Bidens is a genus of flowering plants in the aster family, Asteraceae. The genus include roughly 230 species which are distributed worldwide. Despite their global distribution, the systematics and taxonomy of the genus has been described as complicated and unorganized. The common names beggarticks, black jack, burr marigolds, cobbler's pegs, Spanish needles, stickseeds, tickseeds and tickseed sunflowers refer to the fruits of the plants, most of which are bristly and barbed. The generic name refers to the same character; Bidens comes from the Latin bis ("two") and dens ("tooth").

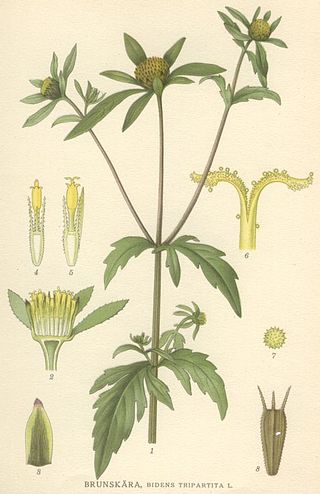
Bidens tripartita is a common and widespread species of flowering plant in the sunflower family, Asteraceae, commonly known as three-lobe beggarticks, three-part beggarticks, leafy-bracted beggarticks or trifid bur-marigold. It is native to much of Eurasia, North Africa, and North America, with naturalized populations in Australia and on some Pacific Islands.

Bidens frondosa is a North American species of flowering plant in the aster family, Asteraceae. It is widespread across much of Canada, the United States, and Mexico It is known in many other parts of the world as an introduced species, including Europe, Asia, Morocco, and New Zealand. Its many common names include devil's beggarticks, devil's-pitchfork, devil's bootjack, sticktights, bur marigold, pitchfork weed, tickseed sunflower, leafy beggarticks, and common beggar-ticks.

Bidens pilosa is an annual species of herbaceous flowering plant in the daisy family Asteraceae. Its many common names include hitch hikers, black-jack, beggarticks, farmer's friends and Spanish needle, but most commonly referred to as cobblers pegs. It is native to the Americas but is widely distributed as an introduced species in other regions worldwide including Eurasia, Africa, Australia, South America and the Pacific Islands. In Chishona, it is called tsine.

Erigeron philadelphicus, the Philadelphia fleabane, is a species of flowering plant in the composite family (Asteraceae). Other common names include common fleabane, daisy fleabane, frost-root, marsh fleabane, poor robin's plantain, skervish, and, in the British Isles, robin's-plantain, but all of these names are shared with other species of fleabanes (Erigeron). It is native to North America and has been introduced to Eurasia.

Gaillardia aristata is a North American species of flowering plant in the sunflower family, known by the common names common blanketflower and common gaillardia. This perennial wildflower is widespread across much of North America, from Yukon east to Québec and south as far as California, Arizona, Illinois, and Connecticut, although it may be naturalized rather than native in parts of that range. It is also naturalized in scattered locations in Europe, Australia, and South America.

Balsamorhiza sagittata is a North American species of flowering plant in the tribe Heliantheae of the family Asteraceae known by the common name Arrowleaf Balsamroot. Also sometimes called Oregon sunflower, it is widespread across western Canada and much of the western United States.

Bidens laevis is a species of flowering plant in the daisy family known by the common names larger bur-marigold and smooth beggarticks. It is native to South America, Mexico, and the southern and eastern United States. It grows in wetlands, including estuaries and riverbanks.

Bidens vulgata is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae known by the common names big devils beggarticks and tall beggarticks. It is native to eastern and central North America from Nova Scotia to northern Georgia and as far west as the Rocky Mountains. It is an introduced species on the West Coast of North America as well as parts of Europe.

Anisocarpus madioides is a North American species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae known by the common name woodland madia.
Microseris bigelovii is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae known by the common name coastal silverpuffs. It is native to the west coast of North America, where its range extends from the southern tip of Vancouver Island to the northern coast of California.

Bidens micrantha is a species of flowering plant in the aster family known by the common name grassland beggarticks. It is endemic to the Hawaiian Islands, where it and other Bidens species are known as kōʻokoʻolau. It occurs in many types of habitat on Lānaʻi, Maui, and Hawaiʻi, including rocky cliffs, dry forests, mesic forests, wet forests, and high shrublands.

Bidens aristosa is a North American species of plants in the sunflower family. Common names include bearded beggarticks, western tickseed, long-bracted beggarticks, tickseed beggarticks, swamp marigold, and Yankee lice. It is native to eastern and central United States and south-central Canada, from Maine south to Florida and west as far as Ontario, Texas, and Nebraska. It grows in wet meadows and abandoned fields.

Actaea elata is a species of flowering plant in the buttercup family known by the common name tall bugbane. It is native to the Pacific Northwest of North America, where it can be found in British Columbia, Washington, and Oregon.

Bidens aurea , the Arizona beggarticks, is a North American species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It is widespread across much of Mexico and found also in Arizona and Guatemala. The species is also naturalized in parts of Europe and South America.

Bidens connata , the purplestem beggarticks or London bur-marigold, is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It is widespread across much of Eurasia, North Africa, and North America, and naturalized in Australia and on certain Pacific Islands.
Bidens eatonii is a North American species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It is native to eastern Canada and the northeastern United States.

Bidens hyperborea is a coastal species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It grows along the coasts of Hudson Bay, the Arctic Ocean, and the North Atlantic Ocean in eastern Canada and the northeastern United States.

Erigeron filifolius is a North American species of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae known by the common names thread-leaf fleabane.

Erigeron poliospermus is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae known by the common names gray-seeded fleabane, purple cushion fleabane, and hairy-seed fleabane. Native to western North America, it is mainly found to the east of the Cascade Range in Washington, Oregon, and Idaho.