| Betasatellite | |
|---|---|
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Family: | Tolecusatellitidae |
| Genus: | Betasatellite |
| Species | |
Betasatellite is a genus of family Tolecusatellitidae containing 119 species. [1]
| Betasatellite | |
|---|---|
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Family: | Tolecusatellitidae |
| Genus: | Betasatellite |
| Species | |
Betasatellite is a genus of family Tolecusatellitidae containing 119 species. [1]
The name Betasatellite is a combination of Beta, because they used to be referred to as DNA-β to distinguish them from DNA-B of Begomovirus, and satellite, the fact that it is a satellite. [2]
The species are ssDNA unless specified ssDNA(+). There are 61 ssDNA(+) and 58 ssDNA viruses
| Name | Abbr | GenBank | REFSEQ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ageratum leaf curl Buea betasatellite | ALCuBB | FR717140 | NC_014746 |
| Ageratum leaf curl Cameroon betasatellite | ALCuCMB | FM164737 | N/A |
| Ageratum yellow leaf curl betasatellite | AYLCB | AJ316026 | NC_005046 |
| Ageratum yellow vein betasatellite | AYVB | AJ252072 | NC_003403 |
| Ageratum yellow vein China betasatellite ssDNA(+) | AYVCNB | AJ971257 | NC_007067 |
| Ageratum yellow vein Sri Lanka betasatellite | AYVSLB | AJ542498 | NC_043429 |
| Alternanthera yellow vein betasatellite | AlYVB | DQ641716 | NC_009562 |
| Andrographis yellow vein leaf curl betasatellite | AnYVLCuB | KC967282 | NC_023876 |
| Bhendi yellow vein mosaic betasatellite | BYVB | AJ308425 | NC_003405 |
| Cardiospermum yellow leaf curl betasatellite | CaYLCuB | AM933578 | NC_010297 |
| Chili leaf curl betasatellite | ChLCuB | AJ316032 | NC_005048 |
| Chili leaf curl Jaunpur betasatellite | ChLCuJB | HM007103 | NC_017678 |
| Chili leaf curl Sri Lanka betasatellite | ChLCuSLB | JN638445 | NC_038676 |
| Codiaeum leaf curl betasatellite ssDNA(+) | CoLCuB | MF278784 | NC_055549 |
| Cotton leaf curl Bahraich betasatellite ssDNA(+) | CLCBahB | EF620566 | N/A |
| Cotton leaf curl Bangalore betasatellite 1 ssDNA(+) | CLCuBaB1 | AY705381 | NC_007219 |
| Cotton leaf curl Bangalore betasatellite 2 ssDNA(+) | CLCuBaB2 | KF964654 | N/A |
| Cotton leaf curl Bangalore betasatellite 3 ssDNA(+) | CLCuBaB3 | LC316186 | N/A |
| Cotton leaf curl Bangalore betasatellite 4 ssDNA(+) | CLCuBaB4 | MG758149 | N/A |
| Cotton leaf curl Burkina Faso betasatellite ssDNA(+) | CLCuBFB | MK032307 | N/A |
| Cotton leaf curl Gezira betasatellite | CLCuGeB | DQ644564 | N/A |
| Cotton leaf curl Kashmir betasatellite ssDNA(+) | CLCuKaB | LN610993 | N/A |
| Cotton leaf curl Multan betasatellite | CLCuMuB | AJ298903 | N/A |
| Cotton leaf curl Tandojam betasatellite ssDNA(+) | CLCuTaB | LT827054 | N/A |
| Croton yellow vein mosaic betasatellite | CroYVMB | AM410551 | NC_008579 |
| Emilia yellow vein betasatellite ssDNA(+) | EmYVB | FJ869906 | NC_012666 |
| Emilia yellow vein Fujian betasatellite ssDNA(+) | EmYVFuB | MH035671 | NC_055560 |
| Erectites yellow mosaic betasatellite ssDNA(+) | ErYMB | DQ641713 | NC_009559 |
| Eupatorium yellow vein betasatellite | EpYVB | AJ438938 | NC_004515 |
| Eupatorium yellow vein mosaic betasatellite | EpYVV | AB300464 | NC_038677 |
