
Acacia murrayana is a tree in the family Fabaceae. It has numerous common names, including sandplain wattle, Murray's wattle, fire wattle, colony wattle and powder bark wattle that is endemic to arid areas in every mainland State except Victoria.

Acacia harpophylla, commonly known as brigalow, brigalow spearwood or orkor, is an endemic tree of Australia. The Aboriginal Australian group the Gamilaraay peoples know the tree as Barranbaa or Burrii. It is found in central and coastal Queensland to northern New South Wales. It can reach up to 25 m (82 ft) tall and forms extensive open-forest communities on clay soils.

Acacia pravissima, commonly known as Ovens wattle, Oven wattle, wedge-leaved wattle and Tumut wattle, is a species of flowering plant in the legume family Fabaceae. It is an evergreen shrub native to Victoria, the South West Slopes and Southern Tablelands of New South Wales, Australia.

Acacia bakeri, known as the marblewood, white marblewood, Baker's wattle or scrub wattle, is one of the largest of all acacias, growing to 40 m (130 ft) tall. It is a long-lived climax rainforest tree from eastern Australia. Unlike most acacias, fire is not required for seed germination. This tree is considered vulnerable to extinction. Its former habitat is lowland sub tropical rainforest which has been mostly cleared in the 19th and 20th centuries.

Acacia notabilis, known colloquially as mallee golden wattle, Flinders wattle or stiff golden wattle, is a species of Acacia native to Australia.

Acacia leptocarpa, commonly known as north coast wattle, is a shrub or small tree native to New Guinea and coastal regions of northern Australia.
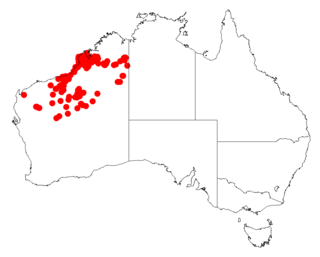
Acacia eriopoda, commonly known as the Broome pindan wattle and the narrow-leaf pindan wattle, is a species of wattle in the legume family that is native to northern Western Australia. It is also known as Yirrakulu to the Nyangumarta people.

Acacia oncinocarpa is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to northern Australia.

Acacia stipuligera is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae. It is native to arid and tropical parts of northern Australia.

Acacia tenuissima, commonly known as narrow-leaved wattle, broom wattle, minyana, slender mulga or slender wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae endemic to temperate and tropical areas of Australia. Indigenous Australians the Kurrama peoples know the plant as Janangungu and the Banyjima know it as Murruthurru.

Acacia trineura, known colloquially as three-nerve wattle or three nerved wattle or green wattle, is a species of Acacia native to south eastern Australia.

Acacia subtilinervis, also known as the net-veined wattle, is a rare wattle in the Juliflorae subgenus found in eastern Australia.

Acacia dietrichiana, commonly known as Dietrich wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to Queensland.

Acacia linearifolia, commonly known as stringybark wattle or narrow-leaved wattle, is a shrub or tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to eastern Australia.
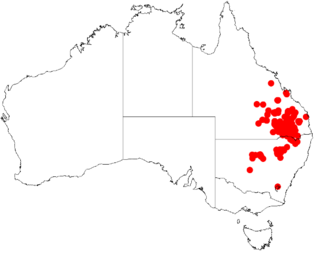
Acacia burrowii, commonly known as Burrow's wattle, is a tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to eastern Australia.

Acacia caroleae, also known as Carol's wattle or narrow leaf currawong, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.
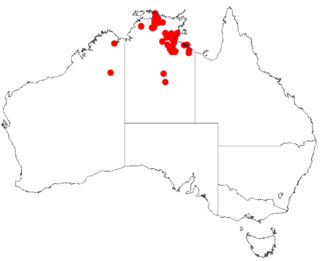
Acacia conspersa is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to northern Australia.

Acacia tenuinervis is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia torulosa is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia subporosa, also commonly known as river wattle, bower wattle, narrow-leaf bower wattle and sticky bower wattle, is a tree or shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area of south eastern Australia. It is considered to be rare in Victoria



















