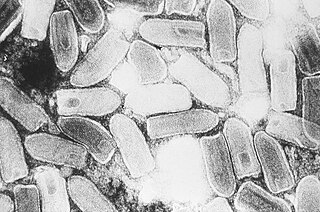
Indiana vesiculovirus, formerly Vesicular stomatitis Indiana virus is a virus in the family Rhabdoviridae; the well-known Rabies lyssavirus belongs to the same family. VSIV can infect insects, cattle, horses and pigs. It has particular importance to farmers in certain regions of the world where it infects cattle. This is because its clinical presentation is identical to the very important foot and mouth disease virus.

In humans, clusterin (CLU) is encoded by the CLU gene on chromosome 8. CLU is an extracellular molecular chaperone which binds to misfolded proteins in body fluids to neutralise their toxicity and mediate their cellular uptake by receptor-mediated endocytosis. Once internalised by cells, complexes between CLU and misfolded proteins are trafficked to lysosomes where they are degraded. CLU is involved in many diseases including neurodegenerative diseases, cancers, inflammatory diseases, and aging.

Hemojuvelin (HJV), also known as repulsive guidance molecule C (RGMc) or hemochromatosis type 2 protein (HFE2), is a membrane-bound and soluble protein in mammals that is responsible for the iron overload condition known as juvenile hemochromatosis in humans, a severe form of hemochromatosis. In humans, the hemojuvelin protein is encoded by the HFE2 gene. Hemojuvelin is a member of the repulsive guidance molecule family of proteins. Both RGMa and RGMb are found in the nervous system, while hemojuvelin is found in skeletal muscle and the liver.

Inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase OCRL-1, also known as Lowe oculocerebrorenal syndrome protein, is an enzyme encoded by the OCRL gene located on the X chromosome in humans.

FYVE, RhoGEF and PH domain-containing protein 1 (FGD1) also known as faciogenital dysplasia 1 protein (FGDY), zinc finger FYVE domain-containing protein 3 (ZFYVE3), or Rho/Rac guanine nucleotide exchange factor FGD1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FGD1 gene that lies on the X chromosome. Orthologs of the FGD1 gene are found in dog, cow, mouse, rat, and zebrafish, and also budding yeast and C. elegans. It is a member of the FYVE, RhoGEF and PH domain containing family.

Lysosome-associated membrane protein 2 (LAMP2), also known as CD107b and Mac-3, is a human gene. Its protein, LAMP2, is one of the lysosome-associated membrane glycoproteins.

Disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 15 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADAM15 gene.

Lysosomal-associated membrane protein 1 (LAMP-1) also known as lysosome-associated membrane glycoprotein 1 and CD107a, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LAMP1 gene. The human LAMP1 gene is located on the long arm (q) of chromosome 13 at region 3, band 4 (13q34).
Podoplanin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PDPN gene.

Thioredoxin-dependent peroxide reductase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRDX3 gene. It is a member of the peroxiredoxin family of antioxidant enzymes.
Lysosomal integral membrane protein 2 (LIMP-2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SCARB2 gene. LIMP-2 is expressed in brain, heart, liver, lung and kidney, mainly in the membrane of lysosome organelles; however, in cardiac muscle, LIMP-2 is also expressed at intercalated discs. LIMP-2 in a membrane protein in lysosomes that functions to regulate lysosomal/endosomal transport. Mutations in LIMP-2 have been shown to cause Gaucher disease, myoclonic epilepsy, and action myoclonus–renal failure syndrome. Abnormal levels of LIMP-2 have also been found in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.

Transmembrane protease, serine 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TMPRSS2 gene. It belongs to the TMPRSS family of proteins, whose members are transmembrane proteins which have a serine protease activity. The TMPRSS2 protein is found in high concentration in the cell membranes of epithelial cells of the lung and of the prostate, but also in the heart, liver and gastrointestinal tract.

WAP four-disulfide core domain protein 2 - also known as Human Epididymis Protein 4 (HE4) - is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WFDC2 gene.

Dolichyl-diphosphooligosaccharide—protein glycosyltransferase subunit 2, also called ribophorin ǁ is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RPN2 gene.

Cadherin-17 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CDH17 gene.

Olfactory receptor 51E2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the OR51E2 gene.

Olfactory receptor 51E1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the OR51E1 gene.

Leucine-rich alpha-2-glycoprotein 1 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the gene LRG1.

Uroplakin-3a(UP3a) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UPK3A gene.

CD96 or Tactile is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD96 gene. CD96 is a receptor protein which is expressed on T cells and NK cells and shares sequence similarity with CD226. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily. It is a type I membrane protein. The protein may play a role in the adhesion of activated T and NK cells to their target cells during the late phase of the immune response. It may also function in antigen presentation. Alternative splicing occurs at this locus and two transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been identified. CD96 is a transmembrane glycoprotein that has three extracellular immunoglobulin-like domains and is expressed by all resting human and mouse NK cells. CD96 main ligand is CD155. CD 96 has approximately 20% homology with CD226 and competed for binding to CD155 with CD226.