| French bean leaf curl betasatellite | FBLCuB | JQ866298 | NC_018091 |
| Hedyotis yellow mosaic betasatellite | HYMB | KF641186 | NC_023015 |
| Hibiscus vein enation betasatellite ssDNA(+) | HVEB | MF140456 | NC_055547 |
| Honeysuckle yellow vein betasatellite | HYVB | AJ316040 | NC_005052 |
| Honeysuckle yellow vein mosaic betasatellite | HYVMB | AB182263 | NC_005953 |
| Honeysuckle yellow vein mosaic Ibaraki betasatellite ssDNA(+) | HYVMIbB | AB287442 | NC_009571 |
| Honeysuckle yellow vein mosaic Nara betasatellite ssDNA(+) | HYVMNaB | AB287443 | N/A |
| Kenaf leaf curl betasatellite ssDNA(+) | KeLCuB | FN678779 | N/A |
| Leucas zeylanica yellow vein betasatellite ssDNA(+) | LzYVB | GQ421324 | NC_013424 |
| Lindernia anagallis yellow vein betasatellite ssDNA(+) | LaYVB | DQ641715 | NC_009561 |
| Ludwigia leaf distortion betasatellite 1 ssDNA(+) | LuLDB1 | AY728262 | N/A |
| Ludwigia leaf distortion betasatellite 2 ssDNA(+) | LuLDB2 | EF614160 | N/A |
| Ludwigia leaf distortion betasatellite 3 ssDNA(+) | LuLDB3 | KT390358 | N/A |
| Ludwigia yellow vein betasatellite ssDNA(+) | LuYMB | AJ965541 | NC_007212 |
| Malvastrum leaf curl betasatellite ssDNA(+) | MaLCuB | AM072289 | NC_007711 |
| Malvastrum yellow vein betasatellite ssDNA(+) | MaYVB | AJ971459 | N/A |
| Malvastrum yellow vein Cambodia betasatellite ssDNA(+) | MaYVKHB | KP188832 | N/A |
| Malvastrum yellow vein Yunnan betasatellite 1 ssDNA(+) | MaYVYnB1 | AJ786712 | NC_006632 |
| Malvastrum yellow vein Yunnan betasatellite 2 ssDNA(+) | MaYVYnB1 | FN806780 | N/A |
| Mirabilis leaf curl betasatellite | MiLCuB | LK054803 | NC_038924 |
| Momordica yellow mosaic betasatellite | MamYMB | KT454829 | N/A |
| Mungbean yellow mosaic betasatellite | MYMB | JX443646 | NC_018869 |
| Okra leaf curl betasatellite ssDNA(+) | OLCuB | GU111963 | N/A |
| Okra leaf curl Oman betasatellite | OLCuOMB | KF267444 | NC_038678 |
| Papaya leaf curl betasatellite | PaLCuB | AY244706 | NC_004706 |
| Papaya leaf curl China betasatellite | PaLCuCNB | KJ642219 | NC_038679 |
| Papaya leaf curl Gandhinagar betasatellite ssDNA(+) | PaLCGB | KT253638 | N/A |
| Papaya leaf curl India betasatellite | PaLCuINA | HM143906 | NC_038680 |
| Papaya leaf curl India betasatellite 2 ssDNA(+) | PaLCINB2 | MN529627 | N/A |
| Pea leaf distortion betasatellite ssDNA(+) | PeLDB | KY001644 | NC_033618 |
| Radish leaf curl betasatellite ssDNA(+) | RaLCuB | EF175734 | NC_010239 |
| Rhynchosia yellow mosaic betasatellite | RhYMB | KP752092 | NC_038681 |
| Rose leaf curl betasatellite | RoLCuB | GQ478344 | N/A |
| Sida leaf curl betasatellite ssDNA(+) | SiLCuB | AM050732 | NC_007639 |
| Sida yellow mosaic betasatellite ssDNA(+) | SiYMB | AJ810093 | NC_006267 |
| Sida yellow vein Barrackpore betasatellite ssDNA(+) | SiYVBaB | EU188921 | N/A |
| Sida yellow vein Madurai betasatellite ssDNA(+) | SiYVMaB | AJ967003 | NC_007213 |
| Sida yellow vein Vietnam betasatellite 1 ssDNA(+) | SiYVVNB1 | DQ641712 | NC_009558 |
| Sida yellow vein Vietnam betasatellite 2 ssDNA(+) | SiYVVNB2 | KF990602 | N/A |
| Siegesbeckia yellow vein betasatellite | SiYVB | KF499590 | NC_038682 |
| Siegesbeckia yellow vein betasatellite 2 ssDNA(+) | SiYVB2 | JF682839 | N/A |
