
Adenocarcinoma is a type of cancerous tumor that can occur in several parts of the body. It is defined as neoplasia of epithelial tissue that has glandular origin, glandular characteristics, or both. Adenocarcinomas are part of the larger grouping of carcinomas, but are also sometimes called by more precise terms omitting the word, where these exist. Thus invasive ductal carcinoma, the most common form of breast cancer, is adenocarcinoma but does not use the term in its name—however, esophageal adenocarcinoma does to distinguish it from the other common type of esophageal cancer, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Several of the most common forms of cancer are adenocarcinomas, and the various sorts of adenocarcinoma vary greatly in all their aspects, so that few useful generalizations can be made about them.

Pancreatic cancer arises when cells in the pancreas, a glandular organ behind the stomach, begin to multiply out of control and form a mass. These cancerous cells have the ability to invade other parts of the body. A number of types of pancreatic cancer are known.
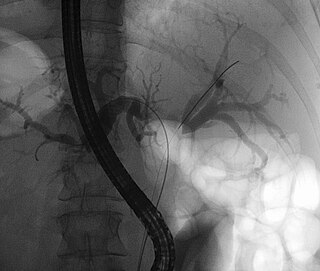
A Klatskin tumor is a cholangiocarcinoma occurring at the confluence of the right and left hepatic bile ducts. The disease was named after Gerald Klatskin, who in 1965 described 15 cases and found some characteristics for this type of cholangiocarcinoma

Cholangiocarcinoma, also known as bile duct cancer, is a type of cancer that forms in the bile ducts. Symptoms of cholangiocarcinoma may include abdominal pain, yellowish skin, weight loss, generalized itching, and fever. Light colored stool or dark urine may also occur. Other biliary tract cancers include gallbladder cancer and cancer of the ampulla of Vater.
This is a list of terms related to oncology. The original source for this list was the US National Cancer Institute's public domain Dictionary of Cancer Terms.
A tumor marker is a biomarker that can be used to indicate the presence of cancer or the behavior of cancers. They can be found in bodily fluids or tissue. Markers can help with assessing prognosis, surveilling patients after surgical removal of tumors, and even predicting drug-response and monitor therapy.

Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) describes a set of highly-related glycoproteins involved in cell adhesion. CEA is normally produced in gastrointestinal tissue during fetal development, but the production stops before birth. Consequently, CEA is usually present at very low levels in the blood of healthy adults. However, the serum levels are raised in some types of cancer, which means that it can be used as a tumor marker in clinical tests. Serum levels can also be elevated in heavy smokers.
Gastrointestinal cancer refers to malignant conditions of the gastrointestinal tract and accessory organs of digestion, including the esophagus, stomach, biliary system, pancreas, small intestine, large intestine, rectum and anus. The symptoms relate to the organ affected and can include obstruction, abnormal bleeding or other associated problems. The diagnosis often requires endoscopy, followed by biopsy of suspicious tissue. The treatment depends on the location of the tumor, as well as the type of cancer cell and whether it has invaded other tissues or spread elsewhere. These factors also determine the prognosis.

