
The family Vampyrellidae is a subgroup of the order Vampyrellida within the supergroup Rhizaria. Based on molecular sequence data, the family currently comprises the genus Vampyrella, and maybe several other vampyrellid amoebae. The cells are naked and characterised by radiating, filose pseudopodia and an orange colouration of the main cell body.

Heliozoa, commonly known as sun-animalcules, are microbial eukaryotes (protists) with stiff arms (axopodia) radiating from their spherical bodies, which are responsible for their common name. The axopodia are microtubule-supported projections from the amoeboid cell body, and are variously used for capturing food, sensation, movement, and attachment. They are similar to Radiolaria, but they are distinguished from them by lacking central capsules and other complex skeletal elements, although some produce simple scales and spines. They may be found in both freshwater and marine environments.
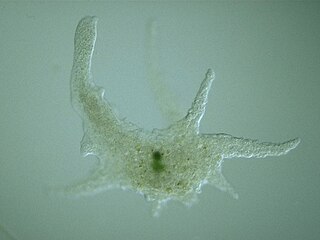
Amoebozoa is a major taxonomic group containing about 2,400 described species of amoeboid protists, often possessing blunt, fingerlike, lobose pseudopods and tubular mitochondrial cristae. In traditional classification schemes, Amoebozoa is usually ranked as a phylum within either the kingdom Protista or the kingdom Protozoa. In the classification favored by the International Society of Protistologists, it is retained as an unranked "supergroup" within Eukaryota. Molecular genetic analysis supports Amoebozoa as a monophyletic clade. Modern studies of eukaryotic phylogenetic trees identify it as the sister group to Opisthokonta, another major clade which contains both fungi and animals as well as several other clades comprising some 300 species of unicellular eukaryotes. Amoebozoa and Opisthokonta are sometimes grouped together in a high-level taxon, variously named Unikonta, Amorphea or Opimoda.

The opisthokonts are a broad group of eukaryotes, including both the animal and fungus kingdoms. The opisthokonts, previously called the "Fungi/Metazoa group", are generally recognized as a clade. Opisthokonts together with Apusomonadida and Breviata comprise the larger clade Obazoa.

The Rhizaria are a diverse and species-rich supergroup of mostly unicellular eukaryotes. Except for the Chlorarachniophytes and three species in the genus Paulinella in the phylum Cercozoa, they are all non-photosynthetic, but many foraminifera and radiolaria have a symbiotic relationship with unicellular algae. A multicellular form, Guttulinopsis vulgaris, a cellular slime mold, has been described. This group was used by Cavalier-Smith in 2002, although the term "Rhizaria" had been long used for clades within the currently recognized taxon.

Lobosa is a taxonomic group of amoebae in the phylum Amoebozoa. Most lobosans possess broad, bluntly rounded pseudopods, although one genus in the group, the recently discovered Sapocribrum, has slender and threadlike (filose) pseudopodia. In current classification schemes, Lobosa is a subphylum, composed mainly of amoebae that have lobose pseudopods but lack cilia or flagella.

Amorphea is a taxonomic supergroup that includes the basal Amoebozoa and Obazoa. That latter contains the Opisthokonta, which includes the Fungi, Animals and the Choanomonada, or Choanoflagellates. The taxonomic affinities of the members of this clade were originally described and proposed by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in 2002.

Cristidiscoidea or Nucleariae is a proposed basal holomycota clade in which Fonticula and Nucleariida emerged, as sister of the fungi. Since it is close to the divergence between the main lineages of fungi and animals, the study of Cristidiscoidea can provide crucial information on the divergent lifestyles of these groups and the evolution of opisthokonts and slime mold multicellularity. The holomycota tree is following Tedersoo et al.

The Apusozoa are a paraphyletic phylum of flagellate eukaryotes. They are usually around 5–20 μm in size, and occur in soils and aquatic habitats, where they feed on bacteria. They are grouped together based on the presence of an organic shell or theca under the dorsal surface of the cell.
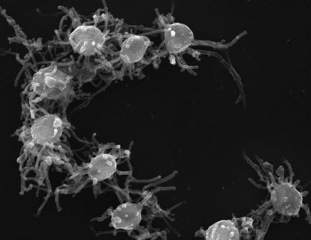
Capsaspora is a monotypic genus containing the single species Capsaspora owczarzaki. C. owczarzaki is a single-celled eukaryote that occupies a key phylogenetic position in our understanding of the origin of animal multicellularity, as one of the closest unicellular relatives to animals. It is, together with Ministeria vibrans, a member of the Filasterea clade. This amoeboid protist has been pivotal to unravel the nature of the unicellular ancestor of animals, which has been proved to be much more complex than previously thought.

