
Diatomic molecules are molecules composed of only two atoms, of the same or different chemical elements. If a diatomic molecule consists of two atoms of the same element, such as hydrogen or oxygen, then it is said to be homonuclear. Otherwise, if a diatomic molecule consists of two different atoms, such as carbon monoxide or nitric oxide, the molecule is said to be heteronuclear. The bond in a homonuclear diatomic molecule is non-polar.

A diatom is any member of a large group comprising several genera of algae, specifically microalgae, found in the oceans, waterways and soils of the world. Living diatoms make up a significant portion of the Earth's biomass: they generate about 20 to 50 percent of the oxygen produced on the planet each year, take in over 6.7 billion tonnes of silicon each year from the waters in which they live, and constitute nearly half of the organic material found in the oceans. The shells of dead diatoms can reach as much as a half-mile deep on the ocean floor, and the entire Amazon basin is fertilized annually by 27 million tons of diatom shell dust transported by transatlantic winds from the African Sahara, much of it from the Bodélé Depression, which was once made up of a system of fresh-water lakes.
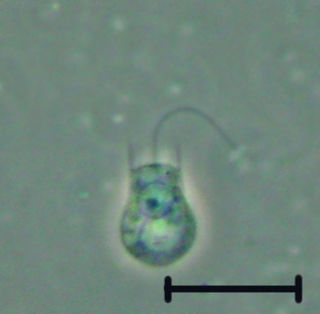
The choanoflagellates are a group of free-living unicellular and colonial flagellate eukaryotes considered to be the closest living relatives of the animals. Choanoflagellates are collared flagellates, having a funnel shaped collar of interconnected microvilli at the base of a flagellum. Choanoflagellates are capable of both asexual and sexual reproduction. They have a distinctive cell morphology characterized by an ovoid or spherical cell body 3–10 μm in diameter with a single apical flagellum surrounded by a collar of 30–40 microvilli. Movement of the flagellum creates water currents that can propel free-swimming choanoflagellates through the water column and trap bacteria and detritus against the collar of microvilli, where these foodstuffs are engulfed. This feeding provides a critical link within the global carbon cycle, linking trophic levels. In addition to their critical ecological roles, choanoflagellates are of particular interest to evolutionary biologists studying the origins of multicellularity in animals. As the closest living relatives of animals, choanoflagellates serve as a useful model for reconstructions of the last unicellular ancestor of animals. According to a 2021 study, crown group craspedids appeared 422.78 million years ago, Although a previous study from 2017 recovered the divergence of the crown group choanoflagellates (craspedids) at 786.62 million years.

Proterospongia is a genus of single-celled aquatic organisms which form colonies. It belongs to the choanoflagellate class. As a colony-forming choanoflagellate, Proterospongia is of interest to scientists studying the mechanisms of intercellular signaling and adhesion present before animals appeared.
Auxospores are specialised cells in diatoms that are produced at key stages in their cell cycle or life history. Auxospores typically play a role in growth processes, sexual reproduction or dormancy.

Corallochytrium belongs to the class of Corallochytrea within Teretosporea and is a sister group to Ichthyosporea. Corallochytrium limacisporum is the only species of Corallochytrium known so far. It was first discovered and named in the Arabian Sea’s coral lagoons by Kaghu-Kumar in 1987. It was first thought to be a member of the fungi-like thraustochytrids, however, this was later disproven due to Corallochytriums lack of cilia and sagenogenetosome. Little research has been done on the life cycle or morphology. Most research concerning this genus has been done to uncover the evolution of animals and fungi, as Corallochytrium possess both animal and fungal enzymatic trademarks.