| Siegesbeckia yellow vein Guangxi betasatellite ssDNA(+) | SiYVGxB | AM238695 | N/A |
| Tobacco curly shoot betasatellite | TobCSB | AJ421484 | NC_004546 |
| Tobacco leaf chlorosis betasatellite ssDNA(+) | TobLCB | JX025223 | N/A |
| Tobacco leaf curl betasatellite | TobLCuB | AM260465 | NC_038891 |
| Tobacco leaf curl Japan betasatellite | TbLCJRB | AB236324 | NC_009450 |
| Tobacco leaf curl Patna betasatellite | TobLCuPatB | HQ180394 | NC_038683 |
| Tobacco leaf curl Sheikhupura betasatellite ssDNA(+) | TobLCuShB | LT795119 | N/A |
| Tobacco leaf curl Yunnan betasatellite ssDNA(+) | TobLCuYnB | KC699042 | NC_005030 |
| Tomato leaf curl Bangalore betasatellite | ToLCBaB | AY428768 | NC_038684 |
| Tomato leaf curl Bangalore betasatellite 2 ssDNA(+) | ToLCuBaB2 | EU280314 | NC_010148 |
| Tomato leaf curl Bangladesh betasatellite | ToLCBDB | AJ542489 | N/A |
| Tomato leaf curl betasatellite ssDNA(+) | ToLCB | AJ316036 | N/A |
| Tomato leaf curl betasatellite 2 ssDNA(+) | ToLCuB2 | KU500806 | N/A |
| Tomato leaf curl Bundi betasatellite | ToLCuBuB | MH577020 | N/A |
| Tomato leaf curl China betasatellite | ToLCCNB | AJ704609 | N/A |
| Tomato leaf curl Gandhinagar betasatellite | ToLCGanB | KC952006 | NC_023038 |
| Tomato leaf curl Ghana betasatellite 1 ssDNA(+) | ToLCuGHB1 | KT382328 | N/A |
| Tomato leaf curl Ghana betasatellite 2 ssDNA(+) | ToLCuGHB2 | KT382329 | N/A |
| Tomato leaf curl Hajipur betasatellite ssDNA(+) | ToLCuHaB | JX262390 | NC_018614 |
| Tomato leaf curl India betasatellite ssDNA(+) | ToLCuINB | JQ012916 | N/A |
| Tomato leaf curl Java betasatellite | ToLCJaB | KC282642 | N/A |
| Tomato leaf curl Joydebpur betasatellite | ToLCJoB | AJ966244 | N/A |
| Tomato leaf curl Joydebpur betasatellite 2 ssDNA(+) | ToLCuJoB2 | MG571522 | N/A |
| Tomato leaf curl Karnataka betasatellite ssDNA(+) | ToLCuKaB | MG758146 | N/A |
| Tomato leaf curl Laguna betasatellite | ToLCLaB | AB307732 | NC_038685 |
| Tomato leaf curl Laos betasatellite | ToLCLAB | AJ542491 | NC_038925 |
| Tomato leaf curl Lucknow betasatellite ssDNA(+) | ToLCuLuB | MG478451 | N/A |
| Tomato leaf curl Malaysia betasatellite | ToLCMYB | KM051528 | NC_038686 |
| Tomato leaf curl Nepal betasatellite | ToLCNPB | AJ542492 | NC_038926 |
| Tomato leaf curl Pakistan betasatellite ssDNA(+) | ToLCuPKB | LN811050 | N/A |
| Tomato leaf curl Panipat betasatellite ssDNA(+) | ToLCuPaB | HM143907 | N/A |
| Tomato leaf curl Patna betasatellite | ToLCPaB | EU862324 | NC_012493 |
| Tomato leaf curl Philippine betasatellite | ToLCPHB | AB308071 | NC_009570 |
| Tomato leaf curl Pune betasatellite ssDNA(+) | ToLCuPuB | AY754815 | NC_008524 |
| Tomato leaf curl Ranchi betasatellite ssDNA(+) | ToLCuRaB | GQ994096 | NC_055541 |
| Tomato leaf curl Sri Lanka betasatellite | ToLCSLB | AJ542493 | N/A |
| Tomato leaf curl Togo betasatellite ssDNA(+) | ToLCuTGB | HQ586965 | NC_014741 |
| Tomato leaf curl Yemen betasatellite | ToLCYEB | JF919717 | NC_018864 |
| Tomato yellow dwarf betasatellite ssDNA(+) | ToYDB | AB294512 | NC_009893 |
| Tomato yellow leaf curl China betasatellite | TYLCCNB | AJ420313 | N/A |
| Tomato yellow leaf curl Shandong betasatellite | ToYLCShB | KP322555 | NC_038688 |
