
Alcohol oxidoreductases are oxidoreductase enzymes that act upon an alcohol functional group. [1] [2]
They are classified under "1.1" in the EC number numbering system.

Alcohol oxidoreductases are oxidoreductase enzymes that act upon an alcohol functional group. [1] [2]
They are classified under "1.1" in the EC number numbering system.
The Enzyme Commission number is a numerical classification scheme for enzymes, based on the chemical reactions they catalyze. As a system of enzyme nomenclature, every EC number is associated with a recommended name for the corresponding enzyme-catalyzed reaction.
In biochemistry, an oxidase is an enzyme that catalyzes oxidation-reduction reactions, especially one involving dioxygen (O2) as the electron acceptor. In reactions involving donation of a hydrogen atom, oxygen is reduced to water (H2O) or hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Some oxidation reactions, such as those involving monoamine oxidase or xanthine oxidase, typically do not involve free molecular oxygen.
In biochemistry, an oxidoreductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from one molecule, the reductant, also called the electron donor, to another, the oxidant, also called the electron acceptor. This group of enzymes usually utilizes NADP+ or NAD+ as cofactors. Transmembrane oxidoreductases create electron transport chains in bacteria, chloroplasts and mitochondria, including respiratory complexes I, II and III. Some others can associate with biological membranes as peripheral membrane proteins or be anchored to the membranes through a single transmembrane helix.
In chemistry, acylation is the chemical reaction in which an acyl group is added to a compound. The compound providing the acyl group is called the acylating agent.
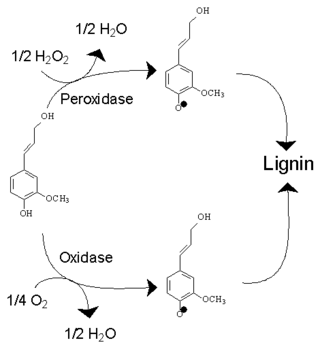
An oxidative enzyme is an enzyme that catalyses an oxidation reaction. Two most common types of oxidative enzymes are peroxidases, which use hydrogen peroxide, and oxidases, which use molecular oxygen. They increase the rate at which ATP is produced aerobically.

Dicarbonyl/L-xylulose reductase, also known as carbonyl reductase II, is an enzyme that in human is encoded by the DCXR gene located on chromosome 17.
In enzymology, a long-chain-alcohol dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.192) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase (EC 1.1.1.100) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an alkane 1-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.15.3) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactions
In enzymology, a Delta12-fatty acid dehydrogenase (EC 1.14.99.33) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a deoxyhypusine monooxygenase (EC 1.14.99.29) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, an alcohol oxidase (EC 1.1.3.13) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (ferredoxin) (EC 1.2.7.6) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a mycothiol-dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.306) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a L-ascorbate oxidase (EC 1.10.3.3) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a ferredoxin—nitrate reductase (EC 1.7.7.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a L-dopachrome isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a trans-2-decenoyl-[acyl-carrier protein] isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a beta-ketoacyl-acyl-carrier-protein synthase I is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
A dismutase is an enzyme that catalyzes a dismutation reaction.