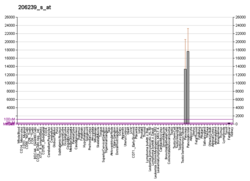
| SPINK1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | SPINK1 , PCTT, PSTI, Spink3, TATI, TCP, serine peptidase inhibitor, Kazal type 1, serine peptidase inhibitor Kazal type 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 167790; MGI: 106202; HomoloGene: 68300; GeneCards: SPINK1; OMA:SPINK1 - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pancreatic secretory trypsin inhibitor (PSTI) also known as serine protease inhibitor Kazal-type 1 (SPINK1) or tumor-associated trypsin inhibitor (TATI) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SPINK1 gene. [5]
Contents
Mutations in SPINK1 has been associated with hereditary pancreatitis and tropical pancreatitis. Trypsinogen is normally created and stored an inactive zymogen of trypsin in the pancreas, but occasionally will autoactivate itself. PSTI serves to cleave prematurely activated trypsin to prevent the enzyme from causing cellular damage to the organ. Without the function of PSTI, the pancreas is subject to repeated episodes of damage. [6]
It has also been associated with prostate cancer. [7]