Holozoa is a clade of organisms that includes animals and their closest single-celled relatives, but excludes fungi and all other organisms. Together they amount to more than 1.5 million species of purely heterotrophic organisms, including around 300 unicellular species. It consists of various subgroups, namely Metazoa and the protists Choanoflagellata, Filasterea, Pluriformea and Ichthyosporea. Along with fungi and some other groups, Holozoa is part of the Opisthokonta, a supergroup of eukaryotes. Choanofila was previously used as the name for a group similar in composition to Holozoa, but its usage is discouraged now because it excludes animals and is therefore paraphyletic.
Lake Burton, also known as Burton Lagoon, is a meromictic and saline lake in the Vestfold Hills of Princess Elizabeth Land in Eastern Antarctica. Princess Elizabeth Land, including the lake, is claimed by Australia as part of the Australian Antarctic Territory. The lake has a surface area of 1.35 km2 (0.52 sq mi), a volume of 9.69 million m3, a maximum depth of 18.3 metres (60 ft) and a mean depth of 7.16 metres (23.5 ft). The lake is named after H. R. Burton, a biologist working in the Vestfold Hills of Antarctica.
Miracula is a genus of parasitic protists that parasite diatoms, containing the type species Miracula helgolandica. More recently, the species Miracula moenusica from the river Main in Frankfurt am Main, Miracula islandica from a shore in the north of Iceland, Miracula einbuarlaekurica from a streamlet in the north of Iceland, and Miracula blauvikensis from the shore at the research station Blávík in the east fjords of Iceland were added to the genus. It is the only genus in the family Miraculaceae, of uncertain taxonomic position within the Oomycetes. They're one of the most basal lineages in the phylogeny of Oomycetes.
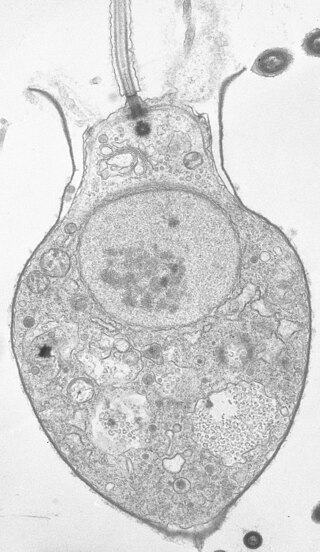
Salpingoeca is a genus of Choanoflagellates in the family Salpingoecidae.
Calotheca is the name used for a genus of choanoflagellates in the family Acanthoecidae, though this name is a junior homonym of the name Calotheca Heyden, 1887, and it must be replaced under the rules of the ICZN. The species C. alata is from Indo-Pacific Localities.

Choanozoa is a clade of opisthokont eukaryotes consisting of the choanoflagellates (Choanoflagellatea) and the animals. The sister-group relationship between the choanoflagellates and animals has important implications for the origin of the animals. The clade was identified in 2015 by Graham Budd and Sören Jensen, who used the name Apoikozoa. The 2018 revision of the classification first proposed by the International Society of Protistologists in 2012 recommends the use of the name Choanozoa.

The Parmales are an order of marine microalgae within the Bolidophyceae class. They are found worldwide and characterized by a cell wall composed of 5-8 interlocking silica plates with distinct forms. They were initially thought to be loricate choanoflagellates but were shown to be a separate phyla entirely upon the discovery of chloroplasts, placing it among the photosynthetic stramenopiles.
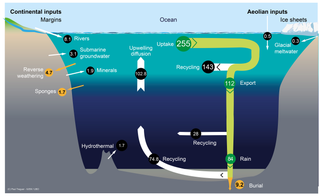
The silica cycle is the biogeochemical cycle in which biogenic silica is transported between the Earth's systems. Silicon is considered a bioessential element and is one of the most abundant elements on Earth. The silica cycle has significant overlap with the carbon cycle and plays an important role in the sequestration of carbon through continental weathering, biogenic export and burial as oozes on geologic timescales.

Many protists have protective shells or tests, usually made from silica (glass) or calcium carbonate (chalk). Protists are a diverse group of eukaryote organisms that are not plants, animals, or fungi. They are typically microscopic unicellular organisms that live in water or moist environments.

Asterionella formosa is a species of diatom belonging to the family Fragilariaceae.
Diaphanoeca is a genus of choanoflagellates belonging to the family Acanthoecidae.
Acanthoecida is an order of Choanoflagellates belonging to the class Choanoflagellatea. It is a type of heterotrophic nanoflagellate that feeds on suspended particles.

Diaphanoeca grandis is a species of choanoflagellate in the family Acanthoecidae which is the type species of the genus Diaphanoeca. It is a unicellular micro-heterotroph with a large protective lorica that is found beneath sea ice in a wide distribution. The lorica is composed of silica and possibly originates from diatoms via Horizontal gene transfer.
Crinolina isefiordensis is a species of choanoflagellate in the family Acanthoecidae. It is the type species of the genus Crinolina and is named for the first location of its collection, the Ise Fjord in Denmark.