The selectins are a family of cell adhesion molecules. All selectins are single-chain transmembrane glycoproteins that share similar properties to C-type lectins due to a related amino terminus and calcium-dependent binding. Selectins bind to sugar moieties and so are considered to be a type of lectin, cell adhesion proteins that bind sugar polymers.
Tumor M2-PK is a synonym for the dimeric form of the pyruvate kinase isoenzyme type M2 (PKM2), a key enzyme within tumor metabolism. Tumor M2-PK can be elevated in many tumor types, rather than being an organ-specific tumor marker such as PSA. Increased stool (fecal) levels are being investigated as a method of screening for colorectal tumors, and EDTA plasma levels are undergoing testing for possible application in the follow-up of various cancers.
Autoimmune Pancreatitis (AIP) is an increasingly recognized type of chronic pancreatitis that can be difficult to distinguish from pancreatic carcinoma but which responds to treatment with corticosteroids, particularly prednisone. Although autoimmune pancreatitis is quite rare, it constitutes an important clinical problem for both patients and their clinicians: the disease commonly presents itself as a tumorous mass which is diagnostically indistinguishable from pancreatic cancer, a disease that is much more common in addition to being very dangerous. Hence, some patients undergo pancreatic surgery, which is associated to substantial mortality and morbidity, out of the fear by patients and clinicians to undertreat a malignancy. However, surgery is not a good treatment for this condition as AIP responds well to immunosuppressive treatment. There are two categories of AIP: Type 1 and Type 2, each with distinct clinical profiles.
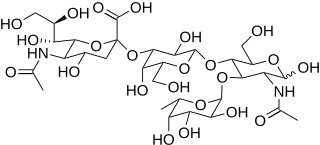
Sialyl LewisX (sLeX), also known as cluster of differentiation 15s (CD15s) or stage-specific embryonic antigen 1 (SSEA-1), is a tetrasaccharide carbohydrate which is usually attached to O-glycans on the surface of cells. It is known to play a vital role in cell-to-cell recognition processes. It is also the means by which an egg attracts sperm; first, to stick to it, then bond with it and eventually form a zygote.

Liver cancer, also known as hepatic cancer, primary hepatic cancer, or primary hepatic malignancy, is cancer that starts in the liver. Liver cancer can be primary in which the cancer starts in the liver, or it can be liver metastasis, or secondary, in which the cancer spreads from elsewhere in the body to the liver. Liver metastasis is the more common of the two liver cancers. Instances of liver cancer are increasing globally.

Mucin-4 (MUC-4) is a mucin protein that in humans is encoded by the MUC4 gene. Like other mucins, MUC-4 is a high-molecular weight glycoprotein.
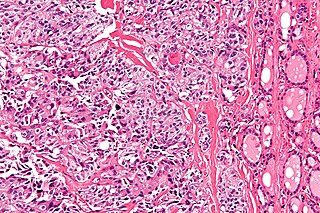
Medullary thyroid cancer is a form of thyroid carcinoma which originates from the parafollicular cells, which produce the hormone calcitonin. Medullary tumors are the third most common of all thyroid cancers and together make up about 3% of all thyroid cancer cases. MTC was first characterized in 1959.
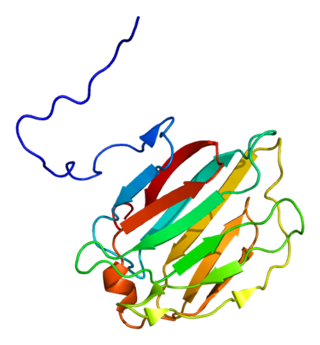
Galectin-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LGALS4 gene.
CA 242 is a tumor marker for sialylated Lewis carbohydrates associated with adenocarcinomas and e-selectin-mediated metastatic risk. It is commonly tested along with CEA, CA19-9, and CA242 for detecting pancreatic cancer. The specificity of CA 242 is higher than similar markers. Current research dictates that diagnostic efficiency is highest when various tumor markers are tested for at once.

Elevated alkaline phosphatase occurs when levels of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) exceed the reference range. This group of enzymes has a low substrate specificity and catalyzes the hydrolysis of phosphate esters in a basic environment. The major function of alkaline phosphatase is transporting chemicals across cell membranes. Alkaline phosphatases are present in many human tissues, including bone, intestine, kidney, liver, placenta and white blood cells. Damage to these tissues causes the release of ALP into the bloodstream. Elevated levels can be detected through a blood test. Elevated alkaline phosphate is associated with certain medical conditions or syndromes. It serves as a significant indicator for certain medical conditions, diseases and syndromes.
Elevated alpha-fetoprotein refers to a state where alpha-fetoprotein levels are outside of the reference range.

A cancer biomarker refers to a substance or process that is indicative of the presence of cancer in the body. A biomarker may be a molecule secreted by a tumor or a specific response of the body to the presence of cancer. Genetic, epigenetic, proteomic, glycomic, and imaging biomarkers can be used for cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and epidemiology. Ideally, such biomarkers can be assayed in non-invasively collected biofluids like blood or serum.













