
The Amiiformes order of fish has only two extant species, the bowfins: Amia calva and Amia ocellicauda, the latter recognized as a separate species in 2022. These Amiiformes are found in the freshwater systems of North America, in the United States and parts of southern Canada. They live in freshwater streams, rivers, and swamps. The order first appeared in the Triassic, and the extinct members include both marine and freshwater species, many of which are morphologically disparate from bowfins, such as the caturids.

The Amiidae are a family of basal ray-finned fishes. The bowfin and the eyespot bowfin are the only two species to survive today, although additional species in all four subfamilies of Amiidae are known from Jurassic, Cretaceous, and Eocene fossils.

Iberomesornis is a monotypic genus of enantiornithine bird of the Cretaceous of Spain.

Pelecanimimus is an extinct genus of basal ("primitive") ornithomimosaurian dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous of Spain. It is notable for possessing more teeth than any other member of the Ornithomimosauria, most of which were toothless.
Spelaeogriphacea is an order of crustaceans that grow to no more than 10 millimetres (0.39 in). Little is known about the ecology of the order.
Lisboasaurus is a small genus of Mesozoic crocodylomorph that lived in fresh water. It is known from fossilized tooth and jaw fragments of Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous age. Two species have been described. In the past Lisboasaurus has been interpreted as an avialan, troodontid, or an anguimorph lizard. Both species are currently assigned to Crocodylomorpha, one is reassigned to the genus Lusitanisuchus.

Mantellisaurus is a genus of iguanodontian dinosaur that lived in the Barremian and early Aptian ages of the Early Cretaceous Period of Europe. Its remains are known from Belgium (Bernissart), England, Spain and Germany. The type and only species is M. atherfieldensis. Formerly known as Iguanodon atherfieldensis, the new genus Mantellisaurus was erected for the species by Gregory Paul in 2007. According to Paul, Mantellisaurus was more lightly built than Iguanodon and more closely related to Ouranosaurus, making Iguanodon in its traditional sense paraphyletic. It is known from many complete and almost complete skeletons. The genus name honours Gideon Mantell, the discoverer of Iguanodon.
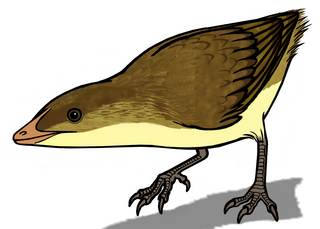
Eoalulavis is a monotypic genus of enantiornithean bird that lived during the Barremian, in the Lower Cretaceous around 125 million years ago. The only known species is Eoalulavis hoyasi.

Holophagus is an extinct genus of coelacanth belonging to Latimeriidae. The type species, Holophagus gulo, is known from the Lower Jurassic marine Lias of England. Some authors have considered the genus restricted to the Lias of England.

The La Huérguina Formation is a geological formation in Spain whose strata date back to the Barremian stage of the Early Cretaceous. Las Hoyas is a Konservat-Lagerstätte within the formation, located near the city of Cuenca, Spain. The site is mostly known for its exquisitely preserved dinosaurs, especially enantiornithines. The lithology of the formation mostly consists of lacustrine limestone deposited in a freshwater wetland environment.
Gyronchus is an extinct genus of prehistoric ray-finned fish from the Jurassic. This genus is currently treated as a wastebasket taxon used for pycnodonts like Macromesodon and Turbomesodon.
Unasuchus is an extinct genus of Early Cretaceous eusuchian belonging to the family Hylaeochampsidae. The genus is named after Uña, a municipality in central Spain where fossils have been found.

Hoyasemys is an extinct genus of basal eucryptodiran freshwater turtle from Lower Cretaceous deposits of Cuenca Province, Spain. It is known from the holotype MCCM-LH 84, a nearly complete and articulated skeleton including the skull. It was found in the 1980s from the Las Hoyas site of the Calizas de La Huérguina Formation, near La Cierva township, Spain. It was first named by Adán Pérez-García, Marcelo S. de la Fuente and Francisco Ortega in 2011 and the type species is Hoyasemys jimenezi. The generic name is derived from the word Hoyas meaning "the basin" in Spanish, which refers to the Las Hoyas fossil site it was found in, and emys. The specific name honors Dr. Emiliano Jiménez Fuentes.

Lonchidion is a genus of extinct hybodont in the family Lonchidiidae. The genus first appears in the fossil record during the Middle Triassic (Ladinian) and was among the last surviving hybodont genera, with its youngest known fossils dating to the very end of the Cretaceous (Maastrichtian).
Jucaraseps is an extinct genus of small squamate lizard known from the Early Cretaceous of Las Hoyas, Spain. It contains a single species, Jucaraseps grandipes. It belonged to the clade Scincogekkonomorpha and was related to the clade Scleroglossa as well to Jurassic and Cretaceous taxa Eichstaettisaurus, Ardeosaurus, Bavarisaurus, Parviraptor, Yabeinosaurus and Sakurasaurus

Europejara is a genus of tapejarid pterosaur from the Early Cretaceous Period of Spain. The type and only species known is Europejara olcadesorum.
Hoyalacerta is an extinct genus of lizard known from the type species Hoyalacerta sanzi, which is from the Early Cretaceous Las Hoyas fossil site in Spain. Hoyalacerta was named in 1999 and is considered either a member of the group Iguania or a stem squamate, meaning that it lies outside the squamate crown group that includes all living lizards and snakes. Hoyalacerta is a small lizard with an elongated body and short limbs. It is thought to have spent most of its time on the ground. Several other lizards are also known from Las Hoyas, including Meyasaurus, Scandensia, and Jucaraseps. Features of Hoyalacerta that distinguish it from other Las Hoyas lizards include smooth skull bones, simple cone-shaped teeth, and short limbs relative to body length.
Spinolestes is an extinct mammal genus from the Early Cretaceous of Spain. A gobiconodontid eutriconodont, it is notable for the remarkable degree of preservation, offering profound insights to the biology of non-therian mammals.
Meyasaurus is an extinct genus of Teiid lizard known from the Barremian of Spain and the Isle of Wight, UK. Four species are known from Spain, from the La Huérguina, Camarillas, and La Pedrera de Rúbies Formations while an indeterminate taxon is known from the Wessex Formation of Isle of Wight. It is a possible close relative of Barbatteius and other members of Barbatteiidae.

Coniopteris is an extinct genus of Mesozoic fern leaves. It was widespread over both hemispheres during the Jurassic and Early Cretaceous, with over 130 species having been described. While traditionally assumed to have been a member of Dicksoniaceae or a close relative of Thyrsopteris, a 2020 cladistic analysis found it to be a stem group of Polypodiales. Most species of Coniopteris probably had a herbaceous habit. Coniopteris laciniata had tufts of leaves sprouting from intervals of a thin, creeping rhizome. The genus is technically a junior synonym of the little used Polystichites, but was conserved by the ICZN in 2013. Some authors suggest a range of Early Jurassic-early Late Cretaceous for the genus, while others suggest a more expansive range spanning from the Middle Triassic to the Eocene.














