
Nucleariida is a group of amoebae with filose pseudopods, known mostly from soils and freshwater. They are distinguished from the superficially similar vampyrellids mainly by having mitochondria with discoid cristae, in the absence of superficial granules, and in the way they consume food.
Amoebozoa is a major taxonomic group containing about 2,400 described species of amoeboid protists, often possessing blunt, fingerlike, lobose pseudopods and tubular mitochondrial cristae. In traditional classification schemes, Amoebozoa is usually ranked as a phylum within either the kingdom Protista or the kingdom Protozoa. In the classification favored by the International Society of Protistologists, it is retained as an unranked "supergroup" within Eukaryota. Molecular genetic analysis supports Amoebozoa as a monophyletic clade. Modern studies of eukaryotic phylogenetic trees identify it as the sister group to Opisthokonta, another major clade which contains both fungi and animals as well as several other clades comprising some 300 species of unicellular eukaryotes. Amoebozoa and Opisthokonta are sometimes grouped together in a high-level taxon, variously named Unikonta, Amorphea or Opimoda.

The opisthokonts are a broad group of eukaryotes, including both the animal and fungus kingdoms. The opisthokonts, previously called the "Fungi/Metazoa group", are generally recognized as a clade. Opisthokonts together with Apusomonadida and Breviata comprise the larger clade Obazoa.

Microsporidia are a group of spore-forming unicellular parasites. These spores contain an extrusion apparatus that has a coiled polar tube ending in an anchoring disc at the apical part of the spore. They were once considered protozoans or protists, but are now known to be fungi, or a sister group to fungi. These fungal microbes are obligate eukaryotic parasites that use a unique mechanism to infect host cells. They have recently been discovered in a 2017 Cornell study to infect Coleoptera on a large scale. So far, about 1500 of the probably more than one million species are named. Microsporidia are restricted to animal hosts, and all major groups of animals host microsporidia. Most infect insects, but they are also responsible for common diseases of crustaceans and fish. The named species of microsporidia usually infect one host species or a group of closely related taxa. Approximately 10 percent of the species are parasites of vertebrates —several species, most of which are opportunistic, can infect humans, in whom they can cause microsporidiosis.

Amorphea is a taxonomic supergroup that includes the basal Amoebozoa and Obazoa. That latter contains the Opisthokonta, which includes the Fungi, Animals and the Choanomonada, or Choanoflagellates. The taxonomic affinities of the members of this clade were originally described and proposed by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in 2002.

The Apusozoa are a paraphyletic phylum of flagellate eukaryotes. They are usually around 5–20 μm in size, and occur in soils and aquatic habitats, where they feed on bacteria. They are grouped together based on the presence of an organic shell or theca under the dorsal surface of the cell.
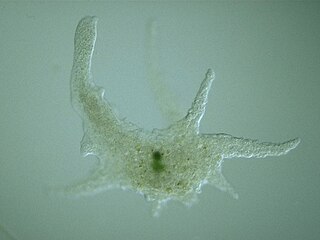
Capsaspora is a monotypic genus containing the single species Capsaspora owczarzaki. C. owczarzaki is a single-celled eukaryote that occupies a key phylogenetic position in our understanding of the origin of animal multicellularity, as one of the closest unicellular relatives to animals. It is, together with Ministeria vibrans, a member of the Filasterea clade. This amoeboid protist has been pivotal to unraveling the nature of the unicellular ancestor of animals, which has been proved to be much more complex than previously thought.

SAR or Harosa is a highly diverse clade of eukaryotes, often considered a supergroup, that includes stramenopiles (heterokonts), alveolates, and rhizarians. It is a node-based taxon, including all descendants of the three groups' last common ancestor, and comprises most of the now-rejected Chromalveolata. Their sister group has been found to be telonemids, with which they make up the TSAR clade.

Filasterea is a proposed basal Filozoan clade of single-celled ameboid eukaryotes that includes Ministeria and Capsaspora. It is a sister clade to the Choanozoa in which the Choanoflagellatea and Animals appeared, originally proposed by Shalchian-Tabrizi et al. in 2008, based on a phylogenomic analysis with 78 genes. Filasterea was found to be the sister-group to the clade composed of Metazoa and Choanoflagellata within the Opisthokonta, a finding that has been further corroborated with additional, more taxon-rich, phylogenetic analyses.

