and acts as a multiple kinase inhibitor against the VEGFR1, VEGFR2 and VEGFR3 kinases.
Elevated alpha-fetoprotein refers to a state where alpha-fetoprotein levels are outside of the reference range.
Patrizia Paterlini-Bréchot, born in the Italian city of Reggio Emilia, is an Italian scientist and a professor of cell biology and oncology working at the Faculté de Médecine Necker-Enfants Malades, Université Paris Descartes and at INSERM in Paris.

Brivanib alaninate (INN/USAN) also known as BMS-582664 is an investigational, anti-tumorigenic drug for oral administration. The drug is being developed by Bristol-Myers Squibb for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma or HCC, the most common type of liver cancer. Brivanib is no longer in active development.
Resminostat is an orally bioavailable inhibitor of histone deacetylases (HDACs), of which inhibitors are antineoplastic agents.
Ultrasonography of liver tumors involves two stages: detection and characterization.
References
- ↑ Kamoto T, Satomura S, Yoshiki T, Okada Y, Henmi F, Nishiyama H, Kobayashi T, Terai A, Habuchi T, Ogawa O (2002). "Lectin-reactive alpha-fetoprotein (AFP-L3%) curability and prediction of clinical course after treatment of non-seminomatous germ cell tumors". Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 32 (11): 472–6. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyf094 . PMID 12499420.
- AFP-L3: a new generation of tumor marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Li D, et al., Clin Chim Acta. 2001 Nov;313(1-2):15-9.
- Clinical evaluation of lentil lectin-reactive alpha-fetoprotein-L3 in histology-proven hepatocellular carcinoma. Khien VV, et al., Int J Biol Markers. 2001 Apr-Jun;16(2):105-11.
- Usefulness of measurement of Lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive fraction of alpha-fetoprotein as a marker of prognosis and recurrence of small hepatocellular carcinoma. Hayashi K, et al., Am J Gastroenterol. 1999 Oct;94(10):3028-33.
- A collaborative study for the evaluation of lectin-reactive alpha-fetoproteins in early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Takata, K., et al., Cancer Res., 53, 5419–5423, 1993.
- Utility of lentil lectin affinity of alpha-fetoprotein in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Wang, S., et al., J. Hepatology, 25, 166–171, 1996.
- Early recognition of hepatocellular carcinoma based on altered profiles of alpha-fetoprotein. Sato, Y., et al., N. Engl. J. Med., 328, 1802–1806, 1993.
- A clinical study of lectin-reactive alpha-fetoprotein as an early indicator of hepatocellular carcinoma in the follow-up of cirrhotic patients. Shiraki, K., Hepatology, 22, 802–807, 1985.
- A clinical study of lectin-reactive alpha-fetoprotein as an early indicator of hepatocellular carcinoma in the follow-up of cirrhotic patients. Shiraki, K., Hepatology, 22, 802–807, 1985.
- Prognostic significance of lens culinaris agglutinin A-reactive alpha-fetoprotein in small hepatocellular carcinoma. Yamashita, F., et al., Gastroenterology, 111, 996–1001, 1996.
- The fucosylation index of alpha-fetoprotein as a possible prognostic indicator for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Aoyagi, Y., et al., Am. Cancer Soc., 83, 2076–2082, 1998.
- Monitoring of lectin-reactive alpha-fetoproteins in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated using transactheter arterial embolization. Yamashita, F., Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol., 7, 627–633, 1995.
- Evaluation of curability and prediction of prognosis after surgical for hepatocellular carcinoma by lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive alpha-fetoprotein. Okuda, K., et al., Inter. J. Oncol., 14, 265–271, 1999.
- Usefulness of lens culinaris agglutinin A-reactive fraction of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP-L3) as a marker of distant metastasis from hepatocellular carcinoma. Yamashiki, N., et al., Oncology Reports, 6, 1229–1232, 1999.
- Relationship between lens culinaris agglutinin reactive alpha-fetoprotein and biological features of hepatocellular carcinoma. Kusaba, T., Kurume Med. J., 45, 113–120, 1998.
- Tumor vascularity and lens culinaris agglutinin reactive alpha-fetoprotein are predictors of long-term prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after percutaneous ethanol injection therapy. Fukuda, H., Kurume Med. J., 45, 187–193, 1998.
- Clinical utility of lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive alpha-fetoprotein in small hepatocellular carcinoma: Special reference to imaging diagnosis. Kumada, T., et al., J. Hepatol., 30, 125–130, 1999.
- Deletion of serum lectin-reactive alpha-fetoprotein by Acyclic Retinoid: A potent biomarker in the chemoprevention of second primary hepatoma. Moriwaki, H., Clin. Cancer Res., 3, 727-731, 1997.
- Clinical utility of simultaneous measurement of serum high-sensitivity des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin and lens culinaris agglutinin A-reactive alpha-fetoprotein in patients with small hepatocellular carcinoma. Sassa, T., et al., Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 11, 1387–1392, 1999.
- A simultaneous monitoring of lens culinaris agglutinin A-reactive alpha-fetoprotein and des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin as an early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in the follow-up of cirrhotic patients. Shimauchi, Y., et al., Oncology Reports, 7, 249–256, 2000.
This article needs additional or more specific categories .(November 2024) |