| Tomato yellow leaf curl Thailand betasatellite | TYLCTHB | AJ566746 | NC_004903 |
| Tomato yellow leaf curl Vietnam betasatellite | TYLCVNB | DQ641714 | NC_009560 |
| Tomato yellow leaf curl Yunnan betasatellite | ToYLCYnB | KF640694 | NC_038689 |
| Vernonia crinkle betasatellite ssDNA(+) | VeCrB | KX831134 | NC_032119 |
| Vernonia yellow vein betasatellite | VYVB | FN435836 | NC_013423 |
| Vernonia yellow vein Fujian betasatellite | VYVFuB | JF733779 | NC_015928 |
| Zinnia leaf curl betasatellite ssDNA(+) | ZiLCuB | AJ542499 | NC_005874 |
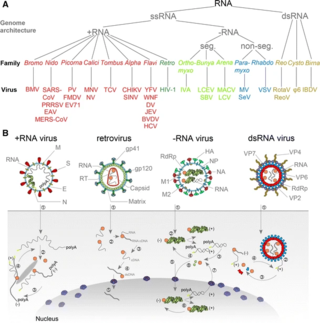
An RNA virus is a virus—other than a retrovirus—that has ribonucleic acid (RNA) as its genetic material. The nucleic acid is usually single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) but it may be double-stranded (dsRNA). Notable human diseases caused by RNA viruses include the common cold, influenza, SARS, MERS, Covid-19, Dengue Virus, hepatitis C, hepatitis E, West Nile fever, Ebola virus disease, rabies, polio, mumps, and measles.
Virus classification is the process of naming viruses and placing them into a taxonomic system similar to the classification systems used for cellular organisms.

Parvoviruses are a family of animal viruses that constitute the family Parvoviridae. They have linear, single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) genomes that typically contain two genes encoding for a replication initiator protein, called NS1, and the protein the viral capsid is made of. The coding portion of the genome is flanked by telomeres at each end that form into hairpin loops that are important during replication. Parvovirus virions are small compared to most viruses, at 23–28 nanometers in diameter, and contain the genome enclosed in an icosahedral capsid that has a rugged surface.
A satellite is a subviral agent that depends on the coinfection of a host cell with a helper virus for its replication. Satellites can be divided into two major classes: satellite viruses and satellite nucleic acids. Satellite viruses, which are most commonly associated with plants, are also found in mammals, arthropods, and bacteria. They encode structural proteins to enclose their genetic material, which are therefore distinct from the structural proteins of their helper viruses. Satellite nucleic acids, in contrast, do not encode their own structural proteins, but instead are encapsulated by proteins encoded by their helper viruses. The genomes of satellites range upward from 359 nucleotides in length for satellite tobacco ringspot virus RNA (STobRV).

Geminiviridae is a family of plant viruses that encode their genetic information on a circular genome of single-stranded (ss) DNA. There are 520 species in this family, assigned to 14 genera. Diseases associated with this family include: bright yellow mosaic, yellow mosaic, yellow mottle, leaf curling, stunting, streaks, reduced yields. They have single-stranded circular DNA genomes encoding genes that diverge in both directions from a virion strand origin of replication. According to the Baltimore classification they are considered class II viruses. It is the largest known family of single stranded DNA viruses.