Holozoa is a clade of organisms that includes animals and their closest single-celled relatives, but excludes fungi and all other organisms. Together they amount to more than 1.5 million species of purely heterotrophic organisms, including around 300 unicellular species. It consists of various subgroups, namely Metazoa and the protists Choanoflagellata, Filasterea, Pluriformea and Ichthyosporea. Along with fungi and some other groups, Holozoa is part of the Opisthokonta, a supergroup of eukaryotes. Choanofila was previously used as the name for a group similar in composition to Holozoa, but its usage is discouraged now because it excludes animals and is therefore paraphyletic.
Rabdiophrys is a genus of amoeboid rhizarians. It has 19 species, including the species Rabdiophrys anulifera.

Holomycota or Nucletmycea are a basal Opisthokont clade as sister of the Holozoa. It consists of the Cristidiscoidea and the kingdom Fungi. The position of nucleariids, unicellular free-living phagotrophic amoebae, as the earliest lineage of Holomycota suggests that animals and fungi independently acquired complex multicellularity from a common unicellular ancestor and that the osmotrophic lifestyle was originated later in the divergence of this eukaryotic lineage. Opisthosporidians is a recently proposed taxonomic group that includes aphelids, Microsporidia and Cryptomycota, three groups of endoparasites.
The initial version of a classification system of life by British zoologist Thomas Cavalier-Smith appeared in 1978. This initial system continued to be modified in subsequent versions that were published until he died in 2021. As with classifications of others, such as Carl Linnaeus, Ernst Haeckel, Robert Whittaker, and Carl Woese, Cavalier-Smith's classification attempts to incorporate the latest developments in taxonomy., Cavalier-Smith used his classifications to convey his opinions about the evolutionary relationships among various organisms, principally microbial. His classifications complemented his ideas communicated in scientific publications, talks, and diagrams. Different iterations might have a wider or narrow scope, include different groupings, provide greater or lesser detail, and place groups in different arrangements as his thinking changed. His classifications has been a major influence in the modern taxonomy, particularly of protists.

Aphelida is a phylum of Fungi that appears to be the sister to true fungi.

Obazoa is a proposed sister clade of Amoebozoa. The term Obazoa is based on the OBA acronym for Opisthokonta, Breviatea, and Apusomonadida, the group's three constituent clades.

Opisthosporidia is a superphylum of intracellular parasites with amoeboid vegetative stage, defined as a common group of eukaryotic groups Microsporidia, Cryptomycota and Aphelidea. They have been considered to represent a monophyletic lineage with shared ecological and structural features, being a sister clade of the Fungi. Together with the Fungi they represent a sister clade of the Cristidiscoidea, together forming the Holomycota.
The Scotokaryotes (Cavalier-Smith) is a proposed basal Neokaryote clade as sister of the Diaphoretickes. Basal Scotokaryote groupings are the Metamonads, the Malawimonas and the Podiata. In this phylogeny the Discoba are sometimes seen as paraphyletic and basal Eukaryotes.

Parvularia atlantis is a filopodiated amoeba which was isolated from a lake in Atlanta and deposited in the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) under the name Nuclearia sp. ATCC 50694 on 1997 by TK Sawyer. It was classified under the genus Nuclearia and morphologically resembles to Nuclearia species, although it is smaller. Later it was determined that it phylogenetically belongs to a new nucleariid lineage., distantly related to Nuclearia and Fonticula genera – the other two previously described nucleriid genera.

The plasmodiophores are a group of obligate endoparasitic protists belonging to the subphylum Endomyxa in Cercozoa. Taxonomically, they are united under a single family Plasmodiophoridae, order Plasmodiophorida, sister to the phagomyxids.

An amoeboflagellate is any eukaryotic organism capable of behaving as an amoeba and as a flagellate at some point during their life cycle. Amoeboflagellates present both pseudopodia and at least one flagellum, often simultaneously.
















