
Acacia aneura, commonly known as mulga or true mulga, is a shrub or small tree native to arid outback areas of Australia. It is the dominant tree in the habitat that it gives its name to (mulga) that occurs across much of inland Australia. Specific regions have been designated the Western Australian mulga shrublands in Western Australia and Mulga Lands in Queensland.

Acacia pycnantha, most commonly known as the golden wattle, is a tree of the family Fabaceae native to southeastern Australia. It grows to a height of 8 m (26 ft) and has phyllodes instead of true leaves. Sickle-shaped, these are between 9 and 15 cm long, and 1–3.5 cm wide. The profuse fragrant, golden flowers appear in late winter and spring, followed by long seed pods. Plants are cross-pollinated by several species of honeyeater and thornbill, which visit nectaries on the phyllodes and brush against flowers, transferring pollen between them. An understorey plant in eucalyptus forest, it is found from southern New South Wales and the Australian Capital Territory, through Victoria and into southeastern South Australia.

Eucalyptus caesia, commonly known as caesia or gungurru, is a species of mallee that is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It has smooth reddish brown bark at first, later shedding in curling flakes, lance-shaped, sometimes curved adult leaves, club-shaped flower buds covered with a waxy, bluish white bloom, pink stamens with yellow anthers and urn-shaped fruit.

Acacia saligna, commonly known by various names including coojong, golden wreath wattle, orange wattle, blue-leafed wattle, Western Australian golden wattle, and, in Africa, Port Jackson willow, is a small tree in the family Fabaceae. Native to Australia, it is widely distributed throughout the south west corner of Western Australia, extending north as far as the Murchison River, and east to Israelite Bay. The Noongar peoples know the tree as Cujong.

Acacia brachystachya, commonly known as umbrella mulga, turpentine mulga or false bowgada, is a shrub in the family Fabaceae. The species occurs in mulga and heath communities on sandhills and rocky ridges in all mainland states of Australia, except Victoria.

Acacia maidenii, also known as Maiden's wattle, is a tree native to Australia. It has been introduced into India, and Argentina, and it grows on plantations in South Africa.

Acacia dealbata, the silver wattle, blue wattle or mimosa, is a species of flowering plant in the legume family Fabaceae, native to southeastern Australia in New South Wales, Victoria, Tasmania, and the Australian Capital Territory and widely introduced in Mediterranean, warm temperate, and highland tropical landscapes.

Callicoma is a plant genus that contains just one species, Callicoma serratifolia, a tall shrub or small tree which is native to Australia. Callicoma serratifolia is commonly known as black wattle. One explanation for the name is the similarity of the flowers to those of Australian Acacia, which are commonly known as wattles. Another is its use in wattle and daub huts of the early settlers. The species has a number of other common names include callicoma, butterwood, silver leaf, silver-leaf butterwood and wild quince.
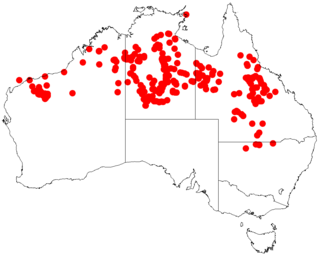
Acacia cowleana, Halls Creek wattle, is a northern Australian native shrub. It is a flowering plant with yellow flowers that only open in winter. Its origin is the Northern Australia's dry tropics. It belongs to the genus of Acacia.

Acacia caesaneura, commonly known as western blue mulga, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to western Australia.

Acacia difficilis is a tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae. It is native to an area in the Kimberley region of Western Australia, to the top end of the Northern Territory, and north-west Queensland.

Acacia stereophylla is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to south western Australia.

Acacia symonii, also known commonly as Symon's wattle, is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to parts of arid central Australia.

Acacia galioides is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Lycopodiifoliae. It is native to an area in the Northern Territory and the Kimberley region of Western Australia, and to northwestern Queensland and the eastern highlands of Queensland.

Acacia pataczekii is a rare leguminous species of flowering plant endemic to Tasmania, Australia. An attractive evergreen shrub to small tree grown ornamentally outside of its native range, it is believed to be the most frost hardy of all the Acacia.

Acacia assimilis is a shrub or tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves. It is native to an area in the Wheatbelt, Great Southern and Goldfields-Esperance regions of Western Australia.
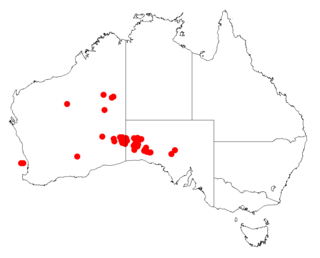
Acacia gilesiana is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves. It is native to an area in the Goldfields-Esperance region of Western Australia, and in South Australia in the Nullarbor region near Maralinga and the North-western region. The specific epithet, gilesiana, honours William Ernest Powell Giles.

Acacia nyssophylla is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves. It is native to an area in the Wheatbelt and Goldfields-Esperance regions of Western Australia, through South Australia to extreme north-western Victoria, and north from South Australia to near Alice Springs in the Northern Territory, to Western New South Wales near Bourke.

Acacia sericophylla is a shrub or tree commonly known as the desert dogwood, desert oak or cork-bark wattle. To the Indigenous Australian people of the area, the Nyangumarta peoples, it is known as Pirrkala. The species is of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves. It is native to an area in the Northern Territory and the Kimberley and Pilbara regions of Western Australia. It is also found in New South Wales and South Australia.

Acacia latzii, also known as Latz's wattle and Tjilpi wattle) is a shrubby tree of the genus Acacia. It is native to the Finke bioregion.




