Breviata anathema is a single-celled flagellate amoeboid eukaryote, previously studied under the name Mastigamoeba invertens. The cell lacks mitochondria, much like the pelobionts to which the species was previously assigned, but has remnant mitochondrial genes, and possesses an organelle believed to be a modified anaerobic mitochondrion, similar to the mitosomes and hydrogenosomes found in other eukaryotes that live in low-oxygen environments.

Filasterea is a proposed basal Filozoan clade of single-celled ameboid eukaryotes that includes Ministeria and Capsaspora. It is a sister clade to the Choanozoa in which the Choanoflagellatea and Animals appeared, originally proposed by Shalchian-Tabrizi et al. in 2008, based on a phylogenomic analysis with 78 genes. Filasterea was found to be the sister-group to the clade composed of Metazoa and Choanoflagellata within the Opisthokonta, a finding that has been further corroborated with additional, more taxon-rich, phylogenetic analyses.

Holozoa is a clade of organisms that includes animals and their closest single-celled relatives, but excludes fungi and all other organisms. Together they amount to more than 1.5 million species of purely heterotrophic organisms, including around 300 unicellular species. It consists of various subgroups, namely Metazoa and the protists Choanoflagellata, Filasterea, Pluriformea and Ichthyosporea. Along with fungi and some other groups, Holozoa is part of the Opisthokonta, a supergroup of eukaryotes. Choanofila was previously used as the name for a group similar in composition to Holozoa, but its usage is discouraged now because it excludes animals and is therefore paraphyletic.
Fonticula is a genus of cellular slime mold which forms a fruiting body in a volcano shape. As long ago as 1979 it has been known to not have a close relationship with either the Dictyosteliida or the Acrasidae, the two well-established groups of cellular slime molds. In 1979, Fonticula was made a new genus of its own due to the unique characteristics of its fruiting body, with only one species: Fonticula alba.

Holomycota or Nucletmycea are a basal Opisthokont clade as sister of the Holozoa. It consists of the Cristidiscoidea and the kingdom Fungi. The position of nucleariids, unicellular free-living phagotrophic amoebae, as the earliest lineage of Holomycota suggests that animals and fungi independently acquired complex multicellularity from a common unicellular ancestor and that the osmotrophic lifestyle was originated later in the divergence of this eukaryotic lineage. Opisthosporidians is a recently proposed taxonomic group that includes aphelids, Microsporidia and Cryptomycota, three groups of endoparasites.

Breviatea, commonly known as breviate amoebae, are a group of free-living, amitochondriate protists with uncertain phylogenetic position. They are biflagellate, and can live in anaerobic (oxygen-free) environments. They are currently placed in the Obazoa clade. They likely do not possess vinculin proteins. Their metabolism relies on fermentative production of ATP as an adaptation to their low-oxygen environment.

An amoeba, often called an amoeboid, is a type of cell or unicellular organism with the ability to alter its shape, primarily by extending and retracting pseudopods. Amoebae do not form a single taxonomic group; instead, they are found in every major lineage of eukaryotic organisms. Amoeboid cells occur not only among the protozoa, but also in fungi, algae, and animals.

Obazoa is a proposed sister clade of Amoebozoa. The term Obazoa is based on the OBA acronym for Opisthokonta, Breviatea, and Apusomonadida, the group's three constituent clades.

Parvularia atlantis is a filopodiated amoeba which was isolated from a lake in Atlanta and deposited in the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) under the name Nuclearia sp. ATCC 50694 on 1997 by TK Sawyer. It was classified under the genus Nuclearia and morphologically resembles to Nuclearia species, although it is smaller. Later it was determined that it phylogenetically belongs to a new nucleariid lineage., distantly related to Nuclearia and Fonticula genera – the other two previously described nucleriid genera.

An amoeboflagellate is any eukaryotic organism capable of behaving as an amoeba and as a flagellate at some point during their life cycle. Amoeboflagellates present both pseudopodia and at least one flagellum, often simultaneously.
