The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) authorizes and organizes the taxonomic classification of and the nomenclatures for viruses. The ICTV has developed a universal taxonomic scheme for viruses, and thus has the means to appropriately describe, name, and classify every virus that affects living organisms. The members of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses are considered expert virologists. The ICTV was formed from and is governed by the Virology Division of the International Union of Microbiological Societies. Detailed work, such as delimiting the boundaries of species within a family, typically is performed by study groups of experts in the families.
Baltimore classification is a system used to classify viruses based on their manner of messenger RNA (mRNA) synthesis. By organizing viruses based on their manner of mRNA production, it is possible to study viruses that behave similarly as a distinct group. Seven Baltimore groups are described that take into consideration whether the viral genome is made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) or ribonucleic acid (RNA), whether the genome is single- or double-stranded, and whether the sense of a single-stranded RNA genome is positive or negative.

Bottigliavirus is the only genus in the family Ampullaviridae and contains 3 species. Ampullaviridae infect archaea of the genus Acidianus. The name of the family and genus is derived from the Latin word for bottle, ampulla, due to the virions having the shape of a bottle. The family was first described during an investigation of the microbial flora of hot springs in Italy.
Dinodnavirus is a genus of viruses that infect dinoflagellates. This genus belongs to the clade of nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses. The only species in the genus is Heterocapsa circularisquama DNA virus 01.
Alphasatellites are a single-stranded DNA family of satellite viruses that depend on the presence of another virus to replicate their genomes. As such, they have minimal genomes with very low genomic redundancy. The genome is a single circular single strand DNA molecule. The first alphasatellites were described in 1999 and were associated with cotton leaf curl disease and Ageratum yellow vein disease. As begomoviruses are being characterised at the molecular level an increasing number of alphasatellites are being described.
Babuvirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Nanoviridae. Musa species serve as natural hosts. There are three species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: stunting, severe necrosis and early plant death. BBTV induces banana bunchy top disease (BBTD).
Lambdatorquevirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Anelloviridae. Sea lions serve as natural hosts. There are six species in this genus.
Spiraviridae is a family of incertae sedis viruses that replicate in hyperthermophilic archaea of the genus Aeropyrum, specifically Aeropyrum pernix.The family contains one genus, Alphaspiravirus, which contains one species, Aeropyrum coil-shaped virus. The virions of ACV are non-enveloped and in the shape of hollow cylinders that are formed by a coiling fiber that consists of two intertwining halves of the circular DNA strand inside a capsid. An appendage protrudes from each end of the cylindrical virion. The viral genome is ssDNA(+) and encodes for significantly more genes than other known ssDNA viruses. ACV is also unique in that it appears to lack its own enzymes to aid replication, instead likely using the host cell's replisomes. ACV has no known relation to any other archaea-infecting viruses, but it does share its coil-like morphology with some other archaeal viruses, suggesting that such viruses may be an ancient lineage that only infect archaea.
In virology, realm is the highest taxonomic rank established for viruses by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV), which oversees virus taxonomy. Six virus realms are recognized and united by specific highly conserved traits:
Pleolipoviridae is a family of DNA viruses that infect archaea.

Bacilladnaviridae is a family of single-stranded DNA viruses that primarily infect diatoms.

Thaspiviridae is a family of incertae sedis spindle-shaped viruses. The family contains a single genus, Nitmarvirus, which contains a single species, Nitmarvirus NSV1.
Tolecusatellitidae is a incertae sedis ssDNA/ssDNA(+) family of biological satellites. The family contains two genera and 131 species. This family of viruses depend on the presence of another virus to replicate their genomes, as such they have minimal genomes with very low genomic redundancy.

Adnaviria is a realm of viruses that includes archaeal viruses that have a filamentous virion and a linear, double-stranded DNA genome. The genome exists in A-form (A-DNA) and encodes a dimeric major capsid protein (MCP) that contains the SIRV2 fold, a type of alpha-helix bundle containing four helices. The virion consists of the genome encased in capsid proteins to form a helical nucleoprotein complex. For some viruses, this helix is surrounded by a lipid membrane called an envelope. Some contain an additional protein layer between the nucleoprotein helix and the envelope. Complete virions are long and thin and may be flexible or a stiff like a rod.
Deltasatellite is a genus of family Tolecusatellitidae containing 12